Member Blog: Reflections On Banking Reform For Cannabis Operators

by Joshua Gilstrap, e2b teknologies
Isn’t it crazy to think that the legal cannabis industry could be worth $57 billion by 2030? Or that nearly half of the country’s adult population (49%) has tried marijuana, the largest number ever recorded.*
At the time of this article, nineteen states, two territories, and Washington D.C. have legalized cannabis for adult recreational use. With more than two-thirds of U.S. states that have legalized the sale of both adult-use and medical cannabis and nearly half the population of potential cannabis consumers – it’s safe to say the cannabis industry is thriving.
But can it continue to grow without banking reform?
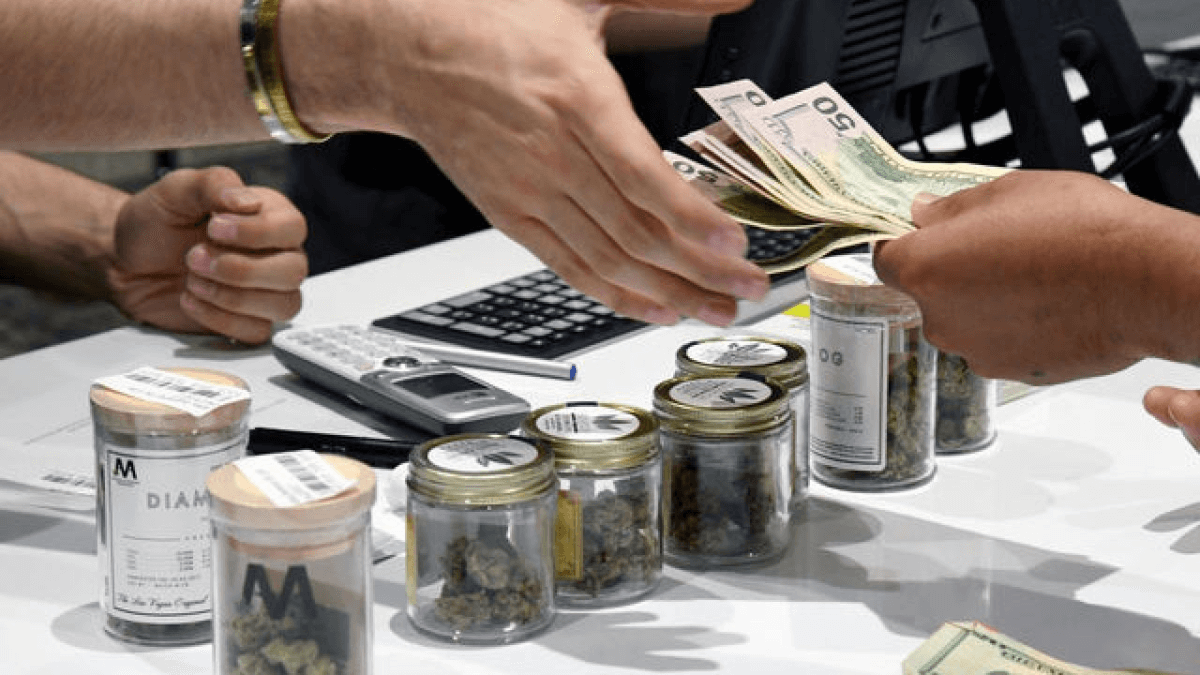
Cannabis businesses have a hard time accessing traditional banking options because the plant is still federally illegal. This means that banks are hesitant to work with cannabis companies for fear of retribution from the federal government.
This lack of banking options creates a difficult environment for cannabis businesses to operate in. Since they can’t deposit money or write checks, they have to operate on a cash-only basis, which can lead to security problems.
Cannabis operators also have a hard time securing financing because most traditional lenders are unwilling to work with them. This leaves them struggling to get the capital they need to grow and scale their business.
When cannabis businesses lack financing options for basic business growth, a banking system more ideal for cannabis operators is needed.
The Federal Law Guides Everything
Despite the growing opportunities in the cannabis industry at the state level, many prospecting business owners are stalled by a lack of capital. Businesses in the cannabis industry might celebrate legalization in their respective states but still deal with the challenge of accessing banking services.
Cannabis dispensaries that run cash-only operations are forced to confront security challenges in a new way. Online ordering, credit and debit card processing, taking business loans, and accessing other revenue-driving financial services are denied to cannabis businesses due to their federal status.
This shows an immediate need for financial reprieve in the cannabis industry.
Getting Financial Reprieve
The House of Representatives has passed several bills supporting the cannabis industry. Some of these bills include:
- Bill to decriminalize marijuana
- The Marijuana Opportunity Reinvestment and Expungement (MORE) Act
- Legalization of adult-use cannabis
- Legislation for medical marijuana programs
- Legislation to reduce barriers to cannabis research
- Approval of measures for adult cannabis use
One such bill that focuses on banking reform is the Secure and Fair Enforcement (SAFE) Banking Act, which aims to reduce the banking services challenges in the cannabis industry. If the SAFE Banking bill passes in Congress, financial institutions can open their services to cannabis businesses without the fear of violating anti-money laundering (AML) laws.
In return, cannabis businesses reduce the risk of theft and employee welfare by transitioning from cash-only services to banking services. However, this financial reprieve doesn’t address the cannabis tax code that prevents cannabis businesses from deducting business expenses from the gross income as per the Controlled Substances Act
Nonetheless, the SAFE Banking bill is a step in the right direction. The remaining concern is whether these financial reprieves will pass in the Senate and legalize cannabis businesses at the federal level.
Another financial option expected to reform the cannabis industry is crypto. The authenticity and security of blockchain currencies like Bitcoin are becoming a lucrative consideration for financial reprieve in the cannabis industry.
Currently, there are cryptocurrencies like PotCoin and CannabisCoin mined to cater to various needs within the cannabis industry. However, the uncertainty in the crypto world makes it challenging for the cannabis industry to settle on using crypto as a financial banking solution.
Granted, some crypto technology like blockchain technology is used to transact sales in the cannabis industry, where buyers make cashless payments, and the dispensaries convert this into crypto. But these transactions are not fully transparent.
Notwithstanding, there is hope for the cannabis industry as the number of banks willing to work with cannabis businesses increases. This could result from the increasing support of cannabis banking reform at the state and Congress levels.
But Is The Banking Industry Prepared For This Reprieve?
Financial institutions are gathering more courage when working with the cannabis industry. In 2021, 755 banks showed working relationships with cannabis clients. However, this comfort is more prevalent at the state level than at the federal level, where cannabis is yet to be legalized.
But since support from the federal government is anticipated, banking institutions must equally prepare for the capability to host cannabis businesses legally. Banks must stay compliant with the anti-money laundering (AML) laws.
Banks should conduct due diligence on cannabis businesses that want to use their services. Since federal legalization of cannabis is still pending, some cannabis operations might be illegal. Therefore, it is prudent for banks to start preparation by ensuring any new partners are not lawbreakers.
This means checking for legalization and registration licenses and conducting due diligence on employees and angel investors. Business transactions are also an excellent indicator of whether a cannabis business is involved in illegal activities.
For instance, a cannabis business in a state that frowns upon international shipments shouldn’t have any international transactions. Avid AML monitoring controls should quickly identify legitimate cannabis businesses.
In a nutshell, every business that partners with a cannabis business should be prepared to support its decisions with factual claims. In case of any suspicious activity, the bank should be ready to give an account of their due diligence procedure and the findings.
Creating relationships with federal regulations is also prudent since they help make the regulation process easier. Regulators also help ensure that banks remain compliant with the Federal cannabis laws, which protect their banking operations.
Cannabis business owners must also prepare for the possibility of using open and traditional banking services for their operations. If, or when, cannabis is Federally legalized, the cannabis industry will streamline its operations throughout the U.S.
This means added investments in research, cultivation, marketing, production, and sales of cannabis and cannabis products, whether medicinal or recreational. And the added boost of a legal banking system would further increase employment and boost the economy.
Cards On The Table
Does the cannabis industry need a banking reform? Absolutely. The challenge, however, is that, despite the willingness of the House of Representatives to support the SAFE Act bill, among other proposed banking reforms for the industry, approval in the Senate is still in question. Cards on the table, bank financing in the cannabis industry will propel businesses into more growth, which, in turn, should pragmatically influence the overall U.S. economy. But this starts with active congressional action.
FAQs
What is the current cannabis banking system?
The current cannabis banking system is not ideal for cannabis businesses because the lack of Federal legalization keeps banks from offering traditional banking services to cannabis businesses for fear of violating anti-money laundering (AML) laws.
What are the challenges of using non-FDIC banking options?
Non-FDIC banking options are not secured by the FDIC, meaning businesses that operate under these banking services are not protected by the Federal laws against theft or failure.
What can a banking reform do for the cannabis industry?
A banking reform allows banking institutions to offer cannabis businesses the same banking services they offer other businesses, like capital loans, online bill payments, and debit and credit cards.
 Joshua Gilstrap is the Marketing Manager for e2b teknologies, in addition to his marketing responsibilities Joshua leads business development for e2b teknologies emerging Canna Suite product line. A business graduate with a focus in marketing from Miami University in Oxford, Ohio, he joined the e2b team in the Fall of 2019. Josh brought with him a wide array of business and practical experience in planning and execution. Since coming aboard he has led multiple project’s including website hosting and theme standardization company wide, marketing automation streamlining the efficiency of the customer journey, and sales automation where he is changing the conversation from promotion to education, from pitching to catching, and from push to pull in order to keep up with the shifting tides of a digital transformation.
Joshua Gilstrap is the Marketing Manager for e2b teknologies, in addition to his marketing responsibilities Joshua leads business development for e2b teknologies emerging Canna Suite product line. A business graduate with a focus in marketing from Miami University in Oxford, Ohio, he joined the e2b team in the Fall of 2019. Josh brought with him a wide array of business and practical experience in planning and execution. Since coming aboard he has led multiple project’s including website hosting and theme standardization company wide, marketing automation streamlining the efficiency of the customer journey, and sales automation where he is changing the conversation from promotion to education, from pitching to catching, and from push to pull in order to keep up with the shifting tides of a digital transformation.
Member Blog: Three Reasons Why Cannabis Business Owners Outsource Their Accounting

By LaKia Bourne and JoAnne Williams, Green Space Accounting
Every entrepreneur knows that staying ahead of business demands is challenging and time-consuming. Unless you have access to enough capital to hire a large team of dedicated employees, you’ll probably have to juggle a wide range of tasks. From promotional marketing to financial forecasting, it seems cannabis business owners always have their plates full.
With this being said, it’s important to understand that taking on too many tasks at once can have negative consequences. The quality of your work is likely to suffer, and you could end up making mistakes that impede your ability to drive growth. Not to mention, doing everything on your own can leave you feeling tired and burnt out.
Unlike companies in many other industries, the cannabis industry is closely regulated, meaning entrepreneurs have to conduct rigorous administrative work. Failure to stay on top of state regulations could result in reputational damage, lost revenue, and even the loss of your business.
So, what’s the solution? Whether you’re a grower, manufacturer, or dispensary owner, outsourcing your accounting burden could significantly lighten your workload. As well as ensuring your accounts are accurately maintained, enlisting the services of a reliable firm will free up time for other important jobs, such as product and vendor management, marketing and promotion, partnership-building, and much more.
Of course, you shouldn’t rely on the first accounting firm you stumble across to look after your financial affairs. As an entrepreneur in the cannabis industry, you must find an accounting firm with knowledge of the sector – and, of course, a non-judgmental approach to hemp and cannabis sales.
This article will explore three key ways working with a cannabis-oriented accounting firm could significantly improve business outcomes.
1. You’ll Maximize Profits by Knowing Your Numbers
To see long-term success in your business endeavors, it’s important to know your numbers forwards and backward. Your financial records tell the story of how your company has evolved from start to finish. If you don’t have a comprehensive understanding of your business’s story, you’re not getting the full picture.
By hiring an accountant, you can rest assured knowing that you have someone on your team to oversee all of your accounting and record-keeping initiatives. An accountant will keep track of tax costs, payroll expenses, retirement plan costs, office equipment purchases, marketing & promotional fees, and much more. This means you can avoid unnecessary expenses and ensure your business is as fiscally responsible as possible.
If you’re overspending, they’ll help you cut back and offer valuable advice about maximizing profits while fulfilling key business goals. If you’re prone to overspending or don’t feel confident with complex mathematics, hiring an accountant could represent one of your smartest business moves.
2. You’ll ensure your business remains compliant with state and federal laws
The rules and regulations surrounding cannabis sales can be confusing and hard to follow. While many states have legalized the sale of medical marijuana, the substance remains a class 1 substance under federal drug laws. Because of this, there is uncertainty surrounding whether banks should service clients working in the cannabis industry and how to handle the Internal Revenue Service’s (IRS) tax regulations surrounding “illicit substances.”
By selecting a skilled accountant with knowledge of the cannabis industry, you can avoid such confusion and avoid penalization. By hiring the services of a company like Green Space Accounting, you can ensure the following:
- That setting up your bank accountant is quick and easy: An accountant will know which documents to bring when setting up a new bank account, including your marijuana license, information about your sales tracking system, legal documents about operating agreements, Employee Identification Numbers (EINs), Articles of Incorporation, and more. Failure to present such documents could slow down the process.
- That you remain compliant with tax code 280E: This rule states that taxpayers cannot claim deductible expenses related to the sale of illicit substances such as cannabis. Given that cannabis remains illegal on a federal level, it can be tricky to get around this law and make the most of business-related write-offs. Fortunately, you can write off expenses related to the cost of goods sold (COGS), an exception that your accountant will help you navigate to ensure you hang on to as much profit as possible.
- That you maintain a healthy relationship with your bank: Hiring an accountant will help you maintain an open and honest relationship with your bank, as they will know precise details about your incoming and outgoing expenses. Failure to provide accurate numbers or meet regularly to discuss the details of your accounts could make your business seem untrustworthy. In the long term, this could lead to legal issues or the closing of your account.
3. You’ll have time to focus on core business tasks
One of the primary reasons entrepreneurs outsource tasks is to make time for the creative aspects of growing a business. Driving business growth requires much more than smooth day-to-day operations and well-maintained accounts. It also requires the ability and motivation to set your business apart from competitors and present customers with dynamic new offerings.
Doing the creative work involved with entrepreneurialism is tricky if you’re faced with a pile of administrative tasks. By enlisting the help of a professional accounting firm, you’ll enhance the quality of your business’s accounting work while freeing up plenty of time for other tasks, such as:
- Expanding your product line or service offering
- Selling your products across new platforms
- Investing in customer acquisition
- Conducting industry research
- Researching new business tools
- Drawing up a growth plan
- Generating new business models
The Bottom Line
Managing the financial side of your business can be daunting, complicated, and most of all: stressful. If you own a business in the cannabis space, it’s wise to consider outsourcing your accounting initiatives to an industry professional.
Whether you are a start-up, a growing business, or a multi-state operator, specialized firms like Green Space Accounting can help you with intimate knowledge of cannabis rules and regulations.
Green Space Accounting is one of the leading cannabis accounting, tax, and advisory firms in North America. Our client service philosophy has helped forge an excellent working relationship with dispensaries, grows and ancillary businesses in the space. From accounting and tax services to business consulting and financial planning, we possess the knowledge and experience needed to assist you with your current and future needs.
 LaKia Bourne has 20+ years of experience as an accomplished and trusted accounting professional. As a women-owned and minority-owned accounting firm, LaKia has a passion for working with other small businesses and engaging in the local community, and her values drive her overall career goals and mission to uplift businesses and encourage financial competency through reliable accounting services.
LaKia Bourne has 20+ years of experience as an accomplished and trusted accounting professional. As a women-owned and minority-owned accounting firm, LaKia has a passion for working with other small businesses and engaging in the local community, and her values drive her overall career goals and mission to uplift businesses and encourage financial competency through reliable accounting services.

With her exceptional credentials and years of accounting experience, JoAnne Williams is a leader in every area of accounting and business consulting. Driven by a deep commitment to client satisfaction, JoAnne has helped non-profits and businesses of all sizes across various industries. Client satisfaction is her number one goal, making her a leader in every area of accounting and business consultation.
Committee Blog: Everything You Wanted to Know About Cannabis Facilities but Were Afraid to Ask Field Guide – Part 4 – Retail

 by NCIA’s Facilities Design Committee
by NCIA’s Facilities Design Committee
Jacques Santucci, Brian Anderson, David Vaillencourt, and David Dixon
Continuing our five-part series on the behind-the-scenes workings of the legal cannabis industry. This series focuses on all of the inner dealings and industry advice from established professionals to craft this unlimited How-to-Guide to assist you in setting up your own facility. These articles cover cultivation, extraction, infused products, and retail facilities as well as support activities. In general, remember to be compliant with all local rules and regulations and contact a licensed contractor and industry expert.
Part Four, Retail & Dispensaries: Top Things to Consider When Planning Your Cannabis Dispensary and Retail Operations
Retail and dispensary design presents challenges that are distinct from the other areas of cannabis production and manufacturing. The biggest difference is that the design must now account for customers as well as employees. Listed below are a number of issues that an operator should consider as they are in the process of designing their retail or dispensary operations. Always remember to be compliant with all local rules and regulations.
Security Camera: Minimum Area of Coverage
Most states require a hundred percent minimum security coverage in any area where marijuana products are stored, displayed, or sold. Designing a camera system and placements to avoid “dead spots’ ‘ (i.e. areas with no camera coverage) can be challenging, especially if the operation is taking over an existing space, as opposed to building a new facility from scratch.
Bonus Consideration: Think about having an HVAC system specially dedicated to your security room. Security rooms for video monitoring and storage can sometimes be an afterthought. But these locations should be treated more like computer server rooms as opposed to standard office space. And with the amount of technology placed in a (typically) small space, things can overheat rather quickly. This can lead to damage to the system and ultimately, you could be out of compliance for video storage and retention.
Another Bonus Consideration: do not forget about placing security cameras to cover the entrance and exit points to the parking lot. Think about the field of view around doors, especially if the door is near the corner of the building or if there are other obstructions that can block the camera’s view of the area. Multiple cameras may be needed for this critical function. Contact a licensed professional.
Security Camera: Minimum Data Storage
Video storage and retention requirements for cannabis facilities are fairly stringent. Typical requirements include 90-days of on-site storage and up to five years of off-site storage. Off-site data storage is required for future legal needs. Many states require a minimum video resolution of 1080p. The video storage needs for even a moderately sized facility can amount to petabytes of data. For this reason, many facilities outsource this function at least in some measure. If you do decide to handle this all yourself, you should be sure that you have the technical expertise on your staff to handle this potentially complex technical issue.
Security Alarm: Monitoring
Like it or not, retail cannabis facilities will probably always be targets for crime. Having a security system probably seems like a no-brainer. But simply having an alarm system isn’t typically enough. You will need a system that is actively monitored. This allows the company to initiate actions on your behalf depending on the alarm status (e.g., call the police or fire department in response to a remote alarm). Your alarm should be monitored by at least one reputable company. Redundancy might not be needed, but check to be sure that you are in compliance with local rules and regulations. Talk to your licensed professional.
Security: Line of Sight
Customers should only see the public retail area of the location. Customers should not see the back-of-house operations. There is no need for them to see how business is conducted other than at the sales counter. Similarly, there is no need for customers to be able to view the offices, inventory areas, working areas, employee break room, etc. Keeping these areas private helps to avoid bad actors from learning operational routines that might make it easier for them to exploit.
Safety and Injury Handling
This is an easily overlooked area but can definitely get your dinged upon inspection. Be sure you have the appropriate amount of first aid kits and burn kits onsite as reunited by local regulations. Pay particular attention to the regulations about the placement of these kits as they are sometimes required to be within visual distance of specific rooms within your facility. It can be a hard pill to swallow to not be able to get your operation certificate for forgetting such a simple item, but it happens all too frequently.
Employee Access
Having a non-customer door or access point is a best practice. Non-customer access points are where employees and products are brought into the facility without customer line-of-sight. In some states, this is a requirement so check to be sure your facility is in compliance with laws and regulations.
Product Delivery
Getting cannabis products into a retail facility is a critical part of the merchandise flow and one of the most vulnerable points for theft. For maximum safety and control, consider the use of an air-lock/man trap/sally port door arrangement. If not possible due to location or architecture, planning for business hours separation and process can keep customers separated from deliveries.
Employee and Counter Safety
The counters where transactions occur in a cannabis retail setting can pose some risks especially since most facilities are cash-based operations. An open style counter can open up opportunities for theft. Consider a security barrier counter. The idea is to attempt to prevent customers from having access to products, cash, or employees where possible.
Security: Egress
Customer flow can be somewhat challenging, especially in facilities that have a registration lobby that is physically separated from the retail sales floor. Having separate entry and exit doors for customers can help with the flow of customers. Not a requirement but potentially a good customer experience design.
Customer Environment
Dispensaries and retail locations can be busy places at times. In COVID times, this can be a big issue. But even under non-pandemic circumstances, there may be a need to control the number and spacing of customers for both safety and privacy. Social distancing- the process of limiting the number of customers for the available space within the building- can be enhanced through various design elements. These can range from the use of rope and stanchion barriers, to signage and floor stickers.
Lobby design for restricted access – if access to the sales floor is restricted to registered customers, a secure lobby space should be provided with a separated check-in space and access-controlled doors both for customer entrance and egress.
And do not forget bathroom access for customers. You can have a single facility that is unisex but it should also be ADA compliant.
Environmental Consciousness
Unfortunately, like most other retail spaces, cannabis retail still generates a significant amount of waste. And much of it may be recyclable. Business recycling bins should be provided.
Energy-saving considerations can also be important for retail facilities. Motion detecting light systems can reduce energy consumption in non-occupied spaces. At the very least, interior lighting switches should be located in the same area for easy use upon space exit. HVAC systems should have an occupied and unoccupied night setback capability.
Parking Lot
Depending on the total number of employees and customers you anticipate visiting your business at its peak times, you will need to design a minimum number of accessible parking spots.
If curbside pickup is legally allowed in your area, be sure to map out and reserve spaces exclusively for this activity. It should be close to the exit door where the product will be delivered to the customer. Remember to keep parking spaces for handicapped people and even maybe for motorcycles.
Check Out These Related Articles for More Top Things to Consider When Planning:
Part 1 – Cannabis Cultivation Facilities
Part 2 – Cannabis Extraction Facilities
Part 3 – Cannabis Food Production Facilities
Part 4 –Cannabis Retail & Dispensary Facilities
Part 5 – Cannabis Facility Support Areas
Member Blog: Key Metrics to Track & Mistakes to Avoid for Cannabis Retail Success in 2022

by Gary Cohen, Cova Software
Despite the pandemic, the cannabis industry has proven to be recession-proof and has grown exponentially over the past few years. Cannabis retail sales in the US are projected to top $30 billion in 2022, and as more states jump onto the legal bandwagon, competition will intensify. As such, dispensary owners must ensure that they are using data and analytics strategically to measure the health of their business. Many cannabis retailers fail because they don’t track crucial dispensary metrics or make avoidable mistakes.

Cannabis dispensary metrics are the data points that you must track regularly to help in better decision-making. Business intelligence reports generated via these metrics help you monitor your daily dispensary operations and create projections for future sales and required inventory. A robust cannabis POS system with advanced analytics and reporting capabilities collects information from various sources and unifies them into a single repository so that you can extract maximum insights for the growth of your retail business. By tracking some of the following important metrics, you can implement strategies to increase dispensary profits, enhance employee productivity, forecast inventory, and elevate the customer experience.
Cannabis Sales & Profits Metrics
- Number of Products Sold per Transaction
- Average Sales Value
- Total Sales for a Period
By tracking the average basket size and transaction value, you can evaluate your customer buying habits and ideal price points and create your marketing and promotional campaigns or upsell opportunities accordingly. Implementing strategies will help you increase these metrics, manage inventory and employees efficiently during your busiest sales periods, and thus, grow your dispensary profits.
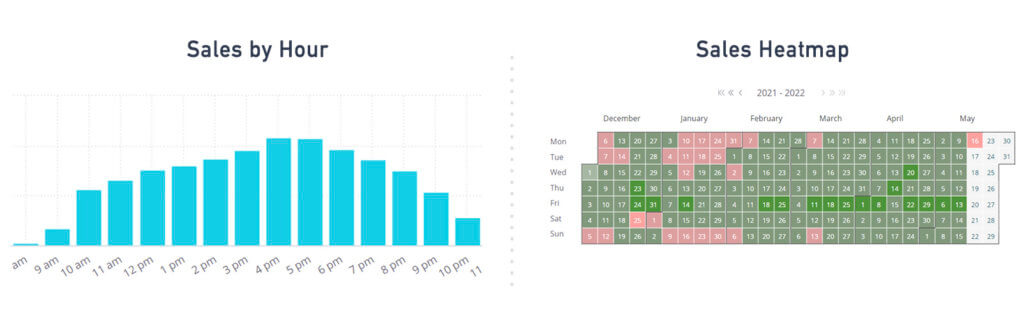
Staff Productivity & Dispensary Traffic
- Individual Budtender Sales
- Busiest Sales Days/Hours
- Discounts and Refunds
Tracking individual budtender sales on your POS system will help you determine your top performers and aid in staff scheduling. Those employees who have higher sales per transaction must be scheduled during your busier hours of the day, and those who may not be performing can be offered training on strategies like deals, upsells, cross-sells, and bundles. Also, potential fraud can be identified by tracking discounts or refunds offered by employees.
Target Market & Customer Retention
- Customer Demographics
- New vs Returning Customers
- Customer Lifetime Value
Segmenting your target market helps design a more customized experience based on age, location, values, buying behavior, etc. By tracking each customer’s average number of transactions over a period of time, you can determine their lifetime value and better tailor your dispensary’s promotions and upselling strategies through targeted marketing campaigns. These metrics help curate an enhanced shopping experience and increase customer retention.

Inventory & Product Performance
- Inventory Turnover
- Shrinkage
- Top-selling Product Categories
Inventory turnover measures the number of times you sold through your entire inventory in a given period and allows you to determine how much of your cash flow is tied up in inventory. Shrinkage is the difference between the inventory you have on paper and the actual inventory in stock and helps you identify theft. Also, tracking your top-selling and lowest-performing products or categories can help in crafting strategic promotions and better inventory planning decisions.
Keep up With Changing Times
Successful cannabis retailers track top-selling products, profit per product, and all other metrics highlighted above, and use this data to make business decisions. If you have a robust and flexible cannabis retail platform that offers you these detailed data insights and can scale and adapt when needed, your dispensary will always stay ahead of the curve.
Learn in detail about all the mistakes to avoid and secrets to succeed in the cannabis retail industry by downloading Cova Software’s e-book, “Why Some Cannabis Retailers Fail”, which presents cautionary tales of what not to do if you want to thrive in the dispensary business.
 Gary Cohen is the CEO of Cova Software, the fastest growing technology brand in the cannabis industry. Cohen’s focus has been driving the company’s overall strategy, including its vision, go-to-market plan, and strategic development. Since joining the cannabis industry in 2016 and launching Cova commercially in 4q17, Cohen has led Cova to dominate the enterprise sector for dispensary Point of Sale, while forging client relationships with hundreds of single-store retailers across North America.
Gary Cohen is the CEO of Cova Software, the fastest growing technology brand in the cannabis industry. Cohen’s focus has been driving the company’s overall strategy, including its vision, go-to-market plan, and strategic development. Since joining the cannabis industry in 2016 and launching Cova commercially in 4q17, Cohen has led Cova to dominate the enterprise sector for dispensary Point of Sale, while forging client relationships with hundreds of single-store retailers across North America.
With Cova’s cannabis POS and its excellent integrations with eCommerce and delivery services, the online order automatically pops up for the budtender to tender the sales, and the POS system updates inventory once payment is approved. Cova offers multiple eCommerce solutions to choose from, as per your needs and budget, and you can legally sell cannabis online stress-free while staying compliant with strict government regulations.
Member Blog: Illinois Adult-Use Dispensary Applicants Hope Licensing Process Doesn’t Go Up in Smoke

by Andrew M. Halbert, Fox Rothschild
Recently, after delays in issuing any adult-use dispensary licenses, Illinois has attempted to push ahead with simplifying the application and issuance process. Interestingly, this has occurred even as recent developments in ongoing litigation indicate potential further delays in issuing the previously awarded licenses that are currently in limbo, and in one case, even threaten to upend the entire process.
Delays and Initial Lottery Announcement
On September 3, 2020, after multiple delays, the Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Responsibility (“IDFPR”) announced the application scoring results for the initial 75 new adult-use dispensary licenses to be issued under the Illinois Cannabis Regulation and Tax Act (the “Act”). Only 21 of the 900-plus applicant groups had achieved a perfect score, and the available licenses would be awarded via a series of lotteries involving only those applicants. Although all 21 applicants with a perfect score were deemed too qualified for “social equity” status under the Act, there were public allegations that only 13 of the 21 accepted applicants were actually owned and controlled by people of color.
Faced with multiple lawsuits claiming various flaws in the process, the Governor suspended the initial lottery. He announced that IDFPR would distribute Supplemental Deficiency Notices explaining where applicants missed out on points, and providing an opportunity to correct any identified issues. Unfortunately, this satisfied neither the excluded applicants nor those applicants who had already received a perfect score, and litigation continued. As of May 1, 2022, none of the proposed new adult-use licenses have been issued.
HB 1443 and New Lotteries
In July 2021, the Illinois legislature adopted H.B. 1443 in an attempt to address social equity concerns and expedite the issuance of dispensary licenses. It established procedures for three adult-use dispensary lotteries to occur in July and August of 2021, in which a total of 185 adult-use dispensary licenses were to be issued.
The first lottery, for 55 new licenses, included only applicants that received 85% or more of the available points. The second lottery, also for 55 additional licenses, included applicants that received a score of 85% or higher and met the ownership and control requirements for Social Equity Applicants. Applicants that qualified for social equity status solely by hiring qualifying employees were excluded from this lottery. The final lottery, for the original 75 licenses, included the 21 applicants who initially received a perfect score, as well as an additional 134 applicants who perfected their application using the Supplemental Deficiency Notice process. Although IDFPR announced the winners, none of the licenses have been awarded yet due to the ongoing litigation.
More recently, on March 15, 2022, Governor Pritzker announced another planned lottery process to occur later this year to award 50 new adult-use dispensary licenses. The proposed rules governing this process were released on March 25, 2022, and include a new, simplified online application process and an administrative review provision designed to help address issues without the need for litigation.
Status of Litigation
As Illinois attempts to streamline its processes, three different ongoing lawsuits involving Illinois dispensary licenses have continued to progress, one of which threatens to upend the entire lottery process.
First, Wah v. IDFPR claims that the additional points given to veteran-owned applicants create a special class of applicants in violation of the Illinois constitution. The most recent relevant development, in this case, was the stay order that prevents IDFPR from issuing any of the 185 dispensary licenses until the issues raised in Wah have been resolved, which remains in place.
A second lawsuit, which is really a group of fourteen different lawsuits involving dozens of plaintiffs consolidated into one “supercase,” challenges the application process on the basis of alleged violations of Illinois administrative law, and asks that the plaintiffs be provided additional licenses beyond the 185 currently allocated. The judge in that case recently had the opportunity to take control over the stay in Wah, but declined. As a result, the resolution of this case will affect only the parties to the case, and will not affect the larger issue of the stayed licenses. At a recent hearing, the parties discussed a supplemental lottery process for the plaintiffs that would attempt to recreate the odds that those plaintiffs would have faced in the original lottery, had their applications not been improperly excluded, and the fact that plaintiffs would need to succeed in that lottery in order to have a viable claim to a license. IDFPR and the judge indicated their belief that this lottery should occur soon so that unsuccessful plaintiffs could avoid further litigation costs. However, not all plaintiffs were amenable to this proposal, raising the issue that if none of the plaintiffs were successful in the proposed lottery, IDFPR might never be held to account for any flaws in the application process.
Finally, a third case was recently filed that could upend the entire licensing process. That case, Finch, et al. v. Mario Tretor, Acting Secretary of IDFPR, 1:22-cv-0158 (N.D. Illinois, March 23, 2002), claims that granting additional application points to Illinois residents (as well as the Illinois residency requirements included in the qualifications for social equity status) should be deemed unconstitutional under what is known as the “dormant commerce clause” because it unfairly discriminates against residents of other states. The plaintiffs in Finch have already won a similar case in federal court challenging similar requirements in Missouri, so those watching the case closely are concerned that this court may reach a similar result. In addition, because this case challenges the constitutionality of the entire scoring process, a win for the plaintiffs could mean a reset for the entire licensing process, even affecting those 185 licenses that have already been awarded.
All that interested Illinois applicants can do now is wait, and hope that these issues are resolved soon and licenses are finally released. Once that happens, expect a flurry of activity as those lucky enough to receive a license seek capital and expertise, with some likely to explore options for selling their newly-acquired license.
 Andrew Halbert is a member of the National Cannabis Law Practice at Fox Rothschild LLP, based in its Chicago office. He focuses his practice on representing public and private clients, including cannabis companies, in a broad range of transactions including: state and local cannabis regulatory and licensing transactions; stock and asset acquisitions and divestitures; mergers; tender offers; private equity investments; reorganizations; private offerings; and financing transactions facilitated through the issuance of equity and debt securities.
Andrew Halbert is a member of the National Cannabis Law Practice at Fox Rothschild LLP, based in its Chicago office. He focuses his practice on representing public and private clients, including cannabis companies, in a broad range of transactions including: state and local cannabis regulatory and licensing transactions; stock and asset acquisitions and divestitures; mergers; tender offers; private equity investments; reorganizations; private offerings; and financing transactions facilitated through the issuance of equity and debt securities.
Member Blog: What in Tarnation? North Carolina Stepping In The Wrong Direction

By Bethany Niebauer, Axial Compliance Consulting
North Carolina, one of the last holdouts for any kind of marijuana program, is finally considering a medical bill. As a North Carolinian, I always thought that I would greet this news with joy and pride. Instead, I feel disappointed at the regressive and paternalistic bill my home is likely to pass.
To give a little bit of context, the state has about 11 million residents. Famous for its tobacco production, the state is quickly becoming a leader in STEM jobs. In 2020, the capital of Raleigh was ranked the third best city in the country for technology, due to the rapid growth of that sector. Meanwhile, Charlotte remains a leader in banking. After New York City, it is home to the country’s second largest financial services hub. North Carolina has a reputation for being regressive, or even backwards, but its residents are at the forefront of some very progressive industries.
Despite all this progress, the proposed medical marijuana bill is a shining step in the wrong direction. North Carolina’s SB 711, also known as the NC Compassionate Care Act, was originally brought forth by Senator Bill Rabon (R- New Bern), in April of 2021. The bill is strangely modeled on Utah’s medical program. Utah has one of the highest rates of prescription drug abuse outside of the rust belt. Yet with a population of just over three million, state regulators licensed a mere 14 dispensaries. This is insufficient to meet the needs of a large, rural population. Still, Utah has 17 qualifying conditions for patients seeking entry into the program.
North Carolina recognizes only 14 conditions and chronic pain is not among them. Post-traumatic stress disorder is a qualifying condition so long as the patient can prove, (with evidence) that he or she experienced a traumatic event. The bill includes a presumption that if a servicemember served in an active combat zone that he or she experienced a traumatic event. North Carolina is a service dense area, but not every veteran will serve in an active combat zone. Many service members will be precluded from accessing the medicine they need. Furthermore, the bill is vague about what constitutes evidence. If a college student is raped at a fraternity party but doesn’t report it to the police, will there be sufficient evidence to qualify under the rules? The bill is unclear.
The bill requires vertical integration at a time when most states are moving away from that model. An application fee is a whopping $50,000. The bill seeks to award 10 licenses and each license will have the ability to cultivate, process, and dispense, (with up to four dispensaries per license). The bill currently requires 10% of gross revenue paid to the Department of Health and Human Services as a monthly fee. Clearly, this bill is designed to suit the interests of multi-state operators. No one else will be able to participate, much less survive, in such a costly environment.
By now, most states see the value in social equity. New York and New Jersey both made strong strides in promoting diversity amongst license holders. The North Carolina bill fails to mention social equity or even diversity. Sensible South, a lobbying group that claims to promote the interests of future North Carolina patients is working hard with some of the largest MSOs, including Cresco, PharmaCann, and Columbia Care to set the playing field in their favor. When I asked Garrett Perdue, the group’s founder, if there was any room for small operators in this legal framework, he shrugged his shoulders and said “I really don’t know.”
North Carolina is contemplating legalizing medical marijuana while looking down its nose at patients and the cannabis industry in general. Anyone in North Carolina interested in a more equitable program should contact their state legislators and make the following requests: (1) broaden the list of qualifying conditions so that more people can access the medicine they need, and (2) permit separate license types so that smaller operators have a chance of success.
 Bethany Niebauer is the CEO and Founder of Axial Compliance Consulting. Based in Denver, Colorado, Axial Compliance assists clients across the country with all aspects of license management, including new license applications, renewals, modifications, and transfers. Bethany grew up in Greensboro, NC.
Bethany Niebauer is the CEO and Founder of Axial Compliance Consulting. Based in Denver, Colorado, Axial Compliance assists clients across the country with all aspects of license management, including new license applications, renewals, modifications, and transfers. Bethany grew up in Greensboro, NC.
Committee Blog: Is American Cannabis Still the Wild West?

 by NCIA’s Risk Management and Insurance Committee
by NCIA’s Risk Management and Insurance Committee
Matthew Johnson, Quadscore Insurance Services
Cannabis is America’s riskiest business.
Cannabis itself is a highly valuable commodity, but cannabis businesses also deal largely in cash – making them a prime target for thieves across the country. Recent headlines have reported a rash of unsolved robberies in the Bay Area and Washington State, not to mention the seizure of cash from Empyreal’s fleet of armored transport vehicles (fortunately, that cash has now been returned by the police).
This is a national problem, which begs the question… What should cannabis businesses do to stay safe during these trying times?
There are many different means of minimizing the risk faced by your modern cannabis business, but we’re going to focus on the big three today – security, technology, and compliance. Through careful consideration of these three tenets, cannabis businesses can take significant steps to mitigate risk and protect their employees. Appropriate investments can yield tenfold savings in the form of fewer stolen assets, lower insurance premiums, peace of mind, and safer employees.
SECURITY
Let’s start with the topic that gets the most attention during a crime spree – security. In cannabis, security means a number of things… video cameras, man traps, motion sensors, hardened glass, ID checks, and more. When building or retrofitting a facility for cannabis operations, it is crucially important to consult with security experts like Sapphire Risk Advisory Group or Cannabis Compliant Security Solutions.
“In many areas, it’s not a question of ‘if’ a cannabis business will be robbed – it’s ‘when,’” cautions Chris Eggers, CEO of Cannabis Compliant Security Solutions. With 13 years of experience as a law enforcement officer in the Bay Area – including several years working as an undercover narcotics officer – Chris is uniquely qualified to address the ongoing issues in Oakland and other areas along the West Coast. “There’s a question of how you navigate and survive an incident, but beyond that, how you ensure that your business will survive too.”
There’s an important distinction between security consultants like CCSS, security integrators, and vendors. To achieve best results, cannabis businesses should work with a security consultant who can identify ways to protect the business – without being tied to commission-based sales contracts or a specific ‘brand’ of security solutions.
TECHNOLOGY
Physical security aside, there are a number of high-tech security tools that can help cannabis business owners protect their operations. For example, let’s take a look at the biggest security company you’ve never heard of – an organization called 3SI Security.
3SI Security began their journey over 50 years ago as the original producer of dye and smoke packs intended to deter bank robbers in the 1970s. Technology has evolved over the years, and so has 3SI’s product offering – now, their GPS tracking tech is ubiquitous throughout banking, pharmaceuticals, luxury retail, and telecommunications.
As VP of Business Development for 3SI, Carlos Casas works to connect cannabis businesses with this tech to protect their assets and employees. “According to a Forbes report from July 2020, an estimated 70% of cannabis businesses are cash-based. This is a staggering statistic which shows the real risk to the industry is on an upward climb.” With the SAFE Banking Act still in the works, savvy business owners have to explore alternative solutions like 3SI’s technology to ensure their business stays safe.
Apart from 3SI, there are a number of technology companies that provide technology to make the cannabis industry a safer place. ADT Security has recently launched a cannabis-focused divison of ADT Commercial to provide critical security technology to cannabis businesses around the country. After spending three years keeping HERBL’s fleet secure on the west coast, Andy Fleet now leads ADT’s efforts to provide security solutions to the cannabis industry.
According to Andy, “Security planning is critical for any cannabis organization. Take the time to evaluate all the risks within your establishment and build a robust plan that ensures all areas of physical safety and security are considered and protected.” Underscoring the points above, Andy continues, “Working with a licensed, experienced consultant will ensure adherence with all relevant regulations and help keep your employees safe while having technology do the heavy lifting for you.”
COMPLIANCE & COVERAGE
Next up, everyone’s favorite topic: compliance. In this sense, we’re not talking about adhering to the myriad regulations imposed on cannabis businesses wherever they operate – but rather, making sure that your operation complies with the protective safeguard requirements in your insurance policy. Non-compliance with or material misrepresentation of your active protective safeguards could result in an uncovered or denied claim – and could even cause problems with your investors. If you’re buying insurance, you want to make sure that your policy will pay out when stuff hits the fan!
Theft Sublimit – Most cannabis insurance policies will only cover theft losses up to a certain ‘sublimit’ depending on the quantity of cash/cannabis being stored, the physical location of the cannabis business, and any relevant losses that the insured business may have sustained due to theft. Make sure that you are comfortable with the sublimit provided and, if you aren’t satisfied, work with your insurance broker to see if you can secure higher limits.
Protective Safeguards – Virtually all cannabis insurance policies carry some warranties around protective safeguards that can impact your coverage in the event of a claim. Make sure to read the Protective Safeguards endorsement and check that all of your security systems are functioning in compliance with these requirements.
Motor Truck Cargo – Similar to the protective safeguards warranty, make sure that you study your policy to ensure that any requisite safeguards are in place. For transportation operations, these safeguards are likely to include vehicular telematics, buddy systems for drivers, GPS tracking, and possibly even an escort vehicle to accompany the transport unit.
Security guards – When hiring security guards, it is recommended to employ a third-party guard service that carries appropriate limits of insurance. Make sure that your business is listed as an additional insured on their insurance policy to ensure coverage in the event of an altercation at your business!
Financing – Lenders and VC firms will often stipulate that the companies accepting their funds will need to adhere to certain requirements, like securing Directors & Officers insurance for the officers and executive board. Beyond insurance, it’s important to make sure you are actually doing what you promised to do in terms of safeguarding the property and not just so that you may be eligible for coverage, but also so that you are not held liable for losses suffered by third parties, such as lenders and investors.
Joseph Cioffi, chair of the Insolvency+Finance practice at the Davis+Gilbert law firm in New York advises, “Operators typically make certain representations to investors, lenders, and other capital providers, and undertake certain activities intended to preserve asset and collateral values. The operator is looking at default if it’s in breach of contract, but worse, the operator and its principals could be sued for misrepresentations made in obtaining funding – and be held liable for losses that flow from those misrepresentations.”
CONCLUSION
Like an onion, there are many layers to a risk management program for cannabis businesses. Through careful implementation of security measures and protective technology, many businesses will be able to prevent damage to their business with proper planning. In case all security measures fail, a comprehensive insurance policy should be able to help make a business whole again after a claim. Make sure to work with the proper insurance, security, and legal experts when building or restructuring a cannabis operation!
Member Blog: 2022 Cannabis Compensation Survey Reports Released

By Matt Finkelstein, FutureSense LLC
We are pleased to announce the release of the 2022 Cannabis Compensation Survey Report. The 3rd annual report seeks to further understand and illuminate pay trends and practices in the legal cannabis industry by aggregating and presenting benchmark data in accordance with federal guidelines.
FutureSense and NCIA laid the foundation for the project in 2019 and released results for the inaugural survey at the end of that year. At the onset of the pandemic in early 2020, both parties took a step back to adjust their trajectories looking to enhance the scope and depth of the project. Marijuana Business Daily came on as a primary partner to assist with publication and distribution. Green Leaf Payroll & Business Solutions came on as a supporting partner, providing the project with anonymized payroll data. NCIA has stayed on as an endorsing partner to promote the shared mutual interest of supporting cannabis businesses and the industry at large. In 2022, the project added Western Management Group to support data management, calculations, and analysis.
This year, the survey focused on the cannabis vertical – gathering data specifically for the cultivation, manufacturing, distribution, and sales sides of the business. It established benchmarks with reportable data for 87 unique positions in 41 jobs families/function. With its continued growth and expansion of participation from the industry, it has also begun to analyze demographic breakouts by state, headcount, and revenue.
The final report is available in two tiers:
- The Summary Report – available free to the public; contains high-level trends & analysis along with three data cuts indicating central tendency.
- The Detailed Report – available to current participants, other cannabis companies, and consultants & ancillary/professional service providers; contains more data cuts, percentiles, and demographic breakouts by state, headcount, and revenue (where appropriate).
For more information and to download your copy, please visit: https://content.futuresense.com/2022ccs
The cannabis industry’s job market continues to evolve. The free Summary Report presents an analysis of the current state of the market, including trends relating to the “Great Migration,” the “Great Resignation,” the pivot to hybrid/remote work, and the challenges faced by major MSOs and small, independent, craft, and legacy operators. The Detailed Report presents in-depth data cuts by job and can be used across every facet of business.
Understanding not just how to pay your employees, but also how to attract, motivate, engage, and retain your employees through compensation can be make-or-break in this rapidly evolving industry. 60-70% of companies’ expenses are typically due to payroll. Being 5% on- or off-the-mark could mean thousands or hundreds of thousands of dollars either lost or gained.
The survey’s success is contingent on participation. More and more companies are realizing the value of this information and the importance of transparency through 3rd party surveys. All submissions and their respective data are held in strict confidentiality. Abiding by the Department of Justice regulations, this survey produces anonymous and unbiased results.
The survey accepts organization-wide submissions for cannabis companies with ten or more employees at this time. Individual submissions are appreciated as anecdotal insights but are typically not included in data calculation.
For any questions and/or to sign up for next year’s survey, please email matt@futuresense.com or visit: https://content.futuresense.com/2022ccs
Survey: NCIA Retail Committee Wants To Hear From Cannabis Retail Employees

 NCIA’s Retail Committee is looking to gauge what educational material may be the most useful in order to better direct our efforts on content creation for all cannabis retail employees.
NCIA’s Retail Committee is looking to gauge what educational material may be the most useful in order to better direct our efforts on content creation for all cannabis retail employees.
We would like to hear from those who are most affected by training and continued education, in hopes of being able to provide tools that will enable all retailers and retail staff to grow and develop.
If you can please share this quick questionnaire to your staff, we would greatly appreciate it!
*All submissions are completely anonymous*
Committee Blog: Social Equity Perspectives on Interstate Commerce – Part 3
 by Mark Slaugh, iComply LLC
by Mark Slaugh, iComply LLC
NCIA’s Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Committee
Previously, in part 1 and part 2 of this series, the DEIC examined the problems inherent in existing social equity programs and the merit for federal social equity in regulating interstate commerce. The DEIC also examined the key components of a proposed framework to address these challenges, how to define social equity federally, and the merit of determining the types and numbers of permits to be issued.
Sadly, as written currently, all proposed federal bills fail to meet the critical objective of creating as much NEW generational wealth for the most number of those disparaged from participating in the legal cannabis industry because of the socioeconomic impacts of more than 80 years of federal marijuana prohibition and due to the barriers to entry created amid state regulatory regimes.
To conclude this policy framework proposal, the DEIC will look at the key considerations for a federal program to ensure it functions as designed and how this framework can create social equity technical assistance, qualification, and a phased approach of implementation to ensure that social equity operators have ample time to qualify, have adequate funded, and are set up for success with an equal starting line in the new interstate commerce industry.
Qualifying Social Equity Operators – Federal Technical Assistance Program
It is imperative that any federal social equity framework helps the industry and their new partners, by ensuring permit holders are qualified in both cannabis and business backgrounds, and by helping them bring financing to the table to start a permitted interstate commerce cannabis business that can be as ready, as quickly as possible, to help import, export, and transport cannabis between the States.
To carry out these provisions in the policy, we recommend that amendments to any federal act include:
- Requiring that qualified social equity interstate commerce permit holders:
- Have a path to educational qualification (training and development)
- Can qualify with equivalent experience
- Can pre-qualify for the SBA’s funding once they obtain education or equivalent experience (funds issued upon state licensing approval)
- Obtain the majority of initial permits offered for interstate commerce (95%)
- In alignment with how long and at what percentage the current industry has been dominating the ownership of licenses
- Entities should have 51% or more verifiable ownership and control by a social equity qualified applicant.
- Advisory Committee to determine how to verify the 51% social equity ownership
- Providing social equity qualified permit holders exclusivity for at least 5 years to ensure the qualifying process takes place equitable to the average time in which the industry developed for adult use without considering social equity.
- Mandating laboratory testing as national permitting for interstate commerce to work.
- Ensure parity amongst states and tribal nations such that tribe-to-tribe trading and interstate trade routes can be protected.
- Avoiding overly limiting interstate commerce permits, but also giving them value by not making them unlimited either.
- DEIC suggests 1,500 permits as a starting point divided among the three primary types as a fair balance initially.
These pillars of federal act amendments will proactively resolve interstate commerce concerns that are inherent in descheduling cannabis. Further, pre-qualifying permit holders based on their experience, education, as well as federal financing for their business (contingent on state licensing), will accomplish two primary concerns:
- Incentivizes state governments to create social equity licensing regimes that emulate federal efforts
- Reduces “predatory” operating agreements that use “token” social equity applicants who do not participate in the business license, contribute little to no financing, and are thereby diluted by existing operators and investors
We believe the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) is best to handle collaboration efforts to define this new “Minority Cannabis Business” (MCB) certification program for both program providers on the educational side and for pre-qualifying federal funding for qualified applicants.
Through this qualification, the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) and (SBA) would issue an interstate commerce permit to be tied to state licenses, and only then would funding be issued to the applicant by the SBA. All funding issued is contingent on obtaining a state licensed facility or partnership with an existing operator in any given state.
Phased Approach:
We believe it is also important that the amendments clearly lay out a multi-phased approach to the rollout of interstate commerce permitting to ensure those most qualified operators proceed first, and to then qualify others with enough time to do so. Encapsulating the proposed amendments, we envision the following steps to ensure a smooth transition that maximizes the opportunity for social equity applicants to succeed:
- Initially, establishing the advisory board for the regulatory agencies and mandates to allow for education providers to apply and be approved to provide the educational qualification to social equity applicants. These education providers may also be prioritized based on social equity and curriculum requirements designed in collaboration with cannabis business experts and diversity, equity, and inclusion advocates in cannabis.
- For those who lack the experience in operating an interstate commerce permitted business, but who are impacted by the war on cannabis, approved educational programs are invaluable to overcoming the barriers in not knowing how to operate a regulated cannabis business.
- Those with experience may qualify, without the need of an educational provider, and each are evaluated for priority licensing according to the following priority:
- Applicants with cannabis and business experience (most qualified)
- Applicants with legacy experience but limited regulated business experience
- Applicants with business experience but limited cannabis experience
- Applicants with little cannabis or business experience (least qualified)
- If qualified in both, the applicant goes first and can qualify for SBA funding fastest.
- If they have limited experience in cannabis or business, then the applicant can take the coursework to qualify and apply for SBA funding.
- During this time, it is also crucial to increase community education efforts so that communities impacted most by the war on cannabis can be made aware of the opportunity to qualify, be trained/educated, and approved, and get access to the information necessary to pursue the opportunity along the above pathways.
- Provide an education fund for state and municipal governments to promote the benefits of cannabis social equity, responsibilities, and risks of cannabis.
Access to financing is critical for social equity applicants and must be made available through the qualification process for social equity qualified businesses. Once qualified on education or equivalent experience, the SBA may pre-approve funding for qualified applicants. By achieving these qualifications, applicants have access to *reserved* funding appropriated by the federal act. Pre-approved financing in the form of grants and low-interest business debt instruments that are contingent on successful completion of course requirements and other “qualifying” factors for a Minority Cannabis Business is critical to ensuring success for operators and the federal government.
These government loans say how one qualifies and is “pre-approved” so that applicants can negotiate with existing industry license holders as valuable partners and receive federal funding contingent on state licensing approval. The idea is to promote partnership and participation between the existing industry and newly established social equity entrepreneurs while ensuring equal opportunity for social equity operators who do not choose to partner with the industry.
Follow Through
To ensure the program functions as designed and that the advisory committee is provided with as much data as possible to improve upon these suggested amendments, the Diversity Equity and Inclusion Committee (DEIC) recommends a final amendment in the form of a best practices study, along with collected data from participating states, to be instituted and reviewed annually for the first five years and subsequently every three years.
The intention of this study and report is to ensure the enforcement of laws, standards, and programs and to monitor that the activities of social equity operators are in alignment with the intention of the program in benefitting the social equity entrepreneurs permitted, that policies against predatory operating agreements are being enforced, and that policies are truly beneficial to creating social equity in the cannabis industry. The study will provide evidence of the benefits and challenges of the program, as well as possible improvements at federal and state levels.
Conclusion
It seems obvious that unless any social equity partner can “bring more to the table” to balance a “mega player’s” contribution, be educated in all aspects of their chosen field in the industry, recognize predatory agreements, and otherwise be positioned more equally to meaningfully participate in the cannabis industry, social equity programs will continue to fall short of meeting the goal of creating new generational wealth.
History has shown that as long as there’s an opportunity for inequality to be wielded as a weapon for those in power, it will be. No amount of good intention can change that fact.
Social equity requires empowerment opportunities for social equity candidates to bring more to the table as equals with “mega players.” We recognize partnerships can be an ideal path forward when the power dynamics within them are balanced and fair. The DEIC proposes these amendments to any federal act to serve as solutions to the traditional problems of inequality, exclusion, and gatekeeping that once spurred prohibition in the first place and that continue to prevail in the inequity the cannabis industry is still experiencing and to solve the shortcomings of social equity programs thus far.
We recognize that the role for the federal government in these federal act amendments is to even the odds in interstate commerce permitting. Their role is to oversee the fairness in qualifying candidates, to ensure a meaningful value for the permits issued, to give permittees the chance to catch up to the privileged few already in the industry with lockout periods for non-social equity applicants, limited licensing, and to provide access to financing for those traditionally locked out of access to financing or wealth as aa result of systemic oppression caused under prohibition.
Interstate commerce permitting seems like the last true chance for America to atone for 80+ years of marijuana madness and its detriment on our society. It is also the last chance for the industry to search for its soul to balance the impacts prohibition has had on these operators in excluding their participation in legal cannabis initially – born as a result of systemic discrimination overall and colonized on by those with clean records.
In doing so, a more equitable federal act can create the bold ideas and incentive to bring traditional wealth and experience into partnership with underprivileged social equity operators and their expertise/culture to form partnerships that truly represent the intent behind the policies intended for social equity and to create a more diverse, equitable, and inclusive industry for all.
Committee Blog: Everything You Wanted to Know About Cannabis Facilities But Were Afraid to Ask Field Guide – Part 3 – Extraction

 by members of NCIA’s Facilities Design Committee
by members of NCIA’s Facilities Design Committee
Jacques Santucci, Brian Anderson, David Vaillencourt, and David Dixon
Continuing our five-part series on the behind-the-scenes workings of the legal cannabis industry. This series focuses on all of the inner dealings and industry advice from established professionals to craft this unlimited How-to-Guide to assist you in setting up your own facility. These articles cover cultivation, extraction, infused products, and retail facilities as well as support activities. In general, remember to be compliant with all local rules and regulations and contact a licensed contractor and industry expert.
Part Three, Food: 10 Things to Consider When Planning Your Manufacturing of Infused Products (MIPs) Operations
Food safety and handling practices are an issue for any industry working with or processing products for human consumption and often come with strict guidelines that need to be followed. In the cannabis industry, edibles and other processed or infused products Manufactured Infused Products (MIPs) are ready-to-eat foods, so many states are regulating them as foods under the cGMP requirements of 21CFR117. We feel this is likely the approach that will be appropriate when cannabis becomes federally legal. These 10 things should be considered as you begin to plan your facility. Always remember to be compliant with all local rules and regulations.
Sanitary Design and Operation
A production room is straightforward, conceptually: design the space so walls, floors, and ceilings can be washed and sanitized, then verified (ATP swabs) to confirm the cleaning process is effective. To facilitate cleaning, everything needs to be pulled away from the walls, the ceiling needs to be solid and the walls need to be sealed. Insulated metal panels (IMP) are a cavity-free construction that is seeing wide acceptance in the industry. To keep the space clean during operation, slope the floors to spot drains, install coves along with the floor/wall interface and avoid ledges and traps for water or dust.
Employee Hand Washing
A stringent internal process for sanitation and washing of hands is crucial. Make sure that lavatories are available throughout your facility for proper sanitation. Confer with the municipal board of health for locations and quantity. Generally locate any place where employees are handling consumable products or encounter the potential for microbiological.
Boot Washing
Sanitation includes making sure all boots/shoes are free of contaminants. Employee captive corporate footwear programs prevent contamination potential from non-business-related employee activities.
Cart Washing
For carts that transport ingredients and materials, it is important to prevent floor debris getting transferred from one area to another. Two areas of concern; are wheels and cart shelves. Either wheel or shelf area can be addressed from multiple washing devices specific to each type of cart used.
Product Storage
Food safety temperature and humidity separation of products are an important factor. The purpose is to store food products at such a temperature and humidity level to prevent the growth of undesirable bacteria.
Allergen cross-contamination
Make sure to arrange products to avoid cross-contamination of open and unopened products. Keep the first pallet off the floor at a height of 6” AFF to avoid picking up contaminants. OHSA SHARP may apply how to organize products.
You can design barriers to keep contamination from entering a room.
Limit contamination by having and always renewing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), since the adjacent hallways may transport raw biomass. Test all ingredients, including THC, to ensure that everything is microbiologically safe. Wipe down, or unpackage ingredients, materials, and supplies before bringing them into the ‘clean environment’ room. Wear specific scrub, clean boots, and wash off any carts entering the room.
Employees entering the food production space
Contaminants can enter via the employees. It is essential to have all employees and agents clean up before entering the food production space. You must provide facilities to wash and sanitize hands as well as boots. Continuous training of employees and monitoring adherence to the procedures is important. Your procedure will include how sanitation is necessary, where are smocks hung, how are shoes cleaned, etc. Typical controls are in the FDA Food Code for jewelry, open sores, illness, etc.
Food Safety Inherent in the Recipes
Complete a Food Safety Hazard Analysis to know if you need to implement an upstream preventative control, such as for chocolate, or if you need to manage a thermal kill-step such as cooking the gummies mass. Low water activity, high acid, or a natural biocide additive, can all be considered.
Control for Allergens
MIPS often contain soy, flour, eggs, dairy, peanuts, tree nuts, coconut, and perhaps others. Each has special considerations for allergen separations and allergen cleaning.
Ware Washing and Clean Parts Storage Room
Don’t Underestimate the Ware Washing and Clean Parts Storage Room. Adjacent to your MIPs production room, consider building a washroom with a commercial dishwasher for utensils, kettles, wetted parts, trays, molds, etc. You might install a three-compartment sink. And make sure to safely store clean items, so they dry and do not get recontaminated prior to use. This room is maintained at negative pressure to the MIPs production room.
Plan for the Pantry
Store ingredients, materials, and supplies in a pantry off the MIPs room can be considered. It is much easier to clean the MIPs room if such items are stored outside production. If you pre-weight, or decant in the pantry, cardboard and plastic are kept out of production. It is a great idea to provide a door also to the adjacent hallway to drop off ingredients, then your staff can enter from the MIPs room. Special care is taken when storing opened products.
Keeping Final Products Food-Safe
The best practice might be to put products such as chocolate bars into primary film envelopes or fin-seal gummies while still in the MIPs room. Often, subsequent packaging is done where there are other possible contaminants such as open bud, pre-rolls, chipboard or corrugated, etc. If the food products are already protected by primary packaging, you will greatly reduce the risk of recontamination.
HVAC, Humidity Control, and Filtration
HVAC, Humidity Control, and Filtration are critical. The MIP production room should be air-conditioned and filtered to at least MERV 14. Cook kettles may be a source of humidity that could be placed under a commercial hood. Cooling and tempering of chocolates and cooling and drying of gummies/jellies have their own special considerations. And consider provide enough HVAC capacity to dry out the production room after a heavy cleaning.
Airlocks and Room Pressurization
Airlocks and room pressurization should be planned properly based on your goals, budget and facility. The MIPs room pressure should be positive to all other adjacent rooms: washroom, pantry, extraction, corridors, lab. There are a wide variety of approaches to airlocks, from a pharma approach with air showers down, to just a door with sufficient air supply to the production room to ensure that it is always positive to the adjacent hallway.
Check Out These Related Articles for More Top Things to Consider When Planning:
Part 1 – Cannabis Cultivation Facilities
Part 2 – Cannabis Extraction Facilities
Part 3 – Cannabis Food Production Facilities
Part 4 –Cannabis Retail & Dispensary Facilities
Part 5 – Cannabis Facility Support Areas
Member Blog: Hard to Get – Why Disposable Gloves are Scarce and Pricey

by Steve Ardagh, founder and CEO of Eagle Protect
Disposable gloves are standard issue for the medical, food, and yes – cannabis industry. But thanks to COVID and subsequent disruptions in the supply chain, the market for procuring disposable gloves has gone from routine to challenging. In fact, the demand for quality disposable gloves has skyrocketed, more than doubling since the global pandemic’s arrival, thereby creating an unpredictable cycle of availability. Demand for single-use gloves is expected to continue increasing in the coming years, as the health and safety of workforces across multiple industries – including medical, food, and cannabis-related operations – are required and dependent upon their usage.
Let’s examine the factors that have made disposable gloves both scarce… and pricey, as of late.
Global Glove Origination
Approximately 99% of all disposable gloves are manufactured in southeast Asia, most notably Malaysia and Thailand. But for these regions, compared to the U.S., lockdown to prevent the spread of COVID infections has a much more literal meaning. The restricted movement, as well as outbreaks, led to output at 60% of its normal capacity. In addition, most experts agree that there’s clearly a shortage of workers – many of whom were immigrants affected by travel restrictions. It’s estimated that an additional 25,000 workers are needed to restore full production capacity.
Supply and Demand
As the demand for disposable gloves increased globally, it put added stress on manufacturers and the supply of raw materials, driving up prices tenfold compared to pre-COVID levels. Though glove costs have recently dropped, prices have not reached pre-COVID levels.
Cost of Gas
The raw materials of nitrile gloves are primarily petrochemical based, subject to the volatile price swings in the oil and gas industry. Combined with the tenfold increase in shipping costs, disposable glove prices are not likely to continue dropping.
Labor Violations
In the midst of this price spike, one of the top importers, Malaysia’s Top Glove, the world’s largest glove producer, was banned from importing gloves to the U.S. from July 2020 to September 2021, due to conclusive evidence of forced labor. However, this ban did not extend to other countries.
Knockoffs
When the pandemic nearly doubled the demand for disposable gloves and other PPE components, several new manufacturers with little to no industry experience, assisted by dealers with nothing more than a financial incentive, flooded the market with cheap, counterfeit, and reject-quality gloves. Spotting these unscrupulous suppliers can be done by looking for a few common signs, as they’re often given away by their offering of discount or wholesale pricing, especially in bulk. It’s estimated that the market has already absorbed an influx of gloves of a defective and dangerous quality.
Safeguarding Your Operation
Currently, poor quality gloves continue to flood the disposable-use market. In business, it’s human nature to seek the lowest price for inventory, but saving a little now may cost you dearly on the backend. Cost is obviously important, but consistent quality will keep you from having to replace gloves that rip and tear too easily. When sourcing disposable gloves, seek reputable suppliers – those who have a clear ownership origin, quality web presence and active social media accounts. Taking it a step further, you can inquire about factory audits and HACCP compliance certifications. The cannabis industry has already dealt with at least one recall due to glove contamination. And recalls can have negative financial and brand ramifications. Lastly, always remember when dealing with a new vendor – you can conduct your own product trial before ordering.
 Steve Ardagh, “The Glove Guy,” is the founder and CEO of Eagle Protect, a disposable glove supplier dedicated to the responsible sourcing of quality products that ensure customer safety and impact reduction, ultimately mitigating customers’ risk. Eagle Protect is the only global PPE supplier that is a Certified B Corporation, a designation that a business has met the highest standards of verified performance, accountability, and transparency. He can be reached at steve@eagleprotect.com.
Steve Ardagh, “The Glove Guy,” is the founder and CEO of Eagle Protect, a disposable glove supplier dedicated to the responsible sourcing of quality products that ensure customer safety and impact reduction, ultimately mitigating customers’ risk. Eagle Protect is the only global PPE supplier that is a Certified B Corporation, a designation that a business has met the highest standards of verified performance, accountability, and transparency. He can be reached at steve@eagleprotect.com.
Equity Member Spotlight: Puff Couture LLC – LaVonne Turner

 NCIA’s editorial department continues the Member Spotlight series by highlighting our Social Equity Scholarship Recipients as part of our Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Program. Participants are gaining first-hand access to regulators in key markets to get insight on the industry, tips for raising capital, and advice on how to access and utilize data to ensure success in their businesses, along with all the other benefits available to NCIA members.
NCIA’s editorial department continues the Member Spotlight series by highlighting our Social Equity Scholarship Recipients as part of our Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Program. Participants are gaining first-hand access to regulators in key markets to get insight on the industry, tips for raising capital, and advice on how to access and utilize data to ensure success in their businesses, along with all the other benefits available to NCIA members.
Tell us a bit about you, your background, and why you launched your company.
 I am LaVonne Turner, President of PUFF COUTURE LLC. Before my interest in cannabis, my career was focused on marketing, communications, public relations, event management, and community advocacy. After working for non-profit and for-profit organizations, I became increasingly interested in public policy and community advocacy to help the underprivileged and unrepresented. I hold a bachelor’s degree in executive leadership/marketing, a master’s in public administration, and currently working on a master’s degree in clinical mental health counseling. I am a block club president and serve on a couple of boards and committees. I have spent many years mentoring children and youth.
I am LaVonne Turner, President of PUFF COUTURE LLC. Before my interest in cannabis, my career was focused on marketing, communications, public relations, event management, and community advocacy. After working for non-profit and for-profit organizations, I became increasingly interested in public policy and community advocacy to help the underprivileged and unrepresented. I hold a bachelor’s degree in executive leadership/marketing, a master’s in public administration, and currently working on a master’s degree in clinical mental health counseling. I am a block club president and serve on a couple of boards and committees. I have spent many years mentoring children and youth.
My journey into the cannabis industry as an entrepreneur started when my mother began experiencing debilitating pain, and her only relief was prescribed medication. While I still haven’t found the right product to deal with her pain, I have taken great interest in the industry and the incredible products born from seeds. I plan to open a microbusiness and consumption lounge in Detroit, MI, that serves aromatic, exotic strains and infused products.
What unique value does your company offer to the cannabis industry?
 PUFF COUTURE LLC is a minority-woman-owned cannabis company slated to open a microbusiness and consumption lounge in Detroit. We want to bring a sophisticated community-driven cannabis business that offers a contemporary atmosphere for clients. It will convey the importance of the cannabis flower by providing a chilled environment for clients to consume unique, flavorful, and aromatic cannabis. PUFF COUTURE will support mental health counseling, volunteerism, public policy, and minority representation in the cannabis industry, especially among women. According to a recent special report by MJBbizDaily Women and Minority Report, only 3.8% of Blacks or African Americans are cannabis business owners, the percentage of minority women in Michigan is even smaller; our responsibility is to open doors for future female entrepreneurs and people of color.
PUFF COUTURE LLC is a minority-woman-owned cannabis company slated to open a microbusiness and consumption lounge in Detroit. We want to bring a sophisticated community-driven cannabis business that offers a contemporary atmosphere for clients. It will convey the importance of the cannabis flower by providing a chilled environment for clients to consume unique, flavorful, and aromatic cannabis. PUFF COUTURE will support mental health counseling, volunteerism, public policy, and minority representation in the cannabis industry, especially among women. According to a recent special report by MJBbizDaily Women and Minority Report, only 3.8% of Blacks or African Americans are cannabis business owners, the percentage of minority women in Michigan is even smaller; our responsibility is to open doors for future female entrepreneurs and people of color.
What is your goal for the greater good of cannabis?
PUFF COUTURE LLC would like to change the face of cannabis through participation and contributions to critical public issues that affect the community values of our clients and neighbors, as well as giving back through donations and mentoring. The organization will support issues affecting women who suffer from traumatic situations through our community advocacy campaign. Still, there will be plenty of time for spoken word, intimate art shows, parties, etc. PUFF COUTURE will take care of our people, support the cannabis industry, and create an atmosphere of excitement.
What challenges do you face in the industry, and what solutions would you like to see?
A few years ago, I couldn’t get anyone to advise me or take the time to mentor me. However, after many no’s, I have been blessed to partake in the City of Detroit’s Homegrown cannabis program and training by the Detroit Cannabis Project. LUME’s Vice President of Retail Operations, Michael Dowdell, has taken the time to speak with me and allowed me to observe the business sales and operations of one of the company’s recreational and medical stores. That first opportunity let me know I could continue to grow in the cannabis industry given a chance.
I have continued to expand my knowledge about cannabis, staffing, and cultivation through a mentorship provided by one of the award-winning co-owners of Oak Canna, LLC/CannaBoys, Jason Tueni. Mr. Tueni has devoted a great deal of time to educating me about caring for the flowers at every growth stage. I am currently interning at the cultivation center, which allows me to see everything first-hand, e.g., flowers, business, human resources, all aspects of creating and running a successful microbusiness and consumption lounge. These types of opportunities should be more readily available. I often hear people complain about not having access to mentors, which I completely understand. I joined the CRA DEI workgroup and from there was able to make a connection to LUME and Mr. Dowdell, who by the way is African American, and I asked for the opportunity. I did the same thing with Mr. Tueni. I was at a Weedmaps event and started talking to people and let them know I was looking for a mentor and from there, introductions were made. We met a few times for two to three hours, a couple of months after, and I asked if I could intern at the cultivation center and he said yes. We continue to meet, although not as often, and I see him on a regular basis. Hopefully, when the time is right, we will partner on a project.
Both of these events have provided a great deal of information for me in preparation for my future cannabis venture and I won’t stop reaching out for more knowledge and advice. Knowing how mentorship has helped me, I will continue to look for opportunities to build my business and while doing so pay it forward by mentoring future Detroiters interested in the cannabis industry. As important is my need to stay involved in public policy and community advocacy.
Why did you join NCIA? What’s the best or most important part about being a member of the Social Equity Scholarship Program?
I joined the NCIA to learn and network. Through the social equity scholarship, I serve on the DEI Committee and am also serving on the Cannabis Regulatory Agency-DEI Workgroup for the state of Michigan. The weekly social equity meetings held by the DEI Director are informative and build camaraderie among social equity entrepreneurs. The added weekly conversations help push to get to the finish line. I believe many social equity members will have an opportunity to work together in the future.
I look forward to growing with the National Cannabis Industry Association.
Committee Blog: Everything You Wanted to Know About Cannabis Facilities But Were Afraid to Ask Field Guide – Part 1 – Cultivation

 by members of NCIA’s Facilities Design Committee
by members of NCIA’s Facilities Design Committee
Jacques Santucci, Brian Anderson, David Vaillencourt, and David Dixon
Introducing our five-part series on the behind-the-scenes workings of the legal cannabis industry. This series focuses on all of the inner dealings and industry advice from established professionals to craft this unlimited How-to-Guide to assist you in setting up your own facility. These articles cover cultivation, extraction, infused products, and retail facilities as well as support activities. In general, remember to be compliant with all local rules and regulations and contact a licensed contractor and industry expert.
Part 1, Cultivation: The Top Things to Consider When Planning Your Cannabis Cultivation Facilities
As you are planning to start your own indoor cultivation facility, there are some often ignored basic parameters that should be taken into account in the design and decision-making process. We have listed the key parameters that will ease the process of going live and may save time and money while you design your facility and the building process. Always remember to be compliant with all local rules and regulations.
Lighting Recommendations
Depending on your goals, building setting, and local requirements, you have many options for lighting, from HPS light to LED lights. Lighting standards are measured in watts per square foot. Recommendations may vary per state or other criteria. For example, Massachusetts recommends an intensity of 36w/sft for energy consumption.
Water Recovery: Minimum Percentage
Cannabis is a water-intensive crop, and consideration of effluent capacity can be inefficient, expensive, and an issue for municipalities. Depending on your cultivation practices, you should consider a water recovery system and what percentage you are able to capture. There are two types of water recovery – leachate, and condensate. An effective system will recover at least 70% of the water for utilization, significantly reducing your water and sewer expenses. Your irrigation and fertigation selection will have an impact on your water consumption.
Generator Capacity: Minimum Recommendations
Your area or your business model may dictate for a generator – which is a critical Business Continuity consideration as a power outage, even if for a brief period of time can destroy a crop. Make sure to calculate the minimum capacity requirements of your facility. Do you plan to have it for emergency or stand-by usage? Typically, 50% of your short lighting load capacity of cultivation, 100% for AHU (air handling), and some back-office and security system, including cameras, access, and server needs.
Carbon Dioxide Enrichment: New Versus Recaptured
You can consider 75% new tanked- or generated- natural gas and 25% recaptured sources, for cultivation rooms, gas-fired chillers, and gas-fired boilers.
Carbon Dioxide Alarms Levels: Cultivation and Common Areas
Carbon Dioxide monitoring is critical for worker safety. You should be monitoring common areas to ensure that you are below 3,500 ppm. Monitoring should be tied to the fire alarm system for building evacuation, with 2,000 ppm alarm levels for the cultivation area. 5000 ppm limits are required by NFPA/OHSA. Alarms should contain visual strobes, red/green room access indicator lights and/or possibly an exhaust system that is triggered by an alarm
Renewable Energy: Minimum Energy Production Percentage
To demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, a minimum target of 10% of your facility’s energy consumption should be from renewable energy production: i.e. solar power, wind energy, geothermal, biomass, and/or battery energy.
Refuse Disposal: Recycling and Composting
Consider certified disposal of horticulture byproducts with a minimum of 25% recycling or composting by volume; rendered unusable. You will want to establish and verify that your shredder or equivalent system is capable of breaking up debris to a specified size.
Airlock Doors for In-Between Uses
You should install an airlock barrier, or at a minimum an air curtain, between the business and the production side, for outside and inside egresses, to keep a controlled environment. Keep in mind considerations for ventilation systems and cascading airflow.
Wall Material
For best performance to mitigate biological hazards and contamination, depending on your region, recommend installing insulated metal panels, that are non-porous, solid core wall, insulated metal panels (IMP), with surface mounted devices.
Security Entrance: Facility Safety
Consider creating a separate mantrap style entrance to allow for better safety at the entrance point, monitor visitors, keep a controlled environment as well as avoid weather-related issues, i.e. wet areas due to rain or snow, or temperature variance due to extreme heat or cold.
Limiting doors access and key sets for employees needs to be part of your overall security plan, with proper door labeling and authorization levels. The idea is to prevent unauthorized personnel from accessing specific spaces, for proper environment control and to be compliant with the local regulatory body. Remember to be compliant with local rules and regulations.
Security Camera: Minimum Area of Coverage
In most states, you will need security coverage for 100% percent of your faculty where cannabis products will be stored or displayed, with proper recording and monitoring. Keep in mind that your security room will likely need its own dedicated HVAC systems
Security Camera: Minimum Data Storage and Resolution
You will need to store all security camera footage on-site for a minimum of 90-days, or more depending on regulations. You may need to store the data offsite for five years for future legal needs. Footage quality may need to be shot in 1080p minimum. An ASTM International Standard Guide for Video Surveillance System provides additional parameters to utilize.
Security Alarm: Monitoring
Security alarm needs to be monitored by a reputable company. A service level agreement (SLA) or similar to ensure there are redundancies in the event of a failure should be considered, and redundancy or a backup system might be necessary.
Odor Control: Exhaust Air Management
Odor mitigation is a crucial part of all operations. All exhaust airflow must be oxidized or ionized. You also need a fogger system and carbon filtration. Refer to local municipal bylaws and regulations for more information.
For interior odor control and non-cultivation areas, consider cascading air flows from non-cultivation areas to provide a common method of control for pressurization control. Plan to control air flow and exhaust.
Fire Sprinkler: Maximum Bench Sizing
Sprinklers are designed to cover a limited surface area. When installed on cultivation tabletops wider than 48”, additional sprinkler coverage may be required.
Flooring Type: Continuous
Cultivation floors shall have continuous resin or epoxy coating with at least a four-inch lip onto the adjacent wall.
Energy Incentives: Minimum HVAC/D Efficiency Rating
Air Conditioning (AC) units should be no less than 16 SEER, High Point (HP) units no less than 9 HSPF. Incentives for this vary by state. Please check with your local utility company and regulatory commission for all available rebates.
HVAC Validation Requirements:
Bi-Annual Third Party Controlled Environment Validation using required Trend Data Metrics is the validation and calibration of control sensors, including temperature, humidity, CO2, and other devices such as scales, flow meters, integral valves, PPM sensors, EC meters, TDS meters, HVAC dampers and other applicable devices that may drift from factory or initial installation specifications.
Good Agricultural and Collection or Manufacturing Practices (GACP/GMP): Ready Versus Complaint
Your operation should be designed with documentation to prepare for GACP or GMP requirements. Depending on final product types, specific food-based GMPs with appropriate risk assessment programs (such as HACCP, and others referenced within the Food Safety Modernization Act) will prepare you for any federal or international trade opportunities in a federally legalized framework.
Employee Locker Access
Plan for gender-specific, male and female locker rooms, with six square feet per employee per shift expected to arrive at the facility at any given time. Employee supplied flock for locker or lock provided by the employer is a business decision. Keep in mind how you will keep the environment of your production facility under control. You might consider having locker access adjacent to the growing area with a proper gowning area.
Locker Room Type
Make sure your locker room is correctly set up for employees to be able to change in a safe way. Specifications for Locker Room and Gowning/PPE Areas should allow access to faucets for washing hands as well as bathrooms. Note gowning areas should be separate from the bathrooms directly off the locker room area.
Employee Shower Access
Per International Building Code (IBC) and State Plumbing Codes, calculate the number of employees and determine the number of showers based on code requirements as well as business policies. Having gender-specific showers is a recommendation as well as a business decision.
Emergency Eye Wash- Shower
For safety and based on OSHA standards, Integrated Pest Management (IPM), fertigation, and extraction operations must-have emergency eye wash showers. Eyewash stations need to be placed throughout the facility so that they are within 10-15 seconds walking distance from employees. Check local requirements for additional needs.
Note: in a facility where corrosives and skin irritants could pose harm to employees and require immediate remediations, you should consider emergency showers.
First Aid Kit Distribution
First aid kits should be available in all rooms where sharp tools and other hazardous materials are intended to be used. These kits need to be within 10-15 seconds of employee walking distances. Per OSHA requirements, first aid kits should be located in all trim, extraction, flower hallway, and shredding areas. This is overall a must-have in your facility.
Safety and Injury Handling
We recommend that you ensure that you have enough first aid and burn kits available throughout your faculty, based on your activity and the number of employees.
Check Out These Related Articles for More Top Things to Consider When Planning:
Part 1 – Cannabis Cultivation Facilities
Part 2 – Cannabis Extraction Facilities
Part 3 – Cannabis Food Production Facilities
Part 4 –Cannabis Retail & Dispensary Facilities
Part 5 – Cannabis Facility Support Areas
Committee Blog: Social Equity Perspectives on Interstate Commerce – Part 2

 by Mark Slaugh, iComply LLC
by Mark Slaugh, iComply LLC
NCIA’s Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Committee
As the debate heats up on “how” rather than “if” cannabis legalization will happen, social equity and comprehensive reform are at the forefront of the minds of national legislators and advocates. Previously, in part 1 of this series, the DEIC examined the problems inherent in existing social equity programs and the merit of federal social equity in regulating interstate commerce. Sadly, as written currently, all proposed federal bills fail to meet the critical objective of creating as much NEW generational wealth as possible for those harmed by the war on drugs. Now, we examine the key components of a proposed framework to address these challenges, how to define social equity federally, and the merit of determining the types and numbers of permits to be issued.
Key Considerations for a Federal Cannabis Social Equity Program:
Fundamentally, any federal act for cannabis legalization should be a social justice bill that deschedules cannabis federally and that creates the most amount of new generational wealth for those most impacted by prohibition. Expungement for all persons with a past criminal record involving cannabis is the bare minimum these bills should do. However, proposed bills so far fall short of the latest innovative solutions to known problems in social equity programs and should be amended to include these key considerations.
Any proposed act must be amended to include provisions on regulating interstate commerce immediately after descheduling. The NCIA’s Diversity Equity and Inclusion Committee (DEIC) believes any federal act must prioritize social equity ownership of interstate commerce permits issued by the federal government. Learning from the municipal and state social equity programs, this policy paper seeks to propose amendments that meet these objectives, by instituting the following amendments to federal legalization bills:
-
Defining the regulatory agency for federal interstate commerce regulation and taxation
- Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) and U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) roles and responsibilities
- Defining number and types of seats for a Federal Cannabis Social Equity advisory board
- Ensure a diverse and representative Federal Cannabis Social Equity advisory board members, e.g., federal, state, tribal nations, diverse city representation, NCIA, and social equity cannabis owners, and operators.
-
Defining who qualifies as a social equity interstate commerce permit holder:
- Outlining what states must meet as a minimum standard set by the federal government to participate with equivalent/reciprocal qualification.
- May be determined by advisory board to define social equity qualifications
- With minimum areas defined such as: income, arrest history, disproportionately impacted area(s), residency or heritage to avoid gentrification issues at large.
-
Defining permit types (similar to wine wholesale model) such as:
- Importing
- Privileges to buy from exporters directly and sell to distributors or transporters and licensees into a state system from another state
-
- Exporting
- Privileges to buy from operators and sell from a state system to an importer in another state
-
- Transporting
- Privileges to sell to or buy from qualified cannabis licensed businesses within a state system and to move product from or to licensees in a state or between importers and exporters interstate
-
- Testing
- State labs that meet national standards to ensure consistency with results for other permit types
- May not be strictly social equity since existing labs are more specialized in converting to federal standards and adding this permit
Defining these basic requirements offers a framework for interstate commerce permitting and establishes the essential agencies required to enact a robust social equity program federally. More importantly, it stalls illegal and gray area activity from taking root under the guise of federal legalization by ensuring interstate commerce activity falls under a specific regulatory agency already well versed in interstate commerce permitting and regulation.
Suggested Social Equity Definition:
To define social equity applicant qualifications, DEIC suggests the TTB and SBA move away from diversity supplier program definitions which are too restrictive for a new industry to qualify. In order to accommodate the cannabis industry, DEIC recommends looking at other state definitions of social equity qualification that have proven to be effective.
- Factors like living in a disproportionately impacted area for 5 out of 10 years, being arrested for cannabis or having a family member who was arrested, as well as income below the poverty line, should become qualifying factors.
- Additionally, minorities, women, and veterans should be given additional consideration in the definition of who qualifies as a minority cannabis business.
- High poverty rate, unemployment rate and participation in federal or state income-based programs, a history of arrests, convictions and other law enforcement practices in a certain geographic area, such as, but not limited to, precincts, zip codes, neighborhoods, census tracts and political subdivisions, reflecting a disparate enforcement of cannabis prohibition during a certain time period (war on drugs started in 1971), when compared to the rest of the state.
- Utilize the advisory committee and collaborate with cannabis social equity groups to make sure gentrification and displacement are taken into account. Many areas have drastically changed over the last 5-10 years. Where a person spent their formative, childhood years should also be factored in. Guarding against ‘gerrymandering’ types of map cutouts, where folks who grew up literally surrounded by DIA’s, and who dealt with many of the same issues growing up, are somehow not considered to be disproportionately impacted.
We believe the federal government should leave regulations within each state alone during this multi-year implementation and defer to the TTB and SBA to work in conjunction with any Federal Drug Administration (FDA) regulations with their primary focus pertaining to interstate commerce and taxation as it relates to social equity permit issuance.
Defining How Many Permits to Issue to Social Equity Operators
To address the common shortfalls of state programs, the DEIC realizes that social equity applicants are already a minority stakeholder in existing cannabis licensing. In most states, sadly, constituting less than 5% ownership. This is a huge difference compared to the proportion of individuals in prison for the same activities a licensed business is allowed to conduct.
-
Accordingly, the DEIC recommends a direct balance in ensuring a lock-out period on issuing new permits and ensuring, during that time, that 95% of the permits go to social equity owners/operators.
While some may consider such a counter-balance to be extreme, more and more states are increasing the committed amount of licenses for social equity to ensure a fair counter-balance. If anything, mega-players should be competing with each other for a select number of limited licenses – not the other way around.
We also realize that, in order to generate investment or value behind interstate commerce permits, there could not be an unlimited number of them initially issued. While the advisory board may issue more in the future, we feel a bold stand to increase the number of valuable permits for initial social equity applicants nationwide is necessary to ensure a balance that reflects the oversight to include social equity business into the industry thus far.
- DEIC suggests 1,500 permits as a starting point divided among the three primary types (import, export, transport) as a fair balance initially.
The above policies may seem bold, but they are designed to seek to balance the industry and state’s failure to allow social equity participation. Most cannabis states left out social equity operators by mandating residency and felony-free requirements.
The reality is that interstate commerce means selling the products already owned and produced by non-social equity folks. Further, if it was not for these legacy operators, there would not be a cannabis culture. A culture that has been co-opted from legacy social equity operators by mega operators who kept “undesirables” from the industry at its inception.
These policies seek to balance the needs of traditional cannabis businesses that would most benefit from interstate commerce, with the needs of social equity businesses to create equal opportunity. By limiting the number and availability of interstate commerce permits for at least a 5 lock-out year period, the policy ensures traditional operators partner with social equity permit holders to export, import, and transport their goods between various markets.
The policy helps ensure partnerships that are more equitable for both parties and, in doing so, seeks to avoid “predatory operating agreements” or “social equity colonialism” that dilute social equity operators who are not given the opportunity or resources to bring anything to the table. Therefore, the DEIC stands by lock-out periods and a dedicated high percentage of limited licenses for social equity interstate commerce permitting as a policy to balance existing inequity.
In the next part of this policy paper series, the DEIC will examine how this framework sets up social equity technical assistance, qualification, and a phased approach of implementation to ensure the widest net is cast and that social equity operators have ample time to qualify, are appropriately funded, and set up for success with an equal starting line for interstate commerce.
Read Part 3 of this blog series.
Member Blog: Cannabis M&A – Protecting the Valuation Calculus Using Cyber Compliance and Due Diligence

by Rebecca L. Rakoski, Esq. and Patrick D. Isbill, Esq. of XPAN Law Partners
When it comes to the intersection of law, business, and technology, the legal cannabis industry is arguably at the center of all three. Relying heavily on creative, innovative technology to distinguish itself while continually analyzing profitability forecasts to take advantage of new business opportunities and having to monitor at the same time the changing data privacy regulatory landscape, it can all seem rather daunting when added up. Securing trade secrets and overseeing reputational management related to cybersecurity and data protection are some of the challenges rooted at the forefront of this industry, especially after last year’s stunning pace of mergers and acquisitions. Increasing consolidation of fragmented segments of the cannabis industry is foreshadowing a strategic, long-term business approach to achieving higher profits and revenue, leaning on market advantages such as relatively favorable interest costs for now and lower valuations.
Data security and past cyber events play a significant role in these transactions, as do regulatory compliance and data privacy laws. One of the primary, if not foremost, objectives of any deal involving a merger or acquisition is of course valuation. Poor cybersecurity practices, lack of a comprehensive security and data protection program, and digitally unsecured proprietary assets on the part of the target company could spell unforeseen financial, not to mention legal liability, headaches for the acquiring organization.
The business of legal cannabis is after all a highly unique industry because of the already intense regulatory oversight and the enormous amounts of data inherently built in and circulating throughout its diverse industry sectors. From cultivation and laboratory research to manufacturing that incorporates processing for global distribution and all the way out to consumer dispensaries, the aggregate value of such data is almost nothing short of priceless. Simply put, data equals money in today’s global digital economy. So when the acquiring organization fails to adequately perform its due diligence when it comes to cyber compliance, it may be in for a rude awakening post merger or acquisition, especially if this data has been unknowingly compromised.
Every company should first seek to identify and classify the type of data it is acquiring to determine regulatory compliance. Personally identifiable information (PII) and/or protected health information (PHI) and where either comes from, e.g., a consumer or patient, will go a long way to understanding whether state and/or federal laws have been violated. Next, discovery of a past cyber event or breach is critical. Compromised data from inadequate cybersecurity or failure to report potential violations of state data privacy laws to any of the corresponding state enforcement agencies could result in hefty fines and unexpected assumption of liability, not to mention the legal costs to fix it after the deal is done.
Almost every cannabis business knows from the outset it has very particularized regulatory requirements, but such knowledge does not obviate it from complying with additional regulatory data privacy and cybersecurity obligations. Regardless of the side of the transaction, businesses need to keep several key end goals in mind during an M&A deal. Questions include but are not limited to the following: (i) prior cyber practices; (ii) prior cyber incidents; (iii) documented cybersecurity and data privacy programs; (iv) whether those programs are operationalized or just “there” for window dressing; (v) whether there is cyber-liability insurance; and (vi) the nature and type of contractual obligations. All of these elements will help to determine the level of data privacy and cybersecurity maturity of a business which, in turn, affects the value of the data and practices of the targeted organization.
Poor data security and privacy practices can lead to a devaluation of the business calculus and create an unforeseen situation where an organization suddenly becomes a liability rather than the intended asset. In the current shifting legal and technological environment, ignoring or leaving cybersecurity and data privacy due diligence in an M&A transaction to the last minute can be a costly enterprise. In addition, the nature and type of contractual obligations in and around data privacy and cybersecurity can also create a potential for substantial liability if the organization has not operationalized its privacy and security program. Each part of this due diligence is interconnected and can wreak havoc if not properly assessed and, in some instances, immediately addressed.
Like water running downhill, any variation in terrain going forward will cause a parallel, and potentially unpredictable, directional shift.
All in, the industry is keenly aware of what consumers value – privacy. For example, trust in the product sold and confidence that their identity is secure topmost consumer surveys on the topic. Any cannabis business understands this fragile balance, and any path to growth in the industry must account for it. Same applies to trade secrets. Often the linchpin of a merger or acquisition will be the result of interest in innovative research or breakthrough technology developed by the target company. If it is discovered later that this proprietary work was potentially compromised or publicly disclosed, then the initial value used as the basis for negotiations could diminish exponentially if the work has been appropriated by a business competitor or industry rival looking for a market share advantage.
Due diligence is already part of the fabric of M&A deals. Reports suggest the large volume of global mergers and acquisitions overall is expected to continue this year from last despite worries over regulations and rising interest rates. But focusing on accounting and finances without spending time on determining past commitments to cyber readiness and compliance can unravel even the best of intentions. Valuation is a key calculus in these deals. Understanding the true value of what is being acquired or consolidated is essential to taking advantage of business opportunities for growth and return on investment for an industry primed for both.

Rebecca L. Rakoski, Esq. is Co-Founder and Managing Partner at XPAN Law Partners, LLP. Rebecca counsels and defends public and private corporations, and their boards, during data breaches and responds to state/federal regulatory compliance and enforcement actions.
 Patrick D. Isbill, Esq. is also Co-Founder and Managing Partner at XPAN Law Partners, LLP. Patrick’s practice focuses on cybersecurity and data privacy compliance and enforcement, addressing the business needs and demands of highly regulated industries.
Patrick D. Isbill, Esq. is also Co-Founder and Managing Partner at XPAN Law Partners, LLP. Patrick’s practice focuses on cybersecurity and data privacy compliance and enforcement, addressing the business needs and demands of highly regulated industries.
This article does not constitute legal advice or create an attorney-client relationship. The information provided herein may not be applicable in all situations and should not be acted upon without specific legal advice based on particular situations.
Member Blog: Cannabis Trends in 2022

by Jennifer Spanos, CannaBusiness ERP
As we approach the end of Q1 2022 and prepare to enter Q2, it’s become clear that this is going to be an important year for the cannabis industry. Cannabis business professionals and investors looking for signs of growth or stagnation in the industry will certainly be interested to see how things unfold. With that in mind, CannaBusiness ERP has put together a list of the top cannabis trends for 2022, and those trends appear to be pointing to more growth. However, it’s clear that difficulties for the cannabis sector are still imminent.
Cannabis Trends for 2022
It almost goes without saying that the cannabis industry is complex and not without its fair share of challenges as the most highly regulated industry on the market. For businesses looking to grow, keeping up with complicated and evolving regulations can be stressful enough on a business in and of itself. Cannabis cultivators, processors, and consultants can look to cannabis industry trends to inform their operational decisions.
Increased legalization in the United States
Support for legalization in the USA continues to rise. In fact, a 2021 Gallup poll found that 68% of Americans are in favor of legalizing cannabis. Not only is this a record number of supporters, but this percentage also reflects a growing sentiment among Americans regarding the use of legal cannabis.
The changing tide towards legalization is clear – more states passed legislation to legalize cannabis either medicinally or recreationally in 2021, with several more introducing legalization bills in 2022. Because states operate independently of each other, every state will have its own policies as well as regulatory and compliance requirements, which can make things very confusing for cannabis businesses, especially multi-state operators (MSOs).
The National Cannabis Industry Association (NCIA) provides a map with state-by-state policies, which is one helpful tool for businesses looking to capitalize on expansion opportunities made possible as more states legalize cannabis. CannaBusiness ERP’s Guide to Expanding Into New Markets is another great resource for MSOs that provides state-by-state information, including Nevada, New York and Pennsylvania, and useful advice to consider when expanding into new cannabis markets.
Sales will continue to increase in 2022
Leading cannabis business experts are predicting strong sales growth this year due to the growth in legalized markets for cannabis. In fact, legal cannabis sales reached $19.5 billion in 2020, and experts are projecting sales to reach $30 billion in 2022. Washington State alone, which legalized cannabis ten years ago in 2012, is expected to generate $1.5 billion in sales, up from $1.2 billion sales in 2020. But Washington’s projected sales are small when you compare them to California’s projected sales of $7.6 billion. And as more states legalize cannabis, more sales will surely follow.
Another contributing factor to increased cannabis sales is related to increased demand and a growing number of product types. More consumers are learning why cannabis can be beneficial to them, including more restful sleep, lowering stress, lessening pain symptoms, and recreational use. Additionally, with so many products on the market, cannabis consumers have many options to choose from, ranging from edibles to tinctures to topical ointments and more.
Cannabis experts are predicting a growth in cannabis consumption lounges – the cannabis equivalent of a bar or restaurant that allows consumers to use cannabis on-site. According to the Cannabis Industry Journal, the popularity of these lounges is growing because they provide consumers with a legal and safe space to consume cannabis. Just as with alcohol, the lounges are regulated according to laws set by each state.
Increasing sales means cannabis businesses are at a critical junction and need to scale operations to meet the growing demand. One way cannabis growers and processors can capitalize on the demand is by streamlining the business end-to-end with cloud-based cannabis business management software. Otherwise known as Cannabis Cloud ERP, it manages production, cultivation, compliance, inventory, financials and traceability, sales, purchasing, and more, all in one system that lives in the Cloud.
Increased legislative bills and pressure for federalization
Under U.S. Federal Law in the Controlled Substances Act, cannabis is still considered a Schedule I substance. However, as the number of states legalizing cannabis either recreationally, medicinally or both has increased, so too has broader support for federalization in the U.S. government. In fact, there are several bills in the U.S. congressional houses that may positively impact the cannabis industry, especially with banking challenges.
Due to the Schedule I federal classification of cannabis, many banks will not work with cannabis companies, creating tedious banking hurdles that are difficult to solve. The National Law Review writes, “Yet, in comparison to other industries, legitimate licensed cannabis-related businesses remain hobbled by the difficulties they face in accessing traditional banking and financial services – largely due to the fact that ‘marijuana’ is still considered illegal on the federal level under the Controlled Substances Act (“CSA”). Currently, financial institutions (including federally insured banks) are hesitant, and oftentimes unwilling, to work with cannabis-related businesses due to fear of reprisal from federal banking regulators.”
Congressional representatives have introduced a decent amount of bills geared towards making much-needed changes to banking processes for cannabis, such as the SAFE Banking Act of 2021, passed by the U.S. House of Representatives in April 2021. It is currently awaiting action in the U.S. Senate with broad support from both sides of the aisle. If it passes both chambers of Congress, the act will allow cannabis companies to have business-critical access to banking and financial services and would reduce their need to operate as cash-only businesses and remove yearly challenges with tax accounting and reconciliation.
In addition to the SAFE Banking Act, there are other bills like U.S. Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer’s Cannabis Administration and Opportunity Act (CAOA), which is a push for federal cannabis legalization as well as an equity play. If passed, it is a measure towards ensuring small businesses and minority-owned businesses have access to financial services.
However, even with the tide of public opinion and legal momentum shifting in the industry’s favor, there remains a challenge with the U.S. tax code. Due to IRS Code Section 280E, if a business is trafficking certain controlled substances, like cannabis, that business is unable to deduct business expenses on their taxes. California has taken steps to address this by signing bills that help cannabis businesses overcome this code, but this is still a prohibitive factor for cannabis companies across the U.S.
Fortunately, cannabis companies that invest in a comprehensive Cannabis Cloud ERP solution with a reputable and experienced industry partner are better able to handle any hurdles that come their way.
Increased Merger and Acquisition (M&A) activity
Merger and Acquisition (M&A) activity has been steady in the industry and 2022 will see even more M&A activity. According to MJBizDaily’s article, “Marijuana M&A sizzled in 2021 and is poised for a hot 2022. Marijuana merger and acquisition activity proceeded at a torrid pace in 2021 – and could accelerate in 2022 – thanks to lower interest costs and pressure on larger companies to expand their footprints and boost revenue.”
Citing prominent cannabis acquisitions in 2021, such as Jazz Pharmaceuticals’ acquisition of GW Pharma (for $7.2 billion) and Trulieve’s acquisition of Harvest Health (for $2.1 billion), it is apparent that M&A is not going to slow down. According to Business of Cannabis, several deals are already taking place in 2022. Massachusetts-based Curaleaf acquired Arizona-based Bloom Dispensaries for $211 million, adding a total of 13 Arizona dispensaries and 121 dispensaries nationwide to Curaleaf’s portfolio.
For cannabis companies dealing in M&As and becoming Multi-state Operators (MSOs), it is essential to have a comprehensive, full-suite Cannabis Cloud ERP system that can run all the companies in one system. It is a crucial ingredient to manage their M&A transactions and handle their financial statements, compliance, business transactions, and more.
Most important of all, cannabis companies need to choose the right cannabis ERP.
 Jennifer Spanos is the VP of Product and Vertical Strategy at CannaBusiness ERP. She has 14+ years of experience in cannabis and food manufacturing software and operations, working to maximize the efficiency and profitability of customers’ businesses.
Jennifer Spanos is the VP of Product and Vertical Strategy at CannaBusiness ERP. She has 14+ years of experience in cannabis and food manufacturing software and operations, working to maximize the efficiency and profitability of customers’ businesses.
CannaBusiness ERP: The Right Cannabis Business Management Software. Cannabis companies can grow their business with an ERP solution designed for the cannabis industry and for MSOs expanding into new markets. Learn how CannaBusiness ERP can set businesses on the right path. Manage financials, operations, quality, compliance, traceability, customers and more.
CannaBusiness ERP is cannabis business management software that is built-in Sage X3 and configured by NexTec industry experts to deliver a complete cannabis business solution. Our specialization in developing solutions for the cannabis cultivation and processing industry has resulted in some of the most respected companies around the world managing their day-to-day operation using CannaBusiness ERP.
To learn more about the fast-paced movement in cannabis legalization and how Cannabis Cloud ERP software can help your company keep pace, reach out to us. We’d love to show you what CannaBusiness ERP can do for your business.
Committee Blog: Protect Against Corporate Identity Theft with Trademark Rights

 By NCIA’s Cannabis Manufacturing Committee
By NCIA’s Cannabis Manufacturing Committee
A company’s brand is its identity. Branding elements – names, logos, colors, graphics, slogans – are how customers recognize a product or service as coming from a particular source. Done properly, brands can be as recognizable to consumers as a person’s face, name, and voice. In some cases, brands may be some of the most valuable assets a company may own. Protecting physical assets is common in the cannabis industry, but how do companies protect intangible assets, like their identity? Fortunately, there are bodies of intellectual property law designed to provide legal protections against others from using brand elements that are too close to your own. To take advantage of these protections, however, cannabis companies must understand how each one works and develop a branding strategy that leverages intellectual property laws.
This is the second article in a 3-part series about cannabis IP. The first article focused on patent law and can be found here. The series will culminate with a Q&A-based webinar on April 19th at 1:00 Eastern. Advance questions can be sent to paul@thalo.io.
Mechanisms of Brand Protection
Brands are protected most prominently by legal domains known as trademark and trade dress. Trademarks include a company’s name, logos, and slogans, as well as those of any individual products. In some instances, trademarks may also include recognizable elements like colors (UPS’s brown) and sounds (NBC’s chimes). Trade dress is a similar concept to trademarks, but applies to the distinct appearance of a product or its packaging. Trade dress can even be used to protect the unique look and feel of a retail establishment, such as a restaurant or dispensary.
Both trademark and trade dress is intended to reduce confusion in the marketplace as to the origin of a product or service. The idea is that the public is best served when they can reliably determine which company to associate with each product. Reliable product-company association increases quality accountability, facilitates safety controls, allows consumers to form powerful brand loyalty.
Companies that avail themselves of trademark and trade dress laws gain access to a set of tools to legally fence off others from using branding that is likely to confuse customers about the source of a product. And, unlike other forms of intellectual property, trademark rights can last indefinitely and even strengthen over time. Some of these rights arise automatically just by using a mark, others must be sought out through registration.
Principles to Consider When Selecting a Brand
Every company should consider trademark principles from day zero, when first selecting a name. U.S. trademark rights only apply to marks that are “distinctive,” meaning they are capable of distinguishing things bearing the mark from goods and services offered by others. The more distinctive a mark is, the stronger protections provided by trademark law. Names that merely describe the goods or services are non-distinctive and are typically not eligible for trademark protection.
There are five general categories along the spectrum of distinctiveness – fanciful, arbitrary, suggestive, descriptive, and generic – arranged from strongest to weakest.
Fanciful marks words that were invented specifically to serve as a trademark, such as Xerox or Nvidia. Because these words have no other meaning than to identify the source of goods or services, they are the most distinctive category of trademark and receive the greatest protections.
Arbitrary marks are the second most distinctive category of mark and include words that have alternative meanings, but only meanings in contexts unrelated to the goods or services being sold. These include Apple computers, Lotus cars, and Bicycle playing cards.
Suggestive marks are less distinctive than Fanciful and Arbitrary marks, but still considered sufficiently distinctive to receive trademark protection, though registration may be more difficult. Suggestive marks imply a quality or characteristic of the good or service the mark is used in connection with. Some examples of suggestive marks would include: Microsoft, a portmanteau of microprocessors and software; ChapStick, for a stick-shaped balm used on chapped lips; and Netflix, which is suggestive of an internet-based video service.
Descriptive marks simply describe the goods or services being offered and are, therefore, not distinctive. In some cases, however, descriptive marks can acquire distinctiveness and achieve a “secondary meaning” as a source-identifier through long-term use (usually +5 years), heavy advertising, or pervasive adoption. Examples of Descriptive Marks would include: International Business Machines (IBM Computers); Best Buy retail stores; and Sports Illustrated magazine.
Generic marks are terms that broadly identify the product or service being offered. Generic marks are so non-distinctive that they are not eligible for trademark registration, even if secondary meaning can be shown. The idea is that these marks are so fundamental to the product that it would be detrimental to consumers and the marketplace to allow a brand to have exclusive use of the term in connection with the goods. “Escalator” and “Dumpster” were once brand names but, because they were used widely to refer to all mechanized stairways and trash receptacles regardless of manufacturer, they lost all trademark distinctiveness.
Parody Does Not Apply – Avoid Famous Brands
A surprising number of cannabis companies have used trademarks that reference or parody famous brands. Gorilla Glue, Girl Scout Cookies, and many others have been used as names for cannabis products. Companies have used packaging that resembles well-known products such as Life Savers and Sour Patch Kids. This is a bad idea. While this practice seems to be increasingly limited to unregulated markets, a recently published (and ill-advised) application for the mark and logo MCWEED for apparel shows that not everyone has received the message:
Registration and Scope of Protection
Some trademark rights are established as soon as a trademark is used in commerce. But to obtain the full scope of legal protections available, trademark owners must register their marks, preferably federally. Federal registration stakes a claim to a nationwide priority date, increases protections available, increases potential damages, and embodies a definities property that can accrue value.
All trademark registrations begin as applications. Trademark applications must, among other things, identify the mark, the applicable dates of use. Applicants must also describe the goods and/or services the mark is (or will be) used with and select one or more classes from an international menu of product classifications. The classes selected and the description of the products can greatly affect the scope and validity of a registration, so it is important to consult with an experienced trademark attorney.
These applications are examined by the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office to ensure they meet the statutory requirements. Typically, the USPTO completes examination within about 6 months, but currently the office is experiencing some delays and it is commonly taking 7-10 months for an application to be evaluated. If the examining attorney identifies any problems, they may issue rejections, to which the applicant will have an opportunity to respond.
If the USPTO approves the application, it will be published for 30 days (expandable to 180 days) to allow other trademark owners to oppose registration of the mark. Sophisticated trademark owners can set up alerts to be notified when any similar applications are published that may be concerning. At the close of that period the mark is recorded in the federal register and the trademark registration is complete.
A qualified trademark attorney can help guide you through the process and provide counseling concerning how to maximize your chances of registering your trademark without prejudicing your rights. Trademark application fees run $250-$350 per class of goods or services and a trademark attorney will typically charge a few hundred to a few thousand dollars, depending on their experience and the level of pre-application clearance. While trademark mills and self-guided applications are available, there are many pitfalls to avoid while preparing and prosecuting a trademark application, and applicants should be wary of attempting to navigate the process without legal guidance.
Applicants should also be aware that many companies mine the USPTO database to send unsolicited offers to trademark applicants. While these offers can look official and typically include some deadline to respond, they are usually scams. Nevertheless, it can be helpful to have an attorney review any correspondence relating to the trademark application to ensure that no important correspondence from the USPTO is missed.
Embrace the Zone of Expansion
There are a lot of benefits to registering trademarks, but registration is not available in all instances. Under federal law, registrations cannot be issued that cover goods or services that are federally illegal. But the same mark can be registered for other, legal products, and the trademark rights will extend to a reasonable “zone of expansion,” covering products that the trademark owner could reasonably branch out to in the future. This allows a brand owner to obtain the benefits of federal trademark registration and use it to provide some umbrella protection for their cannabis brands.
One option is to sell branded accessory products, such as apparel or smoking accessories, for which a trademark registration will pass muster. It is debatable, however, whether cannabis products are within the zone of expansion of t-shirts.
Another option is to develop one or more low-THC hemp products under the same brand as high-THC cannabis products. At least one case is already working its way through the courts where a trademark owner is claiming that cannabis edibles are within the zone of expansion of a line of hemp-infused, low-THC edibles. Edible IP, LLC and Edible Arrangements, LLC v. MC Brands, LLC and Green Thumb Industries, Inc., (Case No. 20-cv-05840). Though that approach is also not without its pitfalls, as discussed below.
A final option that every cannabis company should consider is state trademark registration. State registration requirements are typically governed by state law and, therefore, state trademark registrations can often be obtained for cannabis products. State registrations are more limited than federal registrations, but can be a powerful tool in the current landscape of cannabis IP.
Products with CBD Can Be Trademarked, But You Can’t Trademark “CBD” Products
Companies that produce hemp products do not have the same problem with federal illegality as companies with high-THC products. Federal registration is available for trademarks that are used on hemp and hemp products. However, as most hemp companies should know, the advertising of cannabidiol or “CBD” is regulated by the Federal Drug and Cosmetic Act (“FDCA”), 21 U.S.C. §§ 321(g)(1), 331(d) and 355(a). Because CBD is the active ingredient in an FDA-approved drug (Epidiolex®), the FDCA prohibits marketing CBD products (absent a New Drug Application or Abbreviated New Drug Application). Though that may change. As of now, however, the USPTO will refuse to register marks that identify the goods as “CBD.” In re AgrotecHemp Corp., Serial No. 88979905 (issued Feb. 10, 2022) (finding that PUREXXXCBD for plant extracts should be refused registration).
Notably, the AgrotechHemp decision went further than previous USPTO decisions in that it also criticized the issuance of registrations for marks used on products “derived from hemp.” This may signal a crackdown on all hemp-related registrations, or it may be limited to registrations that explicitly identify the goods as containing “CBD.”
Where’s the Value in Trademarks?
It may come as no surprise that brands can be incredibly valuable assets. In some cases, a company’s brand can make up a significant portion of its balance sheet and brand-centric companies can fetch a premium when they are acquired, known as “goodwill.” Increasingly, specialized lenders are even willing to use secured IP as financing collateral. Nonetheless, the real value for many trademark owners is non-monetary.
When many people think about intellectual property, they recall headlines of jury verdicts with huge damages that can reach into the billions of dollars. The reality is that, absent intentional copying, trademark cases rarely result in large-dollar awards. More often, successful trademark suits result in an injunction preventing further infringement and some relatively minimal damages. The primary value of trademark rights is the ability to control your brand and how consumers perceive your brand in the marketplace. Trademark rights give you the tools to define your brand as a unique identity and preserve that identity in an increasingly crowded industry.
Member Blog: Trends in Cannabis Technology – Data Mining And Compliance

By Joshua Gilstrap, e2b teknologies
Cannabis businesses are looking for the best practices to enhance operations, with a primary focus on optimization and growth. So whether you are in the cultivation, production, manufacturing, or selling and marketing section of the cannabis industry, you need technology to steer your business into the future.
The cannabis industry is still growing, albeit faster than anticipated, with an increasing demand for products that continue propelling innovation. Data is driving this innovation because it’s the differentiating factor for long-term success and sustainability.
Today, cannabis is a $25 billion business in the U.S. In fact, the 2022 Leafly Jobs Report found the legal cannabis industry supports 428,059 right now, a 33% increase over the 280 new jobs created per day, on average, last year.
We know all of this because of data, and it’s a critical decision-making factor in this industry. Without access to real-time information, cannabis companies can’t know where to invest or improve to remain competitive and compliant.
Here are the top 4 data and technology trends transforming the cannabis industry to keep in mind.
Laws and Regulations Software
Cannabis compliance is one of the most challenging yet vital factors to consider in the cannabis industry. Government mandates demand that cannabis companies provide cultivation, production, shipping, and sales information to help monitor the entire distribution process.
This makes sense because lack of transparency in other industries has caused several crises, like the vaping crisis or the romaine lettuce E.coli outbreak of 2019. But collecting, tracking, and monitoring data is challenging for businesses, so is understanding the government regulations and ramifications.
With the emergence of cloud-based cannabis software, cannabis companies remain updated with these tight data restrictions. This software collects the appropriate data and analyzes business operations by checking the right boxes to ensure compliance.
With these industry-specific software solutions, cannabis businesses can establish and implement a standard of operations that comply with cannabis regulations. As an added benefit, these solutions offer convenient avenues for cannabis employees and business owners alike to understand the rules and regulations of the industry. Some also provide security against potential threats like cybersecurity threats.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Cannabis plants usually require significant attention and fixed schedules because of their temperamental nature. As such, AI and ML are taking effect in the cannabis industry. Machine learning gathers data and provides suggestions on what farmers can change in the growing process.
The detail in machine learning makes it possible to collect, monitor, and track the growing cycle every hour, meaning cannabis farms use machine learning to improve these plants’ growing environment significantly.
For instance, farmers are using agricultural sensors to manipulate the growing environment to suit the needs of the cannabis plants. This is achieved by connecting the environment to growing systems with humidity sensors and controls, thermostats, and temperature controls.
These sensors ensure that cannabis is continually growing in optimal conditions. As such, the products cultivated continue to be of high quality.
Also, the machine learning sensors and tracking IDs make it easier to track cannabis products from seed to sale.
Artificial intelligence then automates these processes to make the entire growing experience easy for cannabis farmers. For instance, AI helps to automatically control the humidity levels as per the settings given by the farm moderator.
AI also automatically changes the light in the growing room since it affects the temperature needed for the plants to grow optimally. This continued innovation and adoption of AI and machine learning in the cannabis industry will lead to increased crop production and reduced manual labor.
Hybrid Cloud-Based Storage
Video data is a significant investment in the cannabis industry right now. Some government regulations outline the need for cannabis companies to have immediate access to video surveillance footage and on-demand. This need is driving the demand for storage spaces for the video footage.
While many cannabis businesses store data on-site, it is unpredictable and expensive. This is where hybrid cloud-based storage technology comes in. The technology is enough to hold video data until it is needed, like in the case of a cyberattack and the subsequent investigation.
It also gives cannabis businesses the choice to store data on-site and in the cloud. This enhances the flexibility, accessibility, and security of business files. Cloud platforms also make it easier to access business information from any location.
Blockchain Technology
Traditionally, the cannabis industry is a cash transaction industry, especially in dispensaries where the majority of the cannabis sales take place. Additionally, many cannabis businesses find it challenging to work with banks since most aren’t legally allowed to work with companies in the industry.
There is also the matter of making secure payments and tracking transactions successfully. In a word, the cannabis industry is adopting blockchain technology for cryptocurrency payments and transaction tracking.
Blockchain is secure, and it has processes that make it easy to track and monitor transactions. But because using blockchain as an alternative to traditional payments methods is a relatively new trend, there is still the challenge of getting cannabis companies to agree on solutions that can standardize the trend.
In conclusion
Every business industry is now leveraging data by defining connections between the different data points and gathering actionable insights on processes. As such, you can optimize, strategize, plan, report, and identify problems using business data.
You can also better understand the consumer using data insights like your consumer consumption preferences. As such, data is crucial for determining where to invest, improve, and remain competitive and compliant in the cannabis industry.
FAQs
What is the future of the cannabis industry?
The future of the cannabis industry is very bright… The cannabis industry is expected to grow by about 20 to 30 percent every year to a value of $50 billion by 2026.
How is technology influencing the cannabis industry?
Technology is propelling the growth of the cannabis industry quickly. Cannabis businesses use innovation and technology to identify downtime in workflows, streamline processes, and identify opportunities for success and growth.
What is the role of data in cannabis manufacturing?
Data is critical for improving all the cannabis processes from seed to sale. Decisions driven by data significantly improve the quality of the cannabis operations from cultivation through to marketing, sales, and customer satisfaction. As such, data is now an integral part of cannabis manufacturing.
 Joshua Gilstrap is the Marketing Manager for e2b teknologies, in addition to his marketing responsibilities Joshua leads business development for e2b teknologies emerging Canna Suite product line. A business graduate with a focus in marketing from Miami University in Oxford, Ohio, he joined the e2b team in the Fall of 2019. Josh brought with him a wide array of business and practical experience in planning and execution. Since coming aboard he has led multiple project’s including website hosting and theme standardization company wide, marketing automation streamlining the efficiency of the customer journey, and sales automation where he is changing the conversation from promotion to education, from pitching to catching, and from push to pull in order to keep up with the shifting tides of a digital transformation.
Joshua Gilstrap is the Marketing Manager for e2b teknologies, in addition to his marketing responsibilities Joshua leads business development for e2b teknologies emerging Canna Suite product line. A business graduate with a focus in marketing from Miami University in Oxford, Ohio, he joined the e2b team in the Fall of 2019. Josh brought with him a wide array of business and practical experience in planning and execution. Since coming aboard he has led multiple project’s including website hosting and theme standardization company wide, marketing automation streamlining the efficiency of the customer journey, and sales automation where he is changing the conversation from promotion to education, from pitching to catching, and from push to pull in order to keep up with the shifting tides of a digital transformation.
Member Blog: FDA Cites Multiple Violations for Selling CBD as Supplement, Food, Cosmetic, or Animal Food Ingredient

by Gisela Leon, MS, MBA, Independent Consultant, EAS Consulting Group
The FDA’s position on the use of CBD in dietary supplements and foods is steadfast. In 2021, five warning letters about CBD-containing dietary supplements and foods went out – three based on website reviews and two based on facility inspections. All cited violations relate to pain relief claims. The products are therefore unapproved new drugs. Two warning letters emphasize the FDA’s position that CBD does not meet the definition of a dietary supplement, from which it is excluded due to the authorization for investigation as a new drug.
In November 2019, the FDA published 15 warning letters in a “catch-all” effort regarding cannabidiol products. The products range from articles sold as dietary supplements, conventional foods, cosmetics, and animal food. The FDA sent out the 15 warning letters to companies in a number of states, including California, Texas, Oklahoma, Colorado, Oregon, New York, Florida, North Carolina, Arizona, and Kentucky based on the content of websites and social media sites. This was not the first time the FDA had sent warning letters regarding cannabidiol [CBD]. The first seven CBD warning letters were issued in March 2019, so attentive manufacturers could have been aware of t the FDA’s position and that enforcement actions might be taken.
In the 2019 warning letters, the FDA states that CBD in products sold as dietary supplements does not meet the definition of dietary ingredients in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (321(ff)(B)(i)(ii)). This provision clarifies that a dietary ingredient cannot be a substance that has been approved as an active ingredient in a drug. The FDA has confirmed that CBD is an active ingredient in the approved drug Epidiolex.
Products containing CBD and sold as conventional food often worry the FDA even more, because they are often advertised for toddlers and infants. FDA clarified that CBD does not have an authorization as a food additive. Food additives need to be pre-approved by the FDA and there is no such regulation for CBD. CBD also is not a GRAS substance. This is based on the FDA’s review of publicly available data, which shows that CBD is potentially harmful and may cause liver injuries and interact with other drugs. Furthermore, studies in animals have shown that it might impair sexual behavior in males.
Similarly, the FDA states in relevant warning letters that CBD is an unapproved new animal drug because of the disease claims. The products are also adulterated animal foods because there is no animal food additive regulation that authorizes the use of CBD and there is no basis to conclude that CBD is GRAS for use in animal foods.
Besides the illegal status of CBD as a dietary ingredient, the warning letters regard the products as unapproved new drugs, because they claim that CBD cures, mitigates, treats, or even prevents diseases. Most warning letters are very long because the manufacturers cite numerous diseases for which CBD might be helpful. CBD is often depicted as a “cure-all.” Some of the popular disease claims involve pain relief, anti-inflammatory, diabetes, acne, anxiety, depression, and cancer. For example, one warning letter cites 45 diseases. Simultaneous to being unapproved new drugs, all products are regarded as misbranded drugs.
Most 2019 warning letters were signed by three FDA compliance directors from Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Center for Veterinary Medicine, and Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition. In some of the earlier warning letters, the FDA also involved FTC – Federal Trade Commission – because of unsubstantiated claims. Both agencies are concerned that some of the efficacy claims may not be substantiated by competent and reliable scientific evidence.
There are clearly more than 27 companies in the market selling CBD. My thought is that the FDA has picked some of the worst offenders with respect to claims to establish impressive examples. Throughout the years in articles and press notifications, the FDA has always stated the regulatory position that CBD does not meet the definition of a dietary ingredient. This position has been challenged by industry and is a controversial topic. Some plaintiffs’ lawyers have initiated class-action lawsuits on the basis that clients were harmed by buying an illegal product and paying too much for it. It appears that the FDA is currently only enforcing against CBD products with disease claims. So far, the FDA has not written warning letters solely because a dietary supplement uses CBD. All of the mentioned warning letters could have been written to any dietary supplement making obvious disease claims.
So, what can be learned from the FDA’s actions? The first and most important step for manufacturers would be to “clear” all web pages, social media pages, and third-party referrals of disease statements. A second approach should be to not use CBD as a food ingredient or as an animal food ingredient. As a regulatory strategy, this may buy some time until the controversy about the legality of use in dietary supplements is clarified. For dietary supplements – in a conservative regulatory approach – a next step could be not using CBD as a dietary ingredient, because it is an approved drug.
A possible alternative legal ingredient is a full spectrum hemp extract which contains all hemp components – not just isolated CBD. Hemp-derived ingredients are eligible for use as dietary ingredients by virtue of being “botanicals.” However, hemp-derived substances must submit a New Dietary Ingredient notification 75 days prior to first marketing the hemp supplement. A less conservative regulatory approach for dietary supplements could be to wait and see what the FDA decides under the pressure from industry and consumers. Hopefully soon, the FDA will clarify the legality of use in dietary supplements.
 Gisela Leon brings in over 33 years of experience in international labeling. She is well-experienced in USA labeling requirements of food, dietary supplements and cosmetics, in European food laws and multi-language labeling. As a regulatory consultant, she focuses on a concise review process, having reviewed hundreds of labels for U.S. compliance and helped international products to come into compliance with U.S. regulations. Her international labeling background allows her to point out differences or similarities with other countries.
Gisela Leon brings in over 33 years of experience in international labeling. She is well-experienced in USA labeling requirements of food, dietary supplements and cosmetics, in European food laws and multi-language labeling. As a regulatory consultant, she focuses on a concise review process, having reviewed hundreds of labels for U.S. compliance and helped international products to come into compliance with U.S. regulations. Her international labeling background allows her to point out differences or similarities with other countries.
After receiving her Master’s degree in Food Technology Engineering, Ms. Leon received her DGQ Audit-Specialist Certification from the German Institute for Quality, and her Master’s in Business Administration from George Mason University. For over 20 years she worked at Schöller Lebensmittel GmbH & Co KG as Director of Quality Management and Labeling Compliance. Ms. Leon speaks English, German, and French.
EAS Consulting Group, as part of the Certified Group of companies, merged with Food Safety Net Services, (FSNS), to become the global leader in testing and regulatory solutions for the FDA and USDA regulated industries.
EAS’ network of 200 independent advisors and consultants enables us to provide comprehensive consulting, training and auditing services, ensuring proactive regulatory and quality compliance for food, dietary supplements, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, cosmetics, tobacco, hemp and CBD.
The merger of FSNS (FSNS.com) with the Certified Laboratories group of companies, (certified-laboratories.com), has created a leading, national testing and regulatory consulting platform. EAS can assist with your regulatory and quality requirements and challenges, while offering access to a robust scope of testing services to meet your organization’s sophisticated needs.
From regulatory strategy, auditing, training, FDA inspection preparation, 483 & Warning letter remediation, quality system implementation, labeling compliance, preparation of technical submissions such as GRAS, Food Additive Petitions, DMFs, NDIs, 510(k)s and more; to FSMA compliance, expert witness services and due diligence assessments, EAS offers the expert knowledge and experience your company requires to ensure compliance through accurate and timely assistance. With our vast expertise in FDA’s and USDA’s policies and enforcement, EAS is the proven choice for assistance with product testing and other regulatory and quality consulting solutions. easconsultinggroup.com
Member Blog: 5 Must-Have Features for Your Cannabis eCommerce Website

by Gary Cohen, Cova Software
As the cannabis industry goes mainstream, eCommerce is increasingly becoming a necessary part of cannabis retail operations. But with a plethora of dispensary eCommerce solutions available, not all of these can help you build an online presence. With intense competition in cannabis retail, there are some things that you must not compromise on as a dispensary owner. The following five must-have cannabis eCommerce features will help you grow your dispensary business, differentiate yourself from competitors and establish yourself as a formidable brand in the online cannabis space.
Independent eCommerce Platform
When deciding how to sell cannabis online, retailers can either use a third-party marketplace or have their own eCommerce website. Using a marketplace may be the easier option, but in the long run, you will certainly benefit more from owning an independent eCommerce platform. Having your own cannabis eCommerce website gives you complete control over the design, product information, and branding, unlike a third-party marketplace that offers little room for customization. Another valuable benefit of an independent cannabis eCommerce platform is that you can market it directly to online visitors and existing customers and build brand loyalty.
Data Ownership For Building Relationships
To market your online cannabis platform directly to your target demographics, it’s essential to have access to their contact details, which is not possible when you use third-party marketplace platforms. With an independent eCommerce platform, you will not just own your website but also all customer information and other relevant data to help you create innovative marketing campaigns and offer a more personalized online customer experience. Through email marketing and loyalty program communications, you can keep your customers regularly engaged with your brand and grow your business by building long-lasting relationships.
Mobile and SEO-friendly Website
These days, consumers regularly use their smartphones to search the web and make online purchases. Hence, your eCommerce website must function properly not just on desktops but mobile devices as well. You must avoid using an iFrame embedded menu, employed by many third-party marketplaces, as Google won’t crawl or index your website. To ensure that your online cannabis store is discoverable, use an advanced native eCommerce solution that aids in building SEO authority. If your chosen solution offers the ability to create content, you can also capitalize on SEO best practices to improve the flow of organic traffic to your website.
Age-Gating and Compliance Features
If you’re selling products online that have legal age restrictions, then an age-gate on your website is a must. This is not just a compliance requirement, but it also demonstrates your commitment to not exposing cannabis to minors. Many regulatory authorities in the U.S. and Canada are mandating more robust online age-gating measures beyond a simple “Are you 21+ yes or no” pop-up, and it’s essential to choose a solution that offers the functionalities for you to comply with the laws. Your cannabis eCommerce store also must-have features that allow for compliance with legal purchase limits and any other online regulations within your state or province.
Integration with POS and Cannabis Ecosystem
Most importantly, your chosen eCommerce solution must integrate seamlessly with your POS system for efficient inventory management, transactions, and payment processing. Ensure that you are using an advanced cannabis POS system that syncs with leading cannabis tech ecosystem solutions so that you can streamline your online business and maintain a recurring revenue stream from it. For a seamless shopping experience, your customers should be able to browse the website, place an order, pay online and request for pickup or delivery.
 Gary Cohen is the CEO of Cova Software, the fastest growing technology brand in the cannabis industry. Cohen’s focus has been driving the company’s overall strategy, including its vision, go-to-market plan, and strategic development. Since joining the cannabis industry in 2016 and launching Cova commercially in 4q17, Cohen has led Cova to dominate the enterprise sector for dispensary Point of Sale, while forging client relationships with hundreds of single-store retailers across North America.
Gary Cohen is the CEO of Cova Software, the fastest growing technology brand in the cannabis industry. Cohen’s focus has been driving the company’s overall strategy, including its vision, go-to-market plan, and strategic development. Since joining the cannabis industry in 2016 and launching Cova commercially in 4q17, Cohen has led Cova to dominate the enterprise sector for dispensary Point of Sale, while forging client relationships with hundreds of single-store retailers across North America.
With Cova’s cannabis POS and its excellent integrations with eCommerce and delivery services, the online order automatically pops up for the budtender to tender the sales, and the POS system updates inventory once payment is approved. Cova offers multiple eCommerce solutions to choose from, as per your needs and budget, and you can legally sell cannabis online stress-free while staying compliant with strict government regulations.
Member Blog: Cannabis Extraction – Creating a Competitive Advantage Through Data

By Jack Naito, president and co-founder, Luna Technologies
As customers become more sophisticated and discerning about the fast-growing cannabis extract market, from vapes to dabs to infused pre-rolls, the need to routinely produce consistent, quality extracts at scale is becoming doubly important for processors. Compounding the issue, the potential for federal legalization will bring significant growth opportunities but also increased federal oversight, including the need for Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other onerous standards that will challenge unprepared operators.
Future-Proof Extraction Operations Through Data
To overcome these twin challenges, processors should start developing (if they have not already) a framework to capture, review, and analyze data at every stage of production to produce consistent, quality, and compliant products.
That framework should examine every aspect of the extraction process, starting with the type of material harvested from farms, including how it is stored and handled, through to the final, packaged retail-ready product.
It should also be tied to specific goals and clear objectives. Capturing data simply to capture data within a given framework but without a clear idea of how that data will be used can lead to analysis paralysis, or worse, endless trial-and-error that wastes time and material, eating into expected profits.
Leverage Design of Experiments Methodology
Design of Experiments, or DoE, is a scientific methodology that can help guide processors in determining the key parameters they want to track and how those parameters interact. This starts with assertions that map to specific goals or objectives, such as investigating the yield of a specific terpene with the goal of blending it with a distillate-based vape cartridge. From here, processors can design and set up experiments with varying inputs from temperature to pressure, to biomass composition, all to understand how the yield of a specific terpene is influenced throughout a given process.
When these learnings are applied at production scale, the framework developed through DoE methodology provides a guide for creating consistent products, but also to better manage and rectify issues that may arise. With specific goals in mind, processors can then determine what data they need to capture and analyze.
The Four Steps of Data Capture
Step 1: Chemical Makeup – When selecting or determining what plant material to use for extraction, processors first must examine the chemical makeup of the cannabis biomass. This can include the profiles of cannabinoids, terpenes, and the fat/wax/water content.
The exact chemical makeup of cannabis biomass can be difficult to determine because of its nonhomogeneous nature. Imagine closing your eyes and selecting a random sample from a container of bulk biomass. Maybe you grab a sugar leaf or flower, high in THC-laden trichomes, or maybe you grab a fanleaf with little to nothing to contribute to a high-quality extract. The chemical composition will look significantly different depending on how one selects the sample. So it’s important to be cognizant of what and how biomass testing is conducted, and often a single sample isn’t the answer. Knowing the approximate chemical makeup of the feedstock material will guide the processor to determine what type of recipe they will use for extraction and post processing and, ultimately, what end products are most valuable for a given input.
Once the chemical makeup has been determined, the processor will know the inputs of the material, such as the associated THC, CBD, terpenes, etc. They can then use that data to determine what will (or should) come out of the extraction process at its conclusion. This is the mass balance of the production process. It is difficult or impossible to optimize any process if one doesn’t know exactly what goes in and what comes out. Of course, this is much easier said than done given the nonhomogeneous nature of biomass.
Step 3: Identify and Maintain Key Process Parameters – Depending on the recipe and desired end product as determined through the above steps, the extraction process will need to maintain specific temperatures, pressures, times, and flow rates, among other key variables, to ensure a consistent, quality product. This is where a DoE or other similar process can add significant value. Analytical tools, such as the DoE, can help determine what process parameters need to be precisely controlled, and what parameters can have looser controls or can be ignored altogether. Compliance comes into play here as well. The ability to track and record these key data points is crucial to achieving GMP compliance as well as creating a consistent product that customers expect.
Step 4: Post Process Review – In order to understand how recipe parameters affect the end product, the processor needs to know its chemical composition as well as the composition of any waste materials (e.g., biomass, fats, waxes), or impurities that have been filtered out. Capturing this data is vital as it offers the critical clues to why a particular batch did not turn out as planned, for example, so the processor can investigate potential causes and corresponding solutions.
Step 5: Recording Data Between Each Process – What happens between each process is nearly as important as what happens during the process. Storage conditions can have an impact on quality and consistency, issues that may not be readily evident within the data capturing during processing. Those data points to know, among others, may include monitoring the freezer temperature where biomass is stored, measuring the humidity of the environment, documenting when and how equipment is cleaned, or even tracking how long material sits between extraction and placement in a vacuum oven.
Decision Making Via Data Analysis
After the data is captured and analyzed, managers may need to enact decisions if the data shows deviations from the expected outcomes. For example, as part of post-production lab tests (step 4), are acetone traces appearing in the finished product? If so, the organization may need to change its equipment cleaning practices (step 5) to ensure unwanted trace chemicals are not seeping into finished products.
Although enacting a program to better capture, review, and analyze data can appear to be a daunting task, doing so will provide the processor a significant competitive advantage. Not only will it help ensure consistent production while future-proofing the organization against coming regulations, it may also enable processors to experiment with and develop novel or proprietary extracts derived from a repeatable, scientific method that can’t easily be replicated by competitors.
 Jack Naito is President of Luna Technologies, where he oversees operations, strategic growth, and R&D for the company he co-founded in 2016. Jack entered the cannabis industry after time spent as a Materials, Process, and Physics Engineer for aerospace giant Boeing. Jack obtained an Economics and Business degree from Colorado College and a Master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Washington.
Jack Naito is President of Luna Technologies, where he oversees operations, strategic growth, and R&D for the company he co-founded in 2016. Jack entered the cannabis industry after time spent as a Materials, Process, and Physics Engineer for aerospace giant Boeing. Jack obtained an Economics and Business degree from Colorado College and a Master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Washington.
Luna Technologies engineers state-of-the-art extraction equipment for cannabis processors. The meticulously designed, automated equipment empowers operators to process fresh-frozen or cured plant biomass with stress-tested hardware and built-in failsafes to foster a superior level of workplace safety while also lowering labor costs. Luna’s Earth-conscious engineering approach helps decrease energy consumption while setting the industry standard for safety, quality, consistency, and customization in support of creating clean, consistent cannabis concentrates with medical and social benefits. Learn more at www.lunatechequipment.com.
Committee Blog: Protecting Innovations in Cannabis Technology

 The Role of Patents in the Industry, Now and in the Future
The Role of Patents in the Industry, Now and in the Future
Paul Coble is an intellectual property attorney and Chair of NCIA’s Cannabis Manufacturing Committee; Scott Seeley is an intellectual property attorney with Eastgate IP and is Organizer of the Cannabis Manufacturing Committee
Competition in the cannabis industry has always been fierce. To date, most competition has focused on securing licenses and sales territory. But, as markets saturate and the green pastures are all claimed, the battlefronts must shift. Cannabis companies now look to collect non-geographic assets, such as market share, profitability advantages, and a durable brand presence.
Intellectual property law provides mechanisms to capture and monetize these intangible assets. Assets that give a company a competitive advantage can build value into a business beyond its balance sheet. Well-crafted IP portfolios not only deter freerider copying, but are also valuable assets that can be sold, licensed, or provide incentive for investment or acquisition by larger entities. Businesses with a strong IP strategy are able to maintain their edge over their competitors by protecting their investments in technology and marketing to discourage competitors from utilizing their newfound developments or improperly capitalizing on their brand recognition.
Ignoring cannabis IP not only leaves this value on the table, but exposes the business to unnecessary risk. As in all other industries, cannabis companies must recognize that competitors have IP portfolios that may need to be avoided or licensed. Modern competition requires solidifying your own rights as well as understanding the rights of others.
Intellectual property is often broadly broken out into four major categories. Each category is tailored to protect different forms of intangible assets:
- Patents (Technological Developments)
- Trademarks (Brand Recognition, Consumer Goodwill)
- Copyright (Original Authorships and Expressions)
- Trade Secret (Information Providing Competitive Advantage)
This blog post overviews patents, and how patents can be used by cannabis businesses to protect their technological advancements. This is the first of a 3-part series about cannabis IP. The series will culminate with a Q&A-based webinar on April 19 at 1:00 PM ET. Advance questions can be sent to paul@thalo.io.
What are Patents?
Patents protect technological advancements and can be used to exclude others from making, using, importing, or selling a claimed technological innovation.
Patents are often used by businesses to build walls around technologies they develop to temporarily prevent competitors from using the same advantages. Companies also use patents to build portfolios of technology that can be sold or licensed like any other asset, or used to bolster their valuation for acquisition or investment opportunities.
But patents are not just used to block competition, they can also be a tremendous source of information about technological developments in the field. While patent discovery tools are admittedly lacking at the moment (GooglePatents is a good place to start), the details in a patent can often short-circuit months or years of work. Of course, depending on the patent claims, you may need to license the patent in order to use that information. But that type of information-for-licensing-rights exchange, with the right mentality on both sides, is the foundation of an efficient industry.
Here are just a few examples of the cannabis technology that may be patent eligible:
- Cannabis Strains
- Formulations for Extracts, Topicals, Tinctures, Vape Liquid, Edibles
- Vaporizer Design
- Cartridge Design
- Extraction Methods
- Manufacturing and Processing Methods
There are three types of patents that can be used to protect cannabis technology: Utility, Design, and Plant. These types of protection are not mutually exclusive and sometimes can be combined to form a more comprehensive protection strategy.
Utility Patents
Utility patents are the most popular type of patent, offering the broadest and strongest form of protection. Utility patents last 20 years from the date of filing and are good for protecting nearly any new technological innovation including formulations for extracts, topicals, tinctures, or edibles, new vaporizer designs, new improvements to processing or manufacturing methods, and similar developments. Utility patents can also be used to protect new cannabis genetics, at least theoretically. As discussed below, however, there are several practical barriers to patenting cannabis genetics.
A significant benefit of utility patents is that they can protect the actual function of an innovation, rather than just the outwardly recognizable features or the specific implementation. This aspect of protection sets utility patents apart from other forms of protection like design patents and copyright, which are limited non-functional aspects.
Design Patents
Design patents protect an item’s unique ornamental appearance. Design patent protection is sometimes easier to obtain than utility patents because design patents only protect the look of an item, not how it works. So design patents do not protect against someone selling a functionally identical device with a different outward appearance. This narrower protection also lasts only 15 years instead of 20.
Nevertheless, design patents can be a strong tool to protect products that have a novel and distinct design aesthetic. They can cover the visual appearance of vaporizer batteries or cartridges, retail packaging, even unique dispensary displays. In some cases, design patents can be effectively combined with trademark and trade dress protections to create a highly defensible brand style.
Patenting Cannabis Strains
The most common questions about cannabis patents usually relate to patenting strain genetics. Newly developed strains can be protected by both utility and plant patents, with varying rights and requirements. Cannabis strains may also, theoretically, receive pseudo-patent protection under the Plant Variety Protection Act of 1970 (“PVPA”). As noted below, however, current practical realities make PVPA protection unattainable for most cannabis strains.
Both plant and utility patents can protect cannabis strains, but they do so very differently. Utility patents cover newly invented compositions of matter and, therefore, can be used to prevent copying a novel genetic sequence. These patents literally cover specific sequences of DNA base pairs. A key requirement of utility patents is that the applicant must enable others to make and use the same invention once out of patent. While it may be possible to meet the enablement requirement with a transgenic breeding or CRISPR gene editing, the more common method of enabling plant gene patents is with a biological deposit of seeds or other propagation material with a public organization. So long as cannabis remains federally illegal, it can be difficult or impossible to make the deposit within the U.S. Some applicants have had success making the seed deposit at foreign centers, but the growth of cannabis genetic patents has been slowed by these requirements. When cannabis is eventually descheduled, the practical barriers to genetic patents will fall and that may trigger a rush by more companies to seek patents for their proprietary cannabis strains.
Plant Patents
Another form of patents, plant patents, can protect new plant varietals that have been reproduced asexually. Although cannabis plants are relatively easy to reproduce asexually via cloning or cutting, one disadvantage of this form of protection is that plant patents only cover genetically identical copies, reproduced asexually from the claimed plant. That means to infringe a plant patent, one must physically clone the patented plant–a narrow base for an infringement claim.
Plant Variety Protection Act
The last vehicle that can protect a new cannabis strain is the Plant Variety Protection Act that was designed specifically to protect sexually reproducing plants, such as cannabis.
The PVPA, however, comes along with a strict requirement that at least 3,000 seeds of the claimed plant species be deposited with the U.S. Department of Agriculture in Fort Collins, CO. The USDA will not accept any deposits for plants that are classified as controlled substances, including cannabis. Meaning that, for the time being, PVPA protection is unavailable for cannabis plants that do not qualify as hemp (less than 0.3% d9-THC).
The Process – How to Get a Patent
All patents start as applications which must be examined and approved by the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office (“USPTO”) to become granted patents. The application process, from start to finish, can last 1-5 years and cost anywhere between a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
The examination involves a review of the patent application, as well as related literature published before your application was filed (also called “prior art”). An examiner with technical expertise in the application’s field will search for prior art and determine whether the application meets all statutory requirements. Most notable of those requirements are that the invention must cover eligible subject matter and be sufficiently inventive to warrant a patent.
The prosecution process typically involves letters back-and-forth between the inventor and the Patent Office. It is often thought of as a negotiation — nearly all patent applications receive at least one rejection. The applicant is given an opportunity to change what the patent covers or explain why the rejection was wrong. Only if and when the Examiner is satisfied that all statutory requirements are met will the application be allowed to issue as a patent.
How will Patents Shape the Cannabis Industry?
Like it or not, patents are rapidly becoming a major force in the cannabis industry. The cannabis industry is in a unique position to determine the role intellectual property will play, but one thing is certain: cannabis IP cannot be ignored. Some companies, like Canopy Growth, Nextleaf, and various pharmaceutical companies, are aggressively developing patent portfolios and high-stakes patent litigation is already underway. Additionally, holding companies known as “non-practicing entities” have been formed to purchase valuable patents covering key aspects of cannabis cultivation, manufacturing, and consumption.
But these forces do not have to dominate the industry. Patents were originally designed to promote scientific advancement, not inhibit it. When the IP rights of others are respected and technology is licensed widely at reasonable rates, intellectual property can cut years and millions of dollars from research budgets. Some industries have found success with patent cooperatives and similar pooled-patent arrangements. The future may see some combination of patent licensing with blockchain technology, NFTs, or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
We will continue the discussion as to what an enlightened approach to intellectual property could look like in the cannabis industry in our webinar scheduled for April 19 at 1:00 PM Eastern. Please send any advance questions to paul@thalo.io.
Member Blog: Hemp Cultivators and Processors Get a Head Start in New York Adult-Use Cannabis Industry

by Charles Messina and Jennifer Roselle, Genova Burns LLC
While the Garden State and Land of Steady Habits are convincingly in the lead of the tri-state dash towards adult-use cannabis sales, new legislation passed last week at least gives the Empire State a burst of energy.
There has been much anticipation since the Marijuana Regulation and Taxation Act legalized cannabis in New York for adults last year. But only medical patients in the state can legally purchase products right now. New York’s slow start to recreational sales has reportedly led to even more unregulated products flooding the marketplace, including delta-8 THC — which is banned under NY state law though widely being sold throughout the state.
By Governor Hochul signing Senate Bill 8084A into law on February 22, 2022, the legal cultivation, processing, and distribution of cannabis in New York should be accelerated. Specifically, the new legislation permits hemp cultivators and processors to apply for growing and processing adult-use cannabis, and aims to promote certain equity goals in the process. It creates two new temporary license categories: (1) conditional adult-use cultivator licenses; and (2) conditional adult-use processor licenses. These licenses must be issued by December 31, 2022, and will be valid through June 30, 2024.
Among other requirements, applicants seeking conditional cultivator licenses must be prepared to demonstrate they are authorized hemp growers in good standing. Although they must only show good standing since December 31, 2021, applicants must also show proof of growth for two of the last four years.
Cultivators must also comply with geographic restrictions for growing and are limited to outdoor or greenhouse settings. Outdoor facilities may have a maximum of 43,560 square feet of flowering canopy. Greenhouse canopy may not exceed 25,000 square feet, and can use up to 20 artificial lights. As expected, licensees must also comply with any environmental standards and requirements mandated by the Office of Cannabis Management.
For those seeking conditional processor licenses, licensees must hold an active cannabinoid hemp processor license. This license must have been granted before January 1, 2022. And, as a condition of licensing, transfer of ownership will be restricted through the end of the conditional period. The processor license will allow the acquisition, possession, processing, and sale of cannabis, along with enabling the licensees to engage in blending, extracting, infusing, packaging, labeling, branding, and preparing cannabis products.
In addition, all conditional licensees must enter into a labor peace agreement, participate in an environmental sustainability program and social equity mentorship program. Licensees must also, among other things, become operational within six months from the day they receive the conditional license.
Hemp farmers and processors are no doubt getting a big nugget from the Big Apple. While more regulations on adult-use licensing are anticipated soon, a trail is now blazed for certain New Yorkers in the hemp industry and social equity participants.
Charles J. Messina is a Partner at Genova Burns LLC and specializes in Franchise & Distribution, Agriculture and Cannabis Law. He teaches one of the region’s first cannabis law school courses and devotes much of his practice to advising canna-businesses as well as litigating various types of matters including complex contract and commercial disputes, insurance and employment defense matters, trademark and franchise issues and professional liability, TCPA and shareholder derivative actions.
Jennifer Roselle is a Partner at Genova Burns LLC and specializes in Cannabis Law. She has unique experience with labor compliance planning and labor peace agreements in the cannabis marketplace. In addition to her work in the cannabis industry, Jennifer devotes much of her practice to traditional labor matters, human resources compliance and employer counseling.
For over 30 years, Genova Burns has partnered with companies, businesses, trade associations, and government entities, from around the globe, on matters in New Jersey and the greater northeast corridor between New York City and Washington, D.C. We distinguish ourselves with unparalleled responsiveness and provide an array of exceptional legal services across multiple practice areas with the quality expected of big law, but absent the big law economics by embracing technology and offering out of the box problem-solving advice and pragmatic solutions.
Our firm is proud of its proven track record of assisting multiple clients with being awarded medical licensure in New Jersey, and continuing to counsel clients on the dynamic federal and state regulatory landscape, as well as with corporate transactional, labor/employment, real estate, land-use and other issues.
Given Genova Burns’ significant experience representing clients in the cannabis, hemp and CBD industries from the earliest stages of development in the region, the firm is uniquely qualified to advise investors, cultivators, processors, distributors, retailers and ancillary businesses.
Member Blog: Tax Rules for Cannabis Companies

by Kaveh Newmen of Edlin Gallagher Huie + Blum
The cannabis industry has grown exponentially as an increasing number of states have relaxed state law prohibitions on the use of cannabis for medical and recreational purposes. However, under federal law, cannabis remains classified as a Schedule I controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). This means that the production, distribution, and possession of cannabis remains illegal on the federal level.
Schedule 1 Status of Marijuana: State-Legal Cannabis Businesses and Application of Internal Revenue Code Section 280E
Cannabis businesses are treated differently from many other businesses for tax purposes. Under Internal Revenue Code (IRC) §280E (“280E”), which applies to a federal income tax filing, denies deductions and credits for amounts paid or incurred in carrying on the trade or business of cannabis. Cost of goods sold is allowable because it is not considered a deduction, rather it is a reduction of gross receipts (revenue) to arrive at gross profit.
A report published in March 2020 by the U.S. Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration examined California and found that over 50% of marijuana companies had likely underpaid the IRS under IRC§ 280E. The report confirms the IRS is preparing to increase marijuana industry audits nationwide in response.
Currently, the method by which cost of goods sold may be deducted for producers is to use IRC §471(a). This provision discusses how to clearly reflect income by using an inventory method. Therefore, cannabis producers have less of a 280E problem than retailers and distributors.
After the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), effective for tax years beginning January 1, 2018, a provision was passed in the IRC §471(c). There are various opinions with advisors in the industry on whether this code section and method can be used for retailers and distributors. The idea behind IRC 471(c) is that “certain small businesses” can meet the gross receipts test of this subsection for any taxable year in which the corporation’s or partnership’s average annual gross receipts do not exceed $25,000,000 for the 3-taxable-year period ending with the taxable year that precedes such taxable year. Pursuant to IRC §448(c)(1), this type of small business may be able to use a “books and records” method for deducting all costs – rather than being limited to cost of goods sold only. In other words, if one uses 471(c)(1)(B) as an accounting method, in theory, they may also be able to deduct selling expenses and all other costs that were previously not allowed as deductions.
For further discussion on this topic see the following articles: Bloomberg Tax – Cannabis Taxpayers Find Flaws in New Accounting Method Rules and The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: A Comparison for Businesses
Assembly Bill 37, codified in §17209 of the California Revenue and Taxation Code
Each state in the U.S. is autonomous in that it has the authority to decide whether its income tax laws conform to §280E or not. On October 12, 2019, Governor Newsom signed into law AB 37, which overrides §280E through the following provision:
For each taxable year beginning on or after January 1, 2020, and before January 1, 2025, Section 280E of the Internal Revenue Code, relating to expenditures in connection with the illegal sale of drugs, shall not apply to the carrying on of any trade or business that is commercial cannabis activity by a licensee. – (CAL. REV. & TAX CODE § 17209 (2020). CAL. REV. & TAX CODE § 17209 (2020).
However, AB 37 only applies to state filings with the Franchise Tax Board and is currently only available until January 1, 2025. AB 37 has no impact on federal tax filings, which is where a majority of cannabis entities pay their income taxes with effective tax rates as high as 25% for corporate taxes and up to 37% for individuals.
The IRS Lacks Guidance for Cannabis Tax Payers
The IRS has not published nationwide guidance to taxpayers and tax professionals in the cannabis industry. In addition, cash-intensive business issues unique to the cannabis industry such as IRS §280E and banking limitations will remain unresolved unless and until there is uniformity through federal legalization. As a result, compliance-related issues continue to grow and negatively affect cannabis business owners who operate legally under individual state law.
 Kaveh Newmen is an associate at Edlin Gallagher Huie + Blum who handles cannabis law general litigation, and trucking and transportation matters. Kaveh was admitted to practice law by the State Bar of California in 2021. Kaveh earned his J.D. from the University of San Diego School of Law in 2020, where he was a board member of the Criminal Law Society, the Immigration Law Society, the Middle Eastern Law Student Association, and served as an intern at the school’s Immigration Clinic. He is a first-generation Iranian-American and speaks Farsi.
Kaveh Newmen is an associate at Edlin Gallagher Huie + Blum who handles cannabis law general litigation, and trucking and transportation matters. Kaveh was admitted to practice law by the State Bar of California in 2021. Kaveh earned his J.D. from the University of San Diego School of Law in 2020, where he was a board member of the Criminal Law Society, the Immigration Law Society, the Middle Eastern Law Student Association, and served as an intern at the school’s Immigration Clinic. He is a first-generation Iranian-American and speaks Farsi.
Member Blog: Diversity and Inclusion Emerge as Major Themes in Cannabis

By Morgan Stinson, Social Impact Leader, MGO
While MGO put together its annual Cannabis 50 Impact Report of organizations and individuals pushing the cannabis industry forward, we were able to acquire new insights from some of the most influential leaders in the industry, like Kim Rivers, founder, chairman, and CEO of Trulieve; Berner, co-founder and CEO of Cookies; and Troy Datcher, CEO of The Parent Company. A clear trend that emerged in the report is the number of honorees focusing on social equity. Those who are contributing to the social equity community are bringing awareness, fostering inclusion, increasing diversity and expunging criminal records for cannabis convictions.
Diversity Where it Matters
Visual artist, hip-hop pioneer, and filmmaker Fred Brathwaite aka Fab 5 Freddy wasn’t wrong when he told us, “The biggest obstacle is making sure we’re all focusing on social equity and inclusion so people of color can benefit from the [cannabis] industry, as they’ve been the most victimized for being a part of it.” At this point, the industry at large is starting to acknowledge the debt it owes people of color.
Because underrepresented populations have borne the brunt of cannabis prohibition and many are not reaping the economic benefits of legalization, the logical step is to increase people of color ownership in the industry.
One of the biggest barriers in the industry is the cost of entering the market. Launching a dispensary or cultivation business requires anywhere from $750,000 to $1 million, and acquiring licenses isn’t easy. State and local governments must even the playing field, and although some states have incorporated social equity programs into cannabis legislation, many say the programs are falling short.
Building a Backbone Through Programs and Government Uniformity
So where do we go from here? Some organizations, like The Parent Company, are focusing on discovering the industry’s future entrepreneurs of color, providing the capital and mentorship necessary to build a more equitable and diverse industry.
If we let it, cannabis can be the new economic backbone for many communities, be it on the city, county, or even state level. Troy Datcher, the CEO of The Parent Company, notes where things need to progress. “There’s still so much work to do collectively to improve regulations, taxation policies, and safety,” he said. “But most importantly, we must work together to ensure the industry remains committed to inviting a diverse community to participate as the landscape takes shape.”
The industry is also supporting organizations and programs focused on dispensing education and support to budding minority entrepreneurs — some of which are mentioned in MGO’s Cannabis 50, like Our Academy presented by Our Dream. Hilary Yu, founder of Our Academy, told us, “We have this unique opportunity to carve out generational wealth opportunities for the communities who have been harmed by cannabis legislation,” and she knows building and supporting new leaders is key.
Making a Change
MGO is enthused to see so many organizations and individuals making tangible progress toward social equity and inclusion. If you’re interested in learning more about the honorees in this year’s Cannabis 50 report, click here. For those building a better future for the industry, read the section “Doing Good.”
 Morgan Stinson is a social impact manager, leader of the MGO Diversity, Equity & Inclusion program, and co-creator of The Future Game. She combines a professional background in accounting and finance with a passion for developing actionable solutions for creating professional and educational opportunities for minorities and persons from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Morgan Stinson is a social impact manager, leader of the MGO Diversity, Equity & Inclusion program, and co-creator of The Future Game. She combines a professional background in accounting and finance with a passion for developing actionable solutions for creating professional and educational opportunities for minorities and persons from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Allied Association Blog: Cal NORML Fights Ongoing Discrimination That Hurts Cannabis Businesses in California

 By Ellen Komp, California NORML
By Ellen Komp, California NORML
Assemblymember Bill Quirk has introduced two bills sponsored by California NORML in this year’s legislative session that address ongoing human rights issues that are stumbling blocks for industry.
A pair of online surveys being conducted by California NORML is finding that up to 33% of respondents have been denied employment due to testing positive for cannabis, 19% have been denied prescription drugs by their doctor due to cannabis use, and up to 60% have stopped using cannabis because of drug testing by their employer or doctor.
This means as many as half of businesses’ potential customers aren’t buying cannabis products in California because of current laws. In addition, many Californians report they are underemployed because of their cannabis use, giving them less purchasing power at cannabis retailers.
The first bill to remedy this situation is AB 2188, which would end discrimination based on cannabis metabolites testing by California employers.
Testing or threatening to test bodily fluids for cannabis metabolites is the most common way that employers harass and discriminate against employees who lawfully use cannabis off the job. Cannabis metabolites are the non-psychoactive substances that can be detected in a person’s bodily fluids (mainly, urine and hair) for up to several weeks after they have consumed cannabis.
Testing positive for cannabis metabolites has no scientific value in establishing that a person is impaired on the job. When employers use cannabis metabolites tests to discriminate against employees or prospective employees, they are most likely discriminating against people who consumed cannabis when they were not at work.
Five other states (NV, NY, NJ, CT & MT) have passed laws in recent years protecting adult-use cannabis users’ employment rights, and 21 states protect those rights for medical marijuana users. Philadelphia, Washington D.C., and Atlanta also protect the rights of workers in their cities who use cannabis.
As in other states, the proposed California bill has exemptions for employers who are required to follow federal drug-testing mandates. Assemblymember Quirk’s bill does not bar employers from requiring that employees not be impaired on the job, and it does not prohibit other forms of testing, such as performance-based impairment testing or testing for THC, which may establish that a person has consumed cannabis in the past several hours.
Studies have shown that off-the-job cannabis use is not positively associated with elevated rates of occupational accidents or injuries, and that liberalized cannabis laws are associated greater labor participation, lower rates of absenteeism, declines in workers’ compensation filings, and higher wages.
The cities of Oakland and San Francisco have passed resolutions in favor of the employment rights bill’s language, and Cal NORML has been busy reaching out to unions and other stakeholders for support.
The second Cal NORML-sponsored bill to benefit California cannabis consumers — and the industry — is AB 1954, which seeks to protect the right of patients to medical treatment if they use medical cannabis, and the right of physicians and clinics to treat them.
Many physicians are under the mistaken impression that they can’t prescribe medication to patients who test positive for cannabis. The Quirk bill would clarify that physicians cannot be punished for treating patients who use medical cannabis, notwithstanding its illicit status under federal law.
A great many studies have shown cannabis is effective for pain and can help patients reduce their use of opiates. Cal NORML’s survey shows that 24-30% of respondents have increased their use of opiates or other medications due to drug testing by their doctor or employer. With an opiate overdose crisis continuing to affect California, we need to end policies that drive patients to use more dangerous and addictive drugs.
In Cal NORML’s membership polling, we have found that tax reduction is the #1 issue among our members. We are following and acting on 30-40 bills this year, including the various tax reform bills and other business-oriented proposals that have been introduced in the CA legislature this year, from a consumer rights standpoint.
Cal NORML has begun a Capital Campaign aimed at cannabis companies who do business in California to take us over the finish line on these important bills in 2022. We also offer business memberships with many perks, including discounts on NCIA memberships. We are always interested in hearing from our business members on how we can work together for cannabis consumers’ rights in California.
 Ellen Komp is the Deputy Director of California NORML. Founded in 1972, Cal NORML is a non-profit, member-supported organization dedicated to reforming California’s marijuana laws. As the state chapter of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws, we lobby lawmakers, promote events, publish newsletters, offer legal and consumer health advice, and sponsor scientific research. Check out our website at www.CaNORML.org.
Ellen Komp is the Deputy Director of California NORML. Founded in 1972, Cal NORML is a non-profit, member-supported organization dedicated to reforming California’s marijuana laws. As the state chapter of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws, we lobby lawmakers, promote events, publish newsletters, offer legal and consumer health advice, and sponsor scientific research. Check out our website at www.CaNORML.org.
Member Blog: 9 Standard Operating Procedures Every Dispensary Should Have

by Tommy Truong, Director of Partnerships at KayaPush
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are the documents, protocols, systems, and procedures that your cannabis dispensary should have in place to manage day-to-day operations.
SOPs help dispensaries in many ways: From optimizing proper employee management systems such as dispensary payroll and onboarding to ensuring compliance with regulations are consistently met, and more.
What are the top dispensary SOPs to use?
There are hundreds of dispensary SOPs that could be created, and they should constantly be evolving as your store grows.
Overall the goal of dispensary SOPs is to increase efficiency and help you become more profitable in the long run. That being said, these are the 9 types of dispensary SOPs we recommend you start with as you build and scale your dispensary store.
1 – Opening & closing procedures and SOPs
All brick and mortar retail stores should have SOPs in place for opening and closing the store. But especially stores that require high-security measures like cannabis retail stores.
Opening and closing checklists for this special breed should include the following:
Opening checklist:
- Vibe check: Turn on lights, music, temperature, put out signs, clean.
- Check for any signs of a break-in or forced entry every morning.
- Make sure that all products in the display and stores are accounted for.
- Put away any orders.
- Review inventory.
- Turn on and start up all software systems.
- Ensure you are in dress code (if applicable)
End of day checklist:
- Check that the security cameras are working.
- Lock all the doors and display cabinets.
- Check and report any obvious security threats/ logbook.
- Generate sales and compliance reports.
- Cash-out protocols.
- Closing the cash registers and POS system.
- Turn off lights, music, bring in signs.
- Clean and sanitize the store.
- Lock all doors and perform security checks.
2 – Customer check-in procedures and SOPs
Many cannabis dispensaries violate their customer check-in procedures and end up facing fines and license suspensions by regulators. Due to this, it is crucial that you implement customer check-in SOPs to ensure compliance.
Customer check-in procedures include:
- Proper budtender training on protocols beforehand.
- Screen every customer entering the store to ensure they are of legal age.
- Ensure customers have a valid license to purchase cannabis.
- Scan the customer’s ID to make sure it is genuine and valid.
- Check the customer’s age, and enter these details into your customer database or tracking system.
- Check the system to ensure the customer has not already gone over their purchasing limit at a different store.
- Follow proper serving protocols.
3 – Sales transaction process and SOPs
Sales transaction processes are crucial to the business because this is how the company generates its revenues. Keeping track of these is key. Do you have the following sales SOPs?
Sales transaction processes could include:
- Greeter procedures (first customer contact),
- Boxing and packing procedures.
- Cashier procedures.
- Answering customer product questions.
- Recording product sales information into tracking systems.
- Recording shipping information.
- Processing various forms of payment.
- Gathering sales tax to submit.
It would help if you integrated your SOPs with the technology you’re using, like cannabis-compliant POS systems.
4 – Delivery procedures and SOPs
Cannabis deliveries can get complicated as they tend to include strict guidelines around logistics. This is why it’s essential there are SOPs built around these logistics.
Delivery procedures could include:
- Packaging and shipping guidelines with regards to the different types of products.
- Procedures in place to pack and mark fragile deliveries — like glass bongs — clearly to ensure safe delivery.
- Details and SOPs around third-party deliveries.
- Sop’s around management tools or software.
- Inputting data into the tracking software or POS system.
- Proper accounting and documentation of the aforementioned.
5 – Security, accounting, and cash management protocols and SOPs
Cannabis retail stores face many challenges when storing and moving cash from the store to the bank. Since dispensaries are not legal at the federal level in the United States of America, they are limited in the services they can receive from banks. As a result of those limitations, dispensaries struggle with large amounts of cash being stored on the dispensary’s premises, so tight SOPs surrounding how to navigate these challenges are crucial.
Security and cash management protocols could include:
- What employees are allowed in sensitive areas like stores and cash safes.
- How long to keep security camera recordings and how to report a robbery.
- How often armored trucks can pick up cash.
- Who gives the cash to the trucks.
- How the cash is stored while at the dispensary.
- Who is keeping track of accounting and line items?
- Who is keeping track of inventory management?
- How are taxes being filed and accounted for, and by who?
6 – Track-and-trace & inventory management and SOPs
Track and Trace SOPs are important for every cannabis dispensary. In order to comply with the regulations, you have to adopt track and trace SOPs into your inventory management system.
These track and trace SOPs should cover:
- Inventory management processes like procurement.
- Transportation to store.
- Product transfers.
- Audits.
- Track and trace software procedures that comply with local regulations.
Given how important track and trace SOPs are for compliance, you should automate this process if possible. Track-and-trace automation software can help you define the roles for each activity and integrate compliance checks.
7 – Quality assessment SOPs.
Quality assessment SOPs will make sure your product is up to the required standard by the regulators and that you are not violating any laws over what ingredients can be included in your products and how they are made. Failure to comply with these SOPs or pass a quality assessment could leave a dispensary owner at risk of losing their license.
Quality assessment SOPs could include:
- Purchasing products from verified sellers.
- Ensuring products are tagged within tracking systems.
- Ensuring you are selling products that you can legally sell within your geographic location.
- Product feedback requests.
8 – Product recalls and emergencies and SOPs
Product recall SOPs will come into play when a defective product needs to be recalled from the market. This can be stressful for the team as it will lead to customers complaining, and management concerned about losses being recorded. One of the most valuable assets to have in this situation would be SOPs that guide your team on how to act in this situation without losing their cool or professionalism.
Recall SOPs could be:
- How /who contacts purchasers.
- Who is on top of product updates (do you have a compliance manager?).
- Product recall script.
9 – Employee Management SOPs
Previously, these SOPs have been focused on inventory and store management, however, managing your staff is another large part of any dispensary operation.
When managing your staff it is recommended that you use employee management software to alleviate the stress of manually running operations such as dispensary payroll, scheduling, onboarding, or time clock adjustments.
Using software alone can eliminate the need for some of these SOPs but if you do choose to go the manual route you should have SOPs for the following procedures.
Employee management SOPs could be:
- How do you onboard employees?
- Who manages their forms and licenses?
- Who writes and manages the schedules?
- How do employees swap shifts?
- How do staff clock into shifts?
- How runs payroll?
- How are staff paid?
- How are taxes paid?
- How are employees’ performances reviewed, and by who?
Conclusion
These are the major SOPs that we believe you should have in place before opening or scaling, but don’t forget that enforcing them is just as crucial as implementing them!
The best way to run a compliant, systematic, and streamlined dispensary is to use great technology to help you succeed!
Consider using a project management tool to help you stay on top of all your tasks, a people management solution for payroll, HR, time tracking, and scheduling, and a dispensary POS solution that integrates with track and trace technology and people management solution for the best results. By using the tools paired with standard operating procedures your dispensary is sure to succeed.
 Author Tommy Truong is the Director of Partnerships at KayaPush; the cannabis software helping dispensary owners manage their employee HR, scheduling, and payroll. KayaPush also integrates with leading dispensary POS systems. Tommy loves hot sauce, fried chicken, and running with his Boston terriers.
Author Tommy Truong is the Director of Partnerships at KayaPush; the cannabis software helping dispensary owners manage their employee HR, scheduling, and payroll. KayaPush also integrates with leading dispensary POS systems. Tommy loves hot sauce, fried chicken, and running with his Boston terriers.
Equity Member Spotlight: Toni Brands with Toni Scott

NCIA’s editorial department continues the Member Spotlight series by highlighting our Social Equity Scholarship Recipients as part of our Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Program. Participants are gaining first-hand access to regulators in key markets to get insight on the industry, tips for raising capital, and advice on how to access and utilize data to ensure success in their businesses, along with all the other benefits available to NCIA members.
Tell us a bit about you, your background, and why you launched your company.
 I grew up in Connecticut in the 70s and was repeatedly reminded of the cannabis stigmas, witnessing others partake in regular consumption, yet never noted any of the proclaimed stigmas; in fact, it appeared the exact opposite.
I grew up in Connecticut in the 70s and was repeatedly reminded of the cannabis stigmas, witnessing others partake in regular consumption, yet never noted any of the proclaimed stigmas; in fact, it appeared the exact opposite.
I’m a Master’s prepared Registered Nurse and Certified Yoga teacher, working in the healthcare industry for over 30 years. As a child and well into adulthood, I suffered from debilitating eczema, anxiety, and depression, treated with high-dose topical steroids, sedatives, and antihistamines, eventually leading to overuse. In the mid-’90s, I smoked my first joint; I also began pursuing my first nursing degree.
A few years after graduation, I began working as a travel nurse in Newborn Intensive Care Units across the U.S. Although I was very aware of the relief cannabis brought to my physical and mental wellness, I utilized it with underlying shame, guilt, and fear of a positive urine drug test, a legal pre-employment requirement for nurses.
By the early 2000s, I suffered a traumatic professional burnout; at the time, my health was poor, my stress-induced eczema exacerbations left me with painful cracked skin on my face, hands, arms, and legs. I was prescribed the highest dose of topical steroids and antihistamines with no resolve; I was a mental and emotional wreck.
Unfortunately, that wasn’t my first time feeling defeated in my skin; as a child, I ingested various prescribed medications. I can vividly recall feeling like a walking science experiment, constantly misdiagnosed and prescribed drug after drug. Nothing worked; in fact, the treatments left me worse off; it wasn’t until the professional burnout that I decided to take charge of my physical, mental and emotional health. I stopped taking ALL prescribed and over-the-counter medications; instead, I began to intentionally utilize yoga, meditation, dietary changes, and cannabis for self-care.
I began to dig deeper into the plant, educating myself about the endocannabinoid system phytocannabinoids, researching the history, and regular visits to local dispensaries. It was during the dispensary visits that I identified a massive pain in Gen X and Baby Boomer populations. Stigma, fear, and uncertainty keep many in this demographic away from reaping educational and wellness benefits of a healthy balanced endocannabinoid system, incorporating phytocannabinoids, physical movement, stillness, and creative expression.
I launched my brand to become the sought-after wellness thought leader, educator, and advocate for cannabis health equity in communities most affected and continue to be affected by the war on drugs.

What unique value does your company offer to the cannabis industry?
I bring my personal experiences of the therapeutic effects I’ve received from cannabis. As a nurse, I understand human anatomy and physiology, including the endocannabinoid system. Through continued education, I’m well versed in the relationship between endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids and the effect they have alone and together on human wellness. I understand how incorporating movement and stillness practices in partnership with cannabis can provide many health benefits.
What is your goal for the greater good of cannabis?
I have three primary goals for the good of cannabis.
- Wellness Thought Leader – As an aging woman who utilizes many Eastern wellness practices, my goal is to share with others a new approach to aging, using my handcrafted CBD-infused topical skin products, yoga, meditation, and creative expression practices.
- Education – Cannabis stigma is a significant barrier between acceptance and usage in Gen-X and Baby Boomer populations. It’s my goal through easy to comprehend education, storytelling, retreats, and practice to begin breaking these barriers. Including educating our community leaders, political figures, dispensary owners, and religious leaders.
- Advocacy – Cannabis health equity is not something Black and Brown folks should need to beg for; it’s my goal to be a voice for the voiceless, actively work towards better health and wellness in communities that are often overlooked when it comes to education, yet flooded with legal and illegal access to cannabis without any instruction or understanding. The lack of economic, social, and political health equity in these communities is a recipe for failure as adult use becomes legal and the impending federal legalization. We can’t afford to wait and see this out; we must address cannabis health equity now.
What challenges do you face in the industry, and what solutions would you like to see?
 Unfortunately, being an African American woman in this industry is a challenge. My personal experience with the plant, professional education, and long-standing career in preventative wellness doesn’t seem to hold much weight. The industry is more vested in the marketing and sales of cannabis, touting social equity along the way for good measure. That’s not enough; cannabis health equity, education, resources, and sustainable outcomes must be provided. I’d like to see multi-state operators hire diverse directors of health services to their c-suite. A diverse leadership team can provide a balanced focus on cannabis social and health equity that serves the industry and the end-users.
Unfortunately, being an African American woman in this industry is a challenge. My personal experience with the plant, professional education, and long-standing career in preventative wellness doesn’t seem to hold much weight. The industry is more vested in the marketing and sales of cannabis, touting social equity along the way for good measure. That’s not enough; cannabis health equity, education, resources, and sustainable outcomes must be provided. I’d like to see multi-state operators hire diverse directors of health services to their c-suite. A diverse leadership team can provide a balanced focus on cannabis social and health equity that serves the industry and the end-users.
Why did you join NCIA? What’s the best or most important part about being a member of the Social Equity Scholarship Program?
I joined NCIA for the opportunity to meet, learn, grow, and collaborate with other industry professionals. The membership fees can be steep for those bootstrapping, and I wanted to see what NCIA was about and if they walked the talk before committing to a full membership. It’s been a fantastic journey so far. I’m on the Education Committee, its retail sub-committee, and health equity working group. Our weekly social equity “Power Hour” is highly beneficial, a safe space to collaborate and support each other. It’s also been a great resource, and I appreciate the educational webinars, complimentary conference tickets, and business development support.
Member Blog: Will 2022 Be the Year for Cannabis Consumption Lounges?

By Eric Rahn, Managing Director, S2S Insurance Specialists
Key Questions & Considerations for Those Looking to Ride the Next Big Wave
In the ever-evolving and fiercely competitive cannabis industry, consumption lounges (a.k.a. social or smoking lounges) are generating big buzz. Innovators and proponents for their legalization see it as a prime opportunity to better compete in a saturated market, attract new customers and grow market share. Opponents throw up a heap of red flags, including drugged driving, crime, and the health risks associated with smoke exposure.
Whether this new retail business model blows up in 2022 or not is anybody’s guess. Nevertheless, our industry must prepare for this next big wave in cannabis consumption. As an insurance broker who specializes in the cannabis industry and works with a wide variety of cannabis, hemp, and CBD businesses in every state where marijuana laws are established, we’ve done a deeper dive into the opportunities, and risks versus rewards for businesses looking to ride the potentially next big wave in cannabis.
The Opportunity
The concept of a cannabis consumption lounge is nothing new, really. Similar to a bar that serves alcoholic beverages, consumers at least 21 years of age can not only purchase flower, edibles, etc. from a budtender but also consume these products in a social gathering place. Amsterdam’s “coffee shops” serve as the inspiration and model for cannabis innovation in the U.S. In the Netherlands, however, coffee shops operate in a legal grey area with their products being supplied by an entirely underground cultivation market. Of course, here in the U.S., the burden falls on individual states since marijuana remains illegal at the federal level.
Analysts predict cannabis consumption lounges will be a budding business in states where recreational and/or medical marijuana is legal. This emerging business model is particularly attractive to states with more mature cannabis laws, like California and Nevada. Alaska became the first U.S. state to allow consumption lounges in 2019 and Nevada is the latest to announce plans for the first state-sanctioned lounges by mid-2022. In all, seven states including the aforementioned, as well as New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, and Illinois, are forging ahead with their plans to allow for consumption lounges in 2022. These states will likely serve as a blueprint for other states as their popularity grows.
Risks versus Rewards of Cannabis Consumption Lounges
State regulatory bodies are grappling with how to develop, implement and enforce the rules surrounding social consumption lounges. For example, what will the laws around consumption lounges look like? How will business mitigate the myriad of risks? From an insurance perspective, will there be a need for new products? Should coverages be similar to Bar/Restaurant/Lounge insurance (DRAM Insurance), as both types of businesses face similar risks?
They will also need to carefully address questions and concerns about public health implications. Could public consumption spaces cause people to over-consume? Will there be limits on how much cannabis a person is allowed to consume at a lounge in one visit? What is a “single serving” of cannabis anyway? These are all questions surfacing to the top.
Many see the potential benefits of licensed social consumption lounges as ways to curb the illicit market, regulate public consumption, ensure consumption in a safe space and bolster the economy. A “Designated Consumption Establishment License” is particularly attractive to entrepreneurs looking to enter the cannabis market, but aren’t interested in growing, processing, or operating a traditional dispensary. Furthermore, cannabis consumption lounges are particularly attractive for their potential to attract tourism dollars. The masses of tourists buying cannabis products in states that have legalized recreational marijuana have nowhere to smoke it legally — not on the sidewalk and not in their hotel rooms.
What Lies Ahead?
In order for the cannabis industry to continue to thrive and expand, new retail models must be considered. We believe it is highly likely that social consumption lounges will become increasingly common, especially in major U.S. cities with legal adult-use cannabis programs.
If you’re thinking about opening a cannabis consumption lounge, it’s important to stay on top of your state’s specific laws since they do vary from state to state and are likely to change and evolve. It’s equally important to make sure you have the right insurance policies in place. Many insurance companies have exclusions in their policies that prohibit onsite consumption, meaning your lounge would not be covered if an unexpected event like a theft, fire, data breach, product defect, accident, or any other type of lawsuit occurs. It’s important to examine your current policies and make adjustments, if necessary. It all boils down to the THREE P’s: being “Proactive, Prepared and Protected.”
 Eric Rahn, Managing Director of S2S Insurance Specialists, is a highly specialized insurance broker and risk management professional with over 30 years of experience providing C-Suite executives strategies and solutions that protect and safeguard their businesses.
Eric Rahn, Managing Director of S2S Insurance Specialists, is a highly specialized insurance broker and risk management professional with over 30 years of experience providing C-Suite executives strategies and solutions that protect and safeguard their businesses.
A graduate of Babson College School of Entrepreneurial Studies, Eric has held several executive positions in the maritime and casino/gaming industries, including CEO of the largest privately own casino concessions company operating on cruise ships around the world. Eric transitioned his knowledge of corporate business practices in highly regulated industries into the burgeoning cannabis space, establishing S2S Insurance Specialists in 2017.
Eric has served on the National Cannabis Industry Association’s (NCIA) Risk Management Insurance Committee since 2016. He is also a national speaker on cannabis insurance and author of NCIA’s Risk Management and Insurance’s “Introduction into Cannabis Insurance.”

 Joshua Gilstrap is the Marketing Manager for e2b teknologies, in addition to his marketing responsibilities Joshua leads business development for e2b teknologies emerging Canna Suite product line. A business graduate with a focus in marketing from Miami University in Oxford, Ohio, he joined the e2b team in the Fall of 2019. Josh brought with him a wide array of business and practical experience in planning and execution. Since coming aboard he has led multiple project’s including website hosting and theme standardization company wide, marketing automation streamlining the efficiency of the customer journey, and sales automation where he is changing the conversation from promotion to education, from pitching to catching, and from push to pull in order to keep up with the shifting tides of a digital transformation.
Joshua Gilstrap is the Marketing Manager for e2b teknologies, in addition to his marketing responsibilities Joshua leads business development for e2b teknologies emerging Canna Suite product line. A business graduate with a focus in marketing from Miami University in Oxford, Ohio, he joined the e2b team in the Fall of 2019. Josh brought with him a wide array of business and practical experience in planning and execution. Since coming aboard he has led multiple project’s including website hosting and theme standardization company wide, marketing automation streamlining the efficiency of the customer journey, and sales automation where he is changing the conversation from promotion to education, from pitching to catching, and from push to pull in order to keep up with the shifting tides of a digital transformation.

 LaKia Bourne has 20+ years of experience as an accomplished and trusted accounting professional. As a women-owned and minority-owned accounting firm, LaKia has a passion for working with other small businesses and engaging in the local community, and her values drive her overall career goals and mission to uplift businesses and encourage financial competency through reliable accounting services.
LaKia Bourne has 20+ years of experience as an accomplished and trusted accounting professional. As a women-owned and minority-owned accounting firm, LaKia has a passion for working with other small businesses and engaging in the local community, and her values drive her overall career goals and mission to uplift businesses and encourage financial competency through reliable accounting services.






 Gary Cohen is the CEO of
Gary Cohen is the CEO of 
 Andrew Halbert is a member of the National Cannabis Law Practice at
Andrew Halbert is a member of the National Cannabis Law Practice at 
 Bethany Niebauer is the CEO and Founder of
Bethany Niebauer is the CEO and Founder of 
 by NCIA’s Risk Management and Insurance Committee
by NCIA’s Risk Management and Insurance Committee



 by Mark Slaugh,
by Mark Slaugh, 

 Steve Ardagh, “The Glove Guy,” is the founder and CEO of
Steve Ardagh, “The Glove Guy,” is the founder and CEO of 
 NCIA’s editorial department continues the Member Spotlight series by highlighting our
NCIA’s editorial department continues the Member Spotlight series by highlighting our  I am
I am  PUFF COUTURE LLC is a minority-woman-owned cannabis company slated to open a microbusiness and consumption lounge in Detroit. We want to bring a sophisticated community-driven cannabis business that offers a contemporary atmosphere for clients. It will convey the importance of the cannabis flower by providing a chilled environment for clients to consume unique, flavorful, and aromatic cannabis. PUFF COUTURE will support mental health counseling, volunteerism, public policy, and minority representation in the cannabis industry, especially among women. According to a recent special report by
PUFF COUTURE LLC is a minority-woman-owned cannabis company slated to open a microbusiness and consumption lounge in Detroit. We want to bring a sophisticated community-driven cannabis business that offers a contemporary atmosphere for clients. It will convey the importance of the cannabis flower by providing a chilled environment for clients to consume unique, flavorful, and aromatic cannabis. PUFF COUTURE will support mental health counseling, volunteerism, public policy, and minority representation in the cannabis industry, especially among women. According to a recent special report by 


 Patrick D. Isbill, Esq.
Patrick D. Isbill, Esq.
 Jennifer Spanos is the VP of Product and Vertical Strategy at
Jennifer Spanos is the VP of Product and Vertical Strategy at 



 Gisela Leon brings in over 33 years of experience in international labeling. She is well-experienced in USA labeling requirements of food, dietary supplements and cosmetics, in European food laws and multi-language labeling. As a regulatory consultant, she focuses on a concise review process, having reviewed hundreds of labels for U.S. compliance and helped international products to come into compliance with U.S. regulations. Her international labeling background allows her to point out differences or similarities with other countries.
Gisela Leon brings in over 33 years of experience in international labeling. She is well-experienced in USA labeling requirements of food, dietary supplements and cosmetics, in European food laws and multi-language labeling. As a regulatory consultant, she focuses on a concise review process, having reviewed hundreds of labels for U.S. compliance and helped international products to come into compliance with U.S. regulations. Her international labeling background allows her to point out differences or similarities with other countries.

 Jack Naito is President of Luna Technologies, where he oversees operations, strategic growth, and R&D for the company he co-founded in 2016. Jack entered the cannabis industry after time spent as a Materials, Process, and Physics Engineer for aerospace giant Boeing. Jack obtained an Economics and Business degree from Colorado College and a Master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Washington.
Jack Naito is President of Luna Technologies, where he oversees operations, strategic growth, and R&D for the company he co-founded in 2016. Jack entered the cannabis industry after time spent as a Materials, Process, and Physics Engineer for aerospace giant Boeing. Jack obtained an Economics and Business degree from Colorado College and a Master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Washington.


 Kaveh Newmen is an associate at
Kaveh Newmen is an associate at 
 Morgan Stinson is a social impact manager, leader of the
Morgan Stinson is a social impact manager, leader of the 
 By Ellen Komp,
By Ellen Komp,  Ellen Komp is the Deputy Director of California NORML. Founded in 1972, Cal NORML is a non-profit, member-supported organization dedicated to reforming California’s marijuana laws. As the state chapter of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws, we lobby lawmakers, promote events, publish newsletters, offer legal and consumer health advice, and sponsor scientific research. Check out our website at
Ellen Komp is the Deputy Director of California NORML. Founded in 1972, Cal NORML is a non-profit, member-supported organization dedicated to reforming California’s marijuana laws. As the state chapter of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws, we lobby lawmakers, promote events, publish newsletters, offer legal and consumer health advice, and sponsor scientific research. Check out our website at  Author Tommy Truong is the Director of Partnerships at
Author Tommy Truong is the Director of Partnerships at 
 I grew up in Connecticut in the 70s and was repeatedly reminded of the cannabis stigmas, witnessing others partake in regular consumption, yet never noted any of the proclaimed stigmas; in fact, it appeared the exact opposite.
I grew up in Connecticut in the 70s and was repeatedly reminded of the cannabis stigmas, witnessing others partake in regular consumption, yet never noted any of the proclaimed stigmas; in fact, it appeared the exact opposite.
 Unfortunately, being an African American woman in this industry is a challenge. My personal experience with the plant, professional education, and long-standing career in preventative
Unfortunately, being an African American woman in this industry is a challenge. My personal experience with the plant, professional education, and long-standing career in preventative 
 Eric Rahn, Managing Director of
Eric Rahn, Managing Director of