America’s Own Homegrown Industry
Co-authored by NCIA and BDS Analytics
It all begins with the humble plant.
The fastest-growing industry in the United States relies 100 percent upon the simple cultivation and harvesting of one plant, cannabis sativa — its buds, its leaves, and the diversity of organic compounds the plant provides, including THC.
If the plant is grown indoors, as is most legal cannabis in the United States, it first needs a building before it ever digs roots and spreads a canopy. The building requires complicated lights, many of which are manufactured in the United States. It demands a wilderness of HVAC networks, to maintain a healthy temperature and humidity level. Irrigation systems, potting soil and soil amendments, complex sprinkler systems in case of fire, high-tech security systems — all of these and much more must be in place before the first plant begins to rise towards the light.
And these first steps produce jobs and work: real estate professionals, lawyers, accountants, bookkeepers, electricians, carpenters, plumbers, HVAC specialists, irrigation experts, sprinkler and alarm installation technicians, factory workers. Once the building is ready, the company needs horticulture experts and trimmers, among others. And it requires ongoing work, too, from electricians and other trades specialists, as things break and need to be replaced or updated. The cultivation of the plant alone is a rapidly-developing career field.
But hands-on growing represents just one small patch of the cannabis landscape. Every step along the way, from seed to store, propagates work for people in hardhats, lab coats and blazers. And all of the jobs are Made in the USA. Even more, due to the patchwork regulatory environment, cannabis industry jobs also tend to root, and stay put, within individual states and communities.
Legal cannabis today in the United States is the ultimate homegrown industry. Detailed sales data from industry market research firm BDS Analytics reveals astounding growth within states where cannabis is legal. For example, during the first quarter of 2018 in Colorado, where sales of recreational cannabis have been legal since 2014, dollar sales of concentrates in recreational shops grew by 47.4 percent compared to the first quarter of 2017. Concentrates do not represent a tiny piece of the overall recreational marketplace: During this year’s first quarter, adult use concentrates sales hit $85.35 million, and captured a full 30 percent of the recreational marketplace. That’s an enormous chunk of the state’s mature adult use cannabis market, and yet sales still expand by close to 50% within a year.
And with all of that growth, quarter after quarter, comes increased need for workers.
States with laws that replace criminal marijuana markets with regulated industries are also benefiting from significant tax revenues that support important programs like school construction, law enforcement, and drug education. According to the National Cannabis Industry Association’s , the five states that allowed adult-use sales realized nearly $800 million in combined state tax revenue alone.
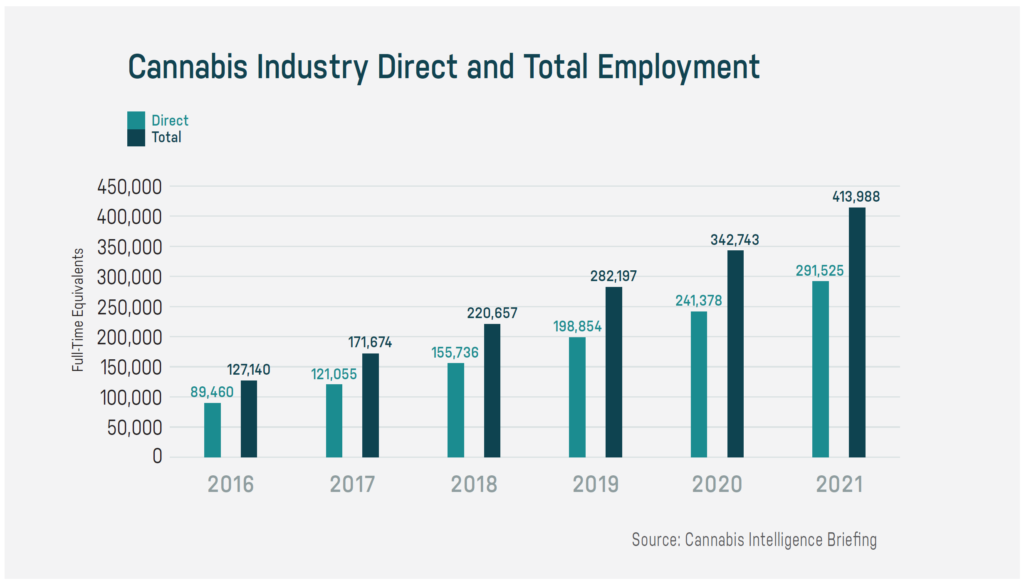
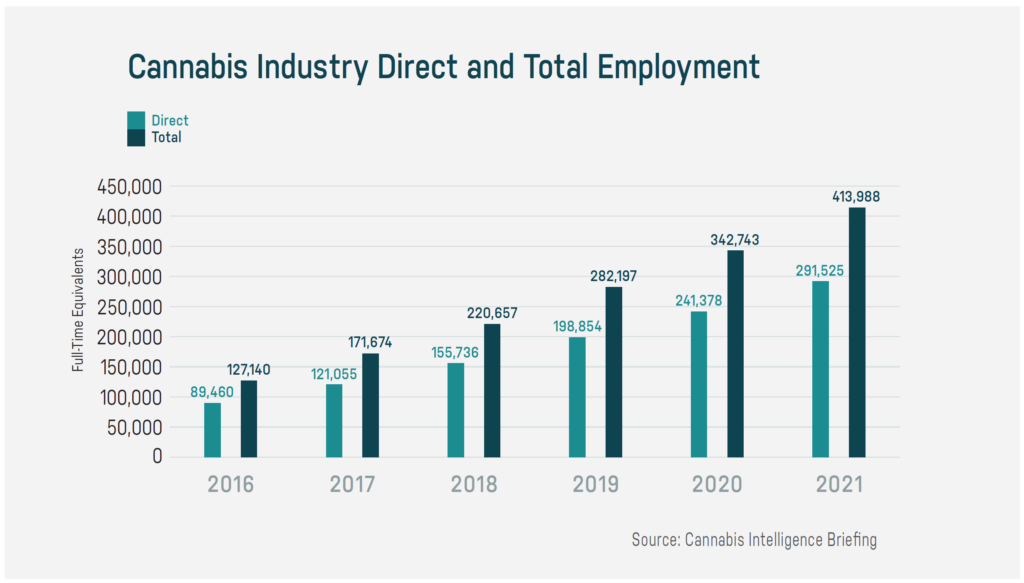
Industry investment and market research firms The Arcview Group and BDS Analytics predicted in their study US Legal Cannabis: Driving $40 Billion Economic Output that the industry will hatch 414,000 jobs in a multitude of fields both directly and ancillary related to cannabis by 2021 — everything from delivery drivers to retail sales pros to extraction technicians, warehouse workers, bakers, marketing gurus, and PhDs in pest control.
The industry’s impact is certainly felt in Colorado, which began retail cannabis sales for adult use on Jan. 1, 2014 — the first in the nation to do so. Many economic experts attribute the state’s lowest-in-the-nation unemployment rate, at least in part, to the cannabis boom.
Colorado’s ascending sales results, as well as those in the other cannabis-legal states, would likely resound with even more oomph if two difficult issues could be resolved: banking, and the ability to write off business expenses for cannabis companies.
As the industry’s leading national advocate, NCIA is working hard on both fronts.
The Small Business Tax Equity Act of 2017, co-sponsored by Rep. Carlos Curbelo (R-FL) and Sen. Ron Wyden (D-OR), seeks to let cannabis companies operating legally under state law to implement business-related tax credits or deductions for expenses — the entire issue is often referred to simply as 280E (the applicable section of the tax code) as shorthand. For now, the federal government treats marijuana sales in legal states the same way it treats sales of illegally-trafficked drugs — needless to say, people illegally selling controlled substances cannot itemize tax deductions or claim business-related tax credits but NCIA believes that state-licensed businesses should not be caught up in the wide net cast by 280E.
Meanwhile, the Secure and Fair Enforcement (SAFE) Banking Act seeks to provide a “safe harbor” and additional protections for depository institutions that want to engage with cannabis companies that are in compliance with state law. Rep. Ed Perlmutter (D-CO) and Sen. Jeff Merkley (D-OR) are co-sponsors of this important legislation, which finally would, among other things, provide cannabis companies access to bank loans — taken for granted in most industries, but long outlawed in legal cannabis.
The success of the industry truly astounds despite such profound roadblocks. Success in alleviating such banking and taxation headaches would further stoke what is already the hottest industry in the country.
Research into the economic benefits of cannabis legalization and regulation is just beginning, and for now it remains too early to make definitive declarations about how legalization will influence the economic path of different communities. Undoubtedly the effects will vary from location to location — the effect on San Francisco, for example, may be entirely different from the effect on Fort Collins, Colorado.
One early study, conducted by the University of Colorado-Pueblo’s Institute of Cannabis Research, found that legalization in Pueblo, a diverse, blue-collar area about two hours south of Denver, could be responsible for the County’s recent success. In addition, the study rejected predictions that legalization would bring increased homelessness and crime to the region.
“When compared to similar communities in states where cannabis is not legal in any form, Pueblo appears to be doing better on a variety of measures,” the study says. “Overall, the positive changes that are noticed in Pueblo County, such as increasing real estate values, higher income per capita, and more construction spending may be attributed to legalization of cannabis in the state of Colorado.”
To date, cannabis still represents a fairly small slice of the employment pie in Colorado. A recent study conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City estimated the industry directly supports 17,821 jobs today. The study’s author writes: “Employment in the marijuana industry is a relatively small share of total employment in Colorado, but in recent years it has been one of the state’s fastest-growing industries,” adding that between 2016 and 2017 jobs in cannabis rose by 17.7 percent.
The study also noted the effect Colorado’s cannabis industry has had on state government coffers; in 2017 alone, it added $247 million to the budget. Cannabis tax receipts go to a variety of places. The state’s Building Excellent Schools Today school construction program, for example, receives the first $40 million from excise taxes on wholesale cannabis, and Colorado Gov. John Hickenlooper recently signed a bill that will drastically increase this amount. Local governments receive another 10 percent of the taxation haul.
Nationwide, the cannabis industry now supports close to 10,000 active cannabis licenses — that is, businesses that need licenses to grow, manufacture, distribute or sell the plant, according to CannaBiz Media, which tracks marijuana licenses. These “touch-the-plant” businesses are the sturdy and rapidly expanding trunk of a flourishing industry — without them, none of the other jobs and businesses that are sprouting up around cannabis sales today would exist.
But if touch-the-plant businesses are the trunks of the industry, the branches, leaves and flowers are the ancillary jobs — those that don’t grow, manufacture or sell marijuana directly. Of those anticipated 414,000 cannabis jobs by 2021, many will not sprout directly from licensed businesses. For example, software developers targeting the cannabis industry are flourishing. Entrepreneurs across the country are opening factories that make everything from plastic containers and child-safe bags for cannabis, to customized extraction equipment. New legal, public relations, marketing, and other professional services appear every day that revolve around the industry.
During a recent economic conference, Ian Siegel, the CEO of ZipRecruiter, which is a prominent job recruitment marketplace, said of cannabis: “Twenty-nine states have legalized marijuana [in some form]. There’s a 445 percent job growth in job listings in the category year-over-year.” By comparison, Siegel said other hard-charging industries like technology and healthcare lag far behind, with job growth at 245 percent and 70 percent respectively. He also noted that cannabis jobs expansion grew at a more rapid pace during Q4 2017, which saw an increase of 693 percent compared to the previous year.
As growth rockets ahead (new jobs, workers with new skills, growing tax revenues, etc.), the same trajectory is beginning to rise in Canada, where adult-use cannabis use is expected to begin later this summer. Despite Canada’s relatively small size — with a population of 35 million, it is smaller than California and dwarfed by the United States population of nearly 326 million — it enjoys a distinct advantage on the global stage: Canada allows cannabis exports. Growers and manufacturers in Canada ship cannabis to Germany, Israel and other countries that seek cannabis for their medical programs (only one other country in the world, Uruguay, enjoys legal adult-use cannabis use and sales). This is a fairly small market, for now. But as more and more countries embrace the medical, if not adult-use, benefits of cannabis, it is a marketplace destined to expand and grow increasingly dynamic. Permitting cannabis exports remains another NCIA priority.
Either way, the cannabis revolution is here, across the United States — where it all began. It is the ultimate homegrown industry, one we all should embrace, nurture and strengthen. It’s good for America, and good for America’s cities, towns and citizens.
This post was co-authored by the National Cannabis Industry Association, the largest cannabis trade association in the U.S. and the only one representing cannabis businesses at the national level and BDS Analytics, the leader in providing comprehensive cannabis market intelligence and consumer research. Learn more about NCIA by visiting: thecannabisindustry.org. Learn more about BDS Analytics by visiting: bdsanalytics.com.

















Follow NCIA
Newsletter
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Instagram
News & Resource Topics
–
This Just In
How THCa Vapes Are Changing Consumer
Announcing NCIA’s 2026-2028 Board of Directors