Video: NCIA Today – Thursday, April 20, 2023

It’s the 4/20 Cannabis Industry Update!
Join NCIA Director of Communication Bethany Moore for an update on what’s going on with NCIA and our members.

It’s the 4/20 Cannabis Industry Update!
Join NCIA Director of Communication Bethany Moore for an update on what’s going on with NCIA and our members.

 by Sevana Janian, Green Plus CPA
by Sevana Janian, Green Plus CPA
Member of NCIA’s Cannabis Cultivation Committee
Managing finances and complying with complex regulations in the highly regulated cannabis market can be challenging for business owners. For this reason, it’s crucial to have a competent cannabis accountant. In this article, we will discuss four major reasons why a good accountant is essential in the cannabis market, grouped into distinct categories.
Having specialized professionals, such as a cannabis accountant, can bring a wealth of knowledge and expertise to your business. They understand the unique challenges and regulations associated with the cannabis industry and can provide guidance and support to help you make informed decisions and navigate potential risks. By leveraging their expertise, you can ensure the success and stability of your business in this rapidly evolving industry.
Accountant who has experience working in volatile and new industries is well-equipped to handle the risks that come with operating in such environments. By regularly identifying and measuring these risks, the accountant can help mitigate them and ensure the stability and success of a business.
At the early stages of starting a business, it’s critical to bring on board a competent cannabis accountant and attorney. Don’t let the simplicity of creating an entity mislead you into missing out on getting proper counsel on the appropriate entity type. Stay attentive to accounting and legal concerns and make informed decisions. If the chosen entity type does not align with your business goals, a knowledgeable cannabis accountant will discuss the potential consequences of each option. This will enable you to make an informed decision.
Given the ongoing discourse surrounding entity type and its status as a commonly asked question, I deemed it worthwhile to introduce this information. It should be noted that a Limited Liability Company (LLC) is not officially classified as a tax entity by the IRS. The taxation of an LLC can vary and may be classified as a single-member LLC, a corporation, or a partnership.
One of the biggest risks in the cannabis industry is the risk of failure and the accumulation of a large tax debt. The cannabis industry is heavily regulated and taxed, which can present significant financial challenges for businesses operating in this field. In order to mitigate this risk, it is important for cannabis businesses to have a strong understanding of the tax laws and regulations applicable to their operations, and to have a robust system in place for tracking and reporting their financial transactions. Working with a knowledgeable and experienced cannabis accountant can help ensure that tax laws are applied correctly and that businesses stay in compliance with the regulations, reducing the risk of financial failure and tax debt. The establishment and enhancement of robust internal controls, coupled with diligent monitoring, can also significantly contribute to mitigating potential risks as well.
It is noteworthy that individuals who own cannabis businesses are known for taking risks. As a result, it is essential to have accountants and attorneys who are skilled in evaluating and reducing these risks. Selecting your advisory team carefully is of utmost importance.
It is necessary for the business owner and accountant to have a clear and transparent understanding of each other’s needs and goals, in order to create a win-win situation. The highly regulated and complex cannabis market can be challenging, and having an accountant who is passionate and aligned with the business owner’s mission and vision can help smooth the business cycle and avoid conflicts. An accountant’s mission is to help their clients manage their financial resources effectively and efficiently. This involves tracking the financial performance of the business, providing advice on financial decisions, and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. In order to carry out this mission effectively, an accountant needs to have a deep understanding of the business owner’s goals, objectives, and overall strategy.
When a cannabis accountant’s mission is aligned with a business owner’s, they can work together to achieve common goals. This alignment helps the accountant understand the business owner’s financial needs, which enables them to provide more targeted advice and recommendations. It also helps the business owner understand the importance of financial management and how it can contribute to the success of their business. It also helps the business owner feel more confident in their accountant’s advice and recommendations, which can lead to collaborative and effective working relationships and more successful outcomes.
The cannabis industry is new and constantly evolving, and it is important to have an accountant who is trained and up-to-date with the latest developments. Many CPA firms are now specializing in the cannabis industry, giving business owners more options to choose from. A cannabis accountant should be familiar with 280E of the Internal Revenue Code, which can be a monster in terms of tax for the industry. They should also have knowledge of cost accounting and inventory management, which are crucial for producing accurate financial statements. Cannabis accountants with a background in manufacturing industry can bring their expertise to the industry and be of even greater value.
The use of the word “trained” is intentional in highlighting the fact that the cannabis industry is new and constantly evolving. Even though accounting firms with decades of experience are doing their best, when they have a high volume of clients, they may not be able to provide timely service and may lack time for innovation and data analysis. There are many cannabis think-tank groups and programs that can give trained accountants the same advantages, or even more, as experienced ones, as technology has revolutionized all industries, including accounting.
A knowledgeable cannabis accountant should be able to provide financial statements and analyze them to help the business understand its financial position and take actionable steps towards its goals. They should be able to simplify complex financial analysis and provide key performance indicators and ratios that can help the business stay on track. They also have the responsibility of managing cash flow, which is key for the success of any business, especially in a competitive market. Many businesses fail because they run out of cash, not profit.
An insightful analysis takes the information one step further and presents the data in context in a way that identifies the necessary actions to be taken to maintain or improve the organization’s operations. Reports that allow managers to do their jobs better and make better decisions will be highly valued.
In a competitive market, the role of accountants and CFOs becomes increasingly important.
Ultimately, conducting business is a spiritual pursuit that involves the right mindset, effective communication, and teamwork. A business will flourish and make a positive impact if it brings together a team with a strong cultural alignment and a growth mindset.
We have great respect for those who work in the cannabis industry, as they often put their lives or licenses on the line. Let us strive for greater compliance and work towards creating a better world for all.
 Sevana Janian is a Certified Public Accountant in California with more than 17 years of experience in tax and accounting. She is a member of the Cultivation Committee of the National Cannabis Industry Association (NCIA) for the year 2023. She is also a member of AICPA and CalCPA organizations. Sevana enjoys traveling with her family and playing the piano during her leisure time. She is committed to networking with others to expand her personal and professional knowledge. Sevana is passionate about inspiring and motivating the younger generation to succeed.
Sevana Janian is a Certified Public Accountant in California with more than 17 years of experience in tax and accounting. She is a member of the Cultivation Committee of the National Cannabis Industry Association (NCIA) for the year 2023. She is also a member of AICPA and CalCPA organizations. Sevana enjoys traveling with her family and playing the piano during her leisure time. She is committed to networking with others to expand her personal and professional knowledge. Sevana is passionate about inspiring and motivating the younger generation to succeed.
Green Plus CPA aims to offer a world-class automated tax and accounting solution nationwide for CEOs and business owners in the cannabis industry who seek accurate financial statements. Established in 2022, we are deeply interested in the medicinal properties of the cannabis plant and firmly believe in its potential to heal. We are enthusiastic about supporting and serving this industry that has been overlooked.

By Nolan Shutler, Director and State and Local Tax Practice Leader, MGO CPA
Operators and investors have long suspected that the IRS targets cannabis businesses for tax audits. And after last year’s disclosures from the agency (requested and published by MJBizDaily) we now know the reason is relatively simple: the IRS gets back 2X or more per hour of audit examination when compared to mainstream industries.
Now, with the Inflation Reduction Act’s infusion of $80 billion in funding over the next 10 years to ramp up enforcement activities, the IRS’ focus on cannabis companies is likely to intensify. Even if Federal legalization and/or descheduling of cannabis occurs, current and prior year’s returns will still be subject to IRC 280E, and the problems causing the high assessments aren’t going to go away overnight. Therefore, cannabis operators and investors are wise to level-up their tax compliance capabilities.
In this article, MGO CPA, lists out the stages of an IRS audit and provides key things to think about.
There is a lot you can do before you get audited that will ease the process and help you arrive at a desirable conclusion. The good news is that “audit preparation” is really just implementing accounting and documentation best practices that will prove useful to the efficient administration of your business – even if you never get audited.
When you get the dreaded letter from the IRS the most important thing is not to panic! You’ll want to respond immediately and get your organization on track to meet the IRS’ requests.
Once the audit begins in earnest, be as responsive and collaborative as possible. Establishing rapport and demonstrating “good faith” intention are essential to securing an optimal conclusion to the audit.
As the audit proceeds your cannabis accountant and/or lawyer will have a good idea about the likely outcome. Stay in regular communication and be collaborative to ensure “good faith” consideration.
If the audit is completed and you feel the outcome is unmanageable or unfair, you may engage the appeals or tax court process.
In the end, both you and the IRS are seeking a quick end to the audit process. By being up-front and collaborative you can save yourself a lot of wasted time (read: fees, penalties, and interest) and heartache. Being adversarial or pursuing frivolous or unsubstantiated arguments will just make your path more difficult.
As the cannabis industry evolves, and compliance functions become more sophisticated, hopefully, the IRS’ assessments and interest will wane. But in the meantime, remember that the IRS can still audit 2019 tax returns for another year (or longer, under certain circumstances). There may be significant risk tied up in an audit of those prior years (especially if you recently acquired the business). We highly recommend working with a dedicated cannabis accountant to proactively implement best practices retroactively and going-forward that will help you avoid getting audited in the first place. But in the unfortunate event of an audit, those same efforts will be helpful in securing an optimal outcome.
To see a more detailed, step-by-step approach to navigating an audit, download the MGO Cannabis IRS Audit Survival Guide.
 Nolan Shutler, JD, is a director in MGO’s tax group focusing on tax controversy representation and general state and local tax (SALT) consulting. He also has experience in indirect tax, tax planning, corporate tax compliance, and real estate transactions for public, private, and closely held businesses. Nolan has the ability to leverage tax and business management acumen to understand and forge paths to optimal outcomes.
Nolan Shutler, JD, is a director in MGO’s tax group focusing on tax controversy representation and general state and local tax (SALT) consulting. He also has experience in indirect tax, tax planning, corporate tax compliance, and real estate transactions for public, private, and closely held businesses. Nolan has the ability to leverage tax and business management acumen to understand and forge paths to optimal outcomes.
MGO has a dedicated cannabis accounting, audit, tax, and business advisory practice built to help cannabis operations survive and thrive in a competitive marketplace.
We help cannabis organizations of all sizes — from multi-state operators to pre-revenue startups — in every vertical and every market, establish optimal accounting processes, manage tax and regulatory compliance, perform audits to raise capital or engage in M&A, and everything else an operator needs to succeed.

The discussion about the future of cannabis legalization is ongoing, to say the least. Recently, Cannabis Regulators Association (CANNRA) held a two-day conference in early June to gather Marijuana government regulators, trade associations, and businesses. The Cannabis Regulators Association (CANNRA) is a national nonpartisan organization of government cannabis regulators that provides policymakers and regulatory agencies with the resources to make informed decisions when considering whether and how to legalize and regulate cannabis.
Representatives from NCIA participated in the conference – NCIA Board Members Khurshid Khoja (Chair Emeritus) and Michael Cooper (Board Secretary), and we caught up with them in this blog interview to better understand the goals and outcomes of the event.
 MC: The conference was an opportunity for regulators from around the nation to hear directly from stakeholders on the current and future challenges that face these markets and different models of regulation to tackle them.
MC: The conference was an opportunity for regulators from around the nation to hear directly from stakeholders on the current and future challenges that face these markets and different models of regulation to tackle them.
KK: I’ll add that our own goals, as the current Policy Co-chairs for NCIA, were to better understand the priorities of state and local cannabis regulators across the country, and anticipate future developments in cannabis policy early on, so we could take that back to the NCIA membership and the staff – especially Michelle Rutter Friberg, Mike Correia, and Maddy Grant from our amazing government relations team.

KK: Michael and I each spoke on a panel. The other speakers included reps from federal trade associations, lobbyists, vendors, and ancillary companies who were helping to underwrite the event (along with NCIA). Given that CANNRA is a non-profit that doesn’t receive any funding from their member jurisdictions, and has a single paid full-time staff member, I thought they were still able to obtain a fairly diverse and interesting set of speakers at the end of the day – including NCIA Board and Committee alums Ean Seeb, Steve DeAngelo, Amber Senter and David Vaillencourt (representing the Colorado Governor’s Office, LPP, Supernova Women and ASTM, respectively), as well as folks from Code for America, Americans for Safe Access, and the Minority Cannabis Business Association, U.S. Pharmacopeia, NIDA, the CDC, and the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, representatives of the pharmaceutical, hemp, tobacco and logistics industries, and public health officials.
MC: No licensed businesses were invited. Instead, organizations that represent industry members were invited. As a result, we felt it was crucial to inform these discussions with the perspective of the multitude of small and medium-sized businesses otherwise known as Main Street Cannabis that have built this industry and continue to serve as its engine.
KK: Sadly, we did not have an opportunity to hear from members of the Coalition of Cannabis Regulators of Color. I can’t speak to why that was, but it was unfortunate for us nonetheless. And while we had some public health officials there, I know that CANNRA Executive Director Dr. Schauer would have preferred to see more of them in attendance.
KK: We covered a ton, given the time we had, including the federal political and policy landscape; interstate commerce; the impact of taxes on the success of the regulated market; social equity and social justice; preventing youth access; regulation of novel, intoxicating and hemp-based cannabinoids; the prospects for uniform state regulations; technological solutions to improve compliance and regulatory oversight; and delivery models.

MC: There really are a wide variety of perspectives on how best to regulate this industry. We felt it was essential that NCIA give a voice to Main Street Cannabis, the small businesses that so many adult-use consumers and medical patients rely upon. We emphasized, for example, that these are often businesses that cannot simply operate in the red indefinitely, but provide essential diversity (in the background and life experience of operators as well as in product selection and choice). NCIA wants to make sure that the future of cannabis isn’t simply the McDonalds and Burger Kings of cannabis. There are times when consumers want that, but there are also times when they want something unique and different. And it’s crucial that policy not destroy the small and medium-sized, frequently social equity-owned, businesses that provide those choices.
MC: There are a ton of different perspectives and approaches to cannabis, and that’s no surprise to anyone who has followed these issues closely because the tensions are very clear in the policy debates that are ongoing.
As the voice for the industry, we sought to urge an approach grounded in reality. Americans want these products. That’s clear from the ballot box and public polling. The question should be about how to encourage Americans to purchase regulated, tested versions of these products.
KK: There was definitely stuff we didn’t agree with – some of it from folks that we otherwise largely agree with. For example, our good friend Steve Hawkins of the USCC shocked a few of us in the audience when he seemed to indicate some receptivity to re-scheduling cannabis on an interim basis, rather than moving to de-scheduling immediately. I think that while rescheduling may benefit scientific research and pharmaceutical development, it could ring the death knell for Main Street Cannabis businesses. NCIA has consistently advocated for de-scheduling rather than re-scheduling.
KK: I think there’s a growing recognition that addressing social equity solely through preferential licensing and business ownership for the few isn’t enough and that the licensing agencies and regulators that execute social equity policies have a very limited (and often underfunded) arsenal to comprehensively redress the harm caused by federal, state and local governments prosecuting the war on drugs. In my remarks, I said it was time for us to start discussing additional forms of targeted reparation and had a number of regulators approach me afterward to continue the discussion. Candidly, I expected my remarks to fall on deaf ears. They didn’t. That was very encouraging.
MC: There was definite progress. At the end of the day, these cannabis regulators are working hard to try to get this right. But in such a new area, and with so many competing perspectives and voices, their job isn’t easy. We were heartened to see the level of engagement from regulators on these points, including follow-ups to get more information on some of the pain points we identified for small and equity businesses in the industry.
It was definitely rewarding to provide NCIA and our members’ perspectives in a forum like this, and we’re looking forward to continuing to further strengthen NCIA’s relationship with CANNRA and regulators around the country.

 by Aaron Smith, NCIA’s CEO and Co-founder
by Aaron Smith, NCIA’s CEO and Co-founder
History was made today as Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-NY) along with Senators Ron Wyden (D-OR) and Cory Booker (D-NJ) introduced the Cannabis Administration and Opportunity Act which would finally remove cannabis from the federal Controlled Substances Act and begin the process of federal regulation.
For the last year, NCIA has been working behind the scenes to ensure this landmark legislation not only ends prohibition but also creates an environment where small and medium-sized businesses can thrive under national legalization. These businesses – who we now call “Main Street Cannabis” – are the heart of our industry and we’re proud to have been giving them a seat at the table in our nation’s halls of power for over 12 years.
We will continue working with our allies in the Senate to advance this bill and advocate for some necessary amendments to better ensure that small, equity, and women-owned businesses (in particular) are well-positioned to thrive after the end of federal prohibition.
We would not be where we are today if not for your support which has allowed us to effectively represent the interests of small businesses like yours in the halls of Congress and in the court of national public opinion.
I hope you’ll join us in making national legalization a reality by making your voice heard at our upcoming 10th Annual Cannabis Industry Lobby Days in Washington, D.C. September 13 & 14!
Thanks to your membership, NCIA’s government relations staff represents Main Street Cannabis in D.C. every day but Lobby Days is your chance to show up and tell your unique story to our nation’s lawmakers, firsthand.
Lobby Days is also the best opportunity to connect with your fellow industry leaders who are truly invested in the future of cannabis and sensible national policy. Please register today so you don’t miss out on making history with us! Reach out to my colleague Madeline Grant to learn more about how you can be as impactful as possible at this year’s Lobby Days.
Thanks, as always, to all NCIA members for their support of the cannabis industry. If your company is not yet a member of NCIA, now’s the time to join and have your voice heard in the halls of Congress.
Watch this video update with Aaron Smith and Michelle Rutter Friberg:

 By Sadaf Naushad, NCIA Intern
By Sadaf Naushad, NCIA Intern
As the cannabis industry progresses nationwide, the public demands Congress to pass major cannabis reforms. After months of opposition met among Congress members, a breath of fresh air awaits cannabis advocates, lobbyists, and consumers.
Last Thursday, two crucial congressmen revealed objectives to establish an extensive package of incremental cannabis proposals.
While Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-NY) expects to file the final version of the Cannabis Administration and Opportunity Act (CAOA) sometime this summer, lawmakers are using the draft language as a guide to propose an alternative backup bill in creating a cannabis “omnibus” package.
With the wide-ranging package garnering support across Democratic and Republican lawmakers, industry insiders have high hopes that both chambers could come together to endorse an effective, bipartisan bill by the end of this year.
Recently, a number of Congress members have discussed the possibility of creating a new cannabis bill that would comprise several incremental measures, including provisions focusing on banking, access to medical cannabis for veterans, research expansion, access to SBA programs, drug sentencing reformations, and more.
Lead sponsor of the Secure and Fair Enforcement (SAFE) Banking Act, Rep. Ed Perlmutter (D-CO) is hoping to incorporate protection for financial institutions operating with state-legal cannabis businesses in a potential package. According to Rep. Perlmutter, members also have interest in including Rep. Dave Joyce’s (R-OH) Harnessing Opportunities by Pursuing Expungement (HOPE) Act, a bill designed to expunge prior marijuana convictions. Additionally, lawmakers are deliberating over granting cannabis businesses access to SBA loans and services that are obtainable to every other industry, a reform initially advocated by Sen. Jacky Rosen (D-NV).
These four concerns –- veterans, research, expungements, and banking – constitute a small portion of the package’s considerations.
Congress will also potentially consider including a non-cannabis item as part of the wider deal, known as the EQUAL Act, which looks to alleviate racial disparities within the criminal justice system by eliminating the federal sentencing disparity between crack and powder cocaine.
Leader Schumer, however, faces the requirement of having a 60-vote threshold to pass legislation. Although the chamber comprises a slim majority of Democrats with the vast majority of GOP members opposing numerous past bills, the 60-vote requirement may be attainable. In contrast to Schumer’s CAOA, indications are that the incremental package has more broad bipartisan support.
Though members have not reached an official deal as these major reforms remain under deliberation, Congress members are not abandoning their efforts to push for a broader-based CAOA bill.
Currently in the bicameral conference committee remains the large-scale manufacturing bill, known as the America COMPETES Act. Leader Schumer has rejected attempts to integrate the SAFE Banking Act as currently written into the COMPETES Act, alleging that it may weaken the ability to approve a slightly larger cannabis reform package. Having passed the House six times, industry insiders feel certain that the Senate will authorize the SAFE Banking Act later this year.
Altogether, the above-mentioned legislation would come up short in federally descheduling cannabis; however, these provisions may acquire the support necessary to reach U.S. President Biden’s desk.

by Jennifer Spanos, CannaBusiness ERP
As we approach the end of Q1 2022 and prepare to enter Q2, it’s become clear that this is going to be an important year for the cannabis industry. Cannabis business professionals and investors looking for signs of growth or stagnation in the industry will certainly be interested to see how things unfold. With that in mind, CannaBusiness ERP has put together a list of the top cannabis trends for 2022, and those trends appear to be pointing to more growth. However, it’s clear that difficulties for the cannabis sector are still imminent.
It almost goes without saying that the cannabis industry is complex and not without its fair share of challenges as the most highly regulated industry on the market. For businesses looking to grow, keeping up with complicated and evolving regulations can be stressful enough on a business in and of itself. Cannabis cultivators, processors, and consultants can look to cannabis industry trends to inform their operational decisions.
Support for legalization in the USA continues to rise. In fact, a 2021 Gallup poll found that 68% of Americans are in favor of legalizing cannabis. Not only is this a record number of supporters, but this percentage also reflects a growing sentiment among Americans regarding the use of legal cannabis.
The changing tide towards legalization is clear – more states passed legislation to legalize cannabis either medicinally or recreationally in 2021, with several more introducing legalization bills in 2022. Because states operate independently of each other, every state will have its own policies as well as regulatory and compliance requirements, which can make things very confusing for cannabis businesses, especially multi-state operators (MSOs).
The National Cannabis Industry Association (NCIA) provides a map with state-by-state policies, which is one helpful tool for businesses looking to capitalize on expansion opportunities made possible as more states legalize cannabis. CannaBusiness ERP’s Guide to Expanding Into New Markets is another great resource for MSOs that provides state-by-state information, including Nevada, New York and Pennsylvania, and useful advice to consider when expanding into new cannabis markets.
Leading cannabis business experts are predicting strong sales growth this year due to the growth in legalized markets for cannabis. In fact, legal cannabis sales reached $19.5 billion in 2020, and experts are projecting sales to reach $30 billion in 2022. Washington State alone, which legalized cannabis ten years ago in 2012, is expected to generate $1.5 billion in sales, up from $1.2 billion sales in 2020. But Washington’s projected sales are small when you compare them to California’s projected sales of $7.6 billion. And as more states legalize cannabis, more sales will surely follow.
Another contributing factor to increased cannabis sales is related to increased demand and a growing number of product types. More consumers are learning why cannabis can be beneficial to them, including more restful sleep, lowering stress, lessening pain symptoms, and recreational use. Additionally, with so many products on the market, cannabis consumers have many options to choose from, ranging from edibles to tinctures to topical ointments and more.
Cannabis experts are predicting a growth in cannabis consumption lounges – the cannabis equivalent of a bar or restaurant that allows consumers to use cannabis on-site. According to the Cannabis Industry Journal, the popularity of these lounges is growing because they provide consumers with a legal and safe space to consume cannabis. Just as with alcohol, the lounges are regulated according to laws set by each state.
Increasing sales means cannabis businesses are at a critical junction and need to scale operations to meet the growing demand. One way cannabis growers and processors can capitalize on the demand is by streamlining the business end-to-end with cloud-based cannabis business management software. Otherwise known as Cannabis Cloud ERP, it manages production, cultivation, compliance, inventory, financials and traceability, sales, purchasing, and more, all in one system that lives in the Cloud.
Under U.S. Federal Law in the Controlled Substances Act, cannabis is still considered a Schedule I substance. However, as the number of states legalizing cannabis either recreationally, medicinally or both has increased, so too has broader support for federalization in the U.S. government. In fact, there are several bills in the U.S. congressional houses that may positively impact the cannabis industry, especially with banking challenges.
Due to the Schedule I federal classification of cannabis, many banks will not work with cannabis companies, creating tedious banking hurdles that are difficult to solve. The National Law Review writes, “Yet, in comparison to other industries, legitimate licensed cannabis-related businesses remain hobbled by the difficulties they face in accessing traditional banking and financial services – largely due to the fact that ‘marijuana’ is still considered illegal on the federal level under the Controlled Substances Act (“CSA”). Currently, financial institutions (including federally insured banks) are hesitant, and oftentimes unwilling, to work with cannabis-related businesses due to fear of reprisal from federal banking regulators.”
Congressional representatives have introduced a decent amount of bills geared towards making much-needed changes to banking processes for cannabis, such as the SAFE Banking Act of 2021, passed by the U.S. House of Representatives in April 2021. It is currently awaiting action in the U.S. Senate with broad support from both sides of the aisle. If it passes both chambers of Congress, the act will allow cannabis companies to have business-critical access to banking and financial services and would reduce their need to operate as cash-only businesses and remove yearly challenges with tax accounting and reconciliation.
In addition to the SAFE Banking Act, there are other bills like U.S. Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer’s Cannabis Administration and Opportunity Act (CAOA), which is a push for federal cannabis legalization as well as an equity play. If passed, it is a measure towards ensuring small businesses and minority-owned businesses have access to financial services.
However, even with the tide of public opinion and legal momentum shifting in the industry’s favor, there remains a challenge with the U.S. tax code. Due to IRS Code Section 280E, if a business is trafficking certain controlled substances, like cannabis, that business is unable to deduct business expenses on their taxes. California has taken steps to address this by signing bills that help cannabis businesses overcome this code, but this is still a prohibitive factor for cannabis companies across the U.S.
Fortunately, cannabis companies that invest in a comprehensive Cannabis Cloud ERP solution with a reputable and experienced industry partner are better able to handle any hurdles that come their way.
Merger and Acquisition (M&A) activity has been steady in the industry and 2022 will see even more M&A activity. According to MJBizDaily’s article, “Marijuana M&A sizzled in 2021 and is poised for a hot 2022. Marijuana merger and acquisition activity proceeded at a torrid pace in 2021 – and could accelerate in 2022 – thanks to lower interest costs and pressure on larger companies to expand their footprints and boost revenue.”
Citing prominent cannabis acquisitions in 2021, such as Jazz Pharmaceuticals’ acquisition of GW Pharma (for $7.2 billion) and Trulieve’s acquisition of Harvest Health (for $2.1 billion), it is apparent that M&A is not going to slow down. According to Business of Cannabis, several deals are already taking place in 2022. Massachusetts-based Curaleaf acquired Arizona-based Bloom Dispensaries for $211 million, adding a total of 13 Arizona dispensaries and 121 dispensaries nationwide to Curaleaf’s portfolio.
For cannabis companies dealing in M&As and becoming Multi-state Operators (MSOs), it is essential to have a comprehensive, full-suite Cannabis Cloud ERP system that can run all the companies in one system. It is a crucial ingredient to manage their M&A transactions and handle their financial statements, compliance, business transactions, and more.
Most important of all, cannabis companies need to choose the right cannabis ERP.
 Jennifer Spanos is the VP of Product and Vertical Strategy at CannaBusiness ERP. She has 14+ years of experience in cannabis and food manufacturing software and operations, working to maximize the efficiency and profitability of customers’ businesses.
Jennifer Spanos is the VP of Product and Vertical Strategy at CannaBusiness ERP. She has 14+ years of experience in cannabis and food manufacturing software and operations, working to maximize the efficiency and profitability of customers’ businesses.
CannaBusiness ERP: The Right Cannabis Business Management Software. Cannabis companies can grow their business with an ERP solution designed for the cannabis industry and for MSOs expanding into new markets. Learn how CannaBusiness ERP can set businesses on the right path. Manage financials, operations, quality, compliance, traceability, customers and more.
CannaBusiness ERP is cannabis business management software that is built-in Sage X3 and configured by NexTec industry experts to deliver a complete cannabis business solution. Our specialization in developing solutions for the cannabis cultivation and processing industry has resulted in some of the most respected companies around the world managing their day-to-day operation using CannaBusiness ERP.
To learn more about the fast-paced movement in cannabis legalization and how Cannabis Cloud ERP software can help your company keep pace, reach out to us. We’d love to show you what CannaBusiness ERP can do for your business.
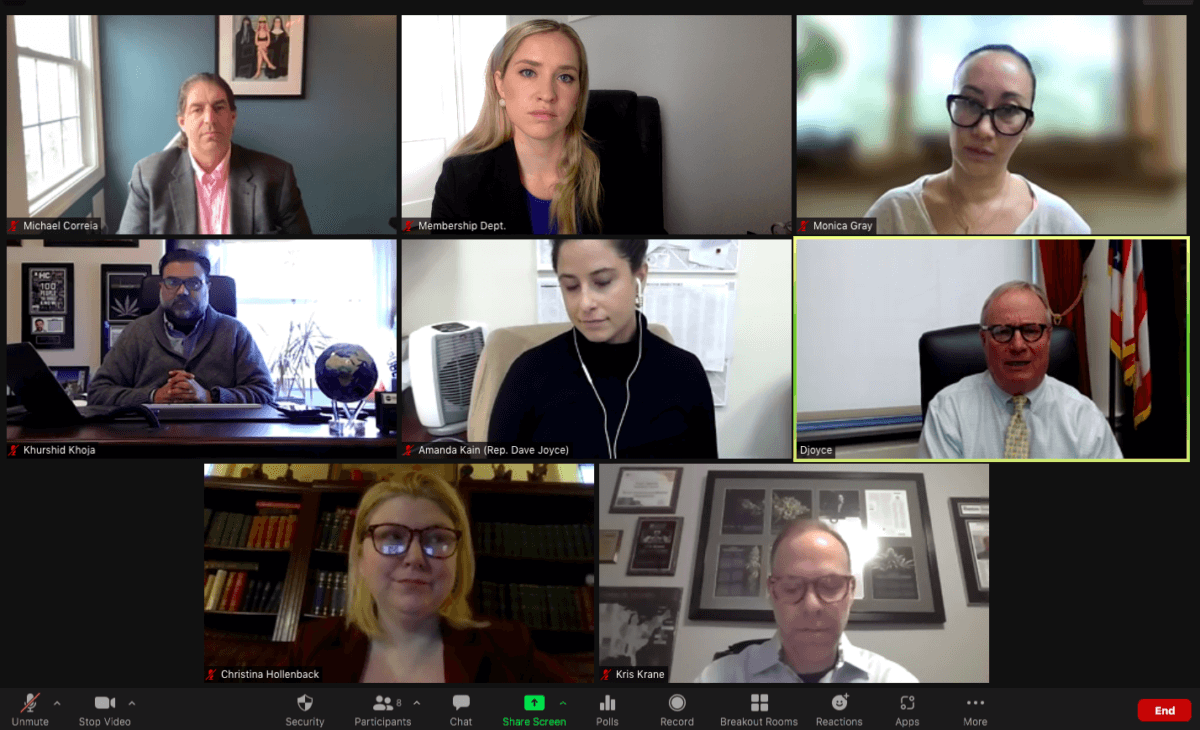
 by Madeline Grant, NCIA’s Government Relations Manager
by Madeline Grant, NCIA’s Government Relations Manager
The National Cannabis Industry Association (NCIA) held its very first Virtual Mini Lobby Days with NCIA’s Evergreen Roundtable members. Before the pandemic and closure of our Nation’s Capital, the Government Relations team planned an in-person annual fly-in every spring, the Annual Cannabis Industry Lobby Days, for all NCIA members. For our first Virtual Mini Lobby Days, it was important to facilitate conversations between our Roundtable and Capitol Hill offices. The Evergreen membership tier is for leading businesses looking to make a meaningful investment in shaping policy for the cannabis industry. Evergreen members receive exclusive access to private briefings from members of Congress, inside information from NCIA’s government relations team, and many more opportunities to participate in the national conversation around cannabis policy.
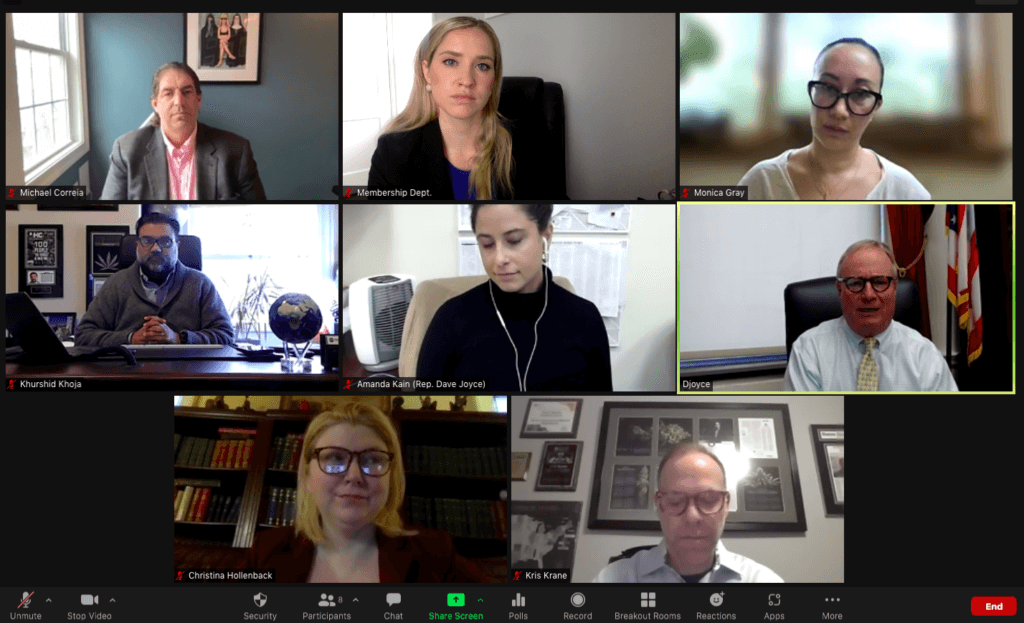
The NCIA team, Monica Gray with Nice Guys Delivery, Khurshid Khoja with Greenbridge Corporate Counsel, and Christina Hollenback with The People’s Ecosystem meeting with Congressman Dave Joyce (OH-14), a co-chair of the Congressional Cannabis Caucus.
As we hopped on our zoom calls, our main focus was education. The Evergreen Roundtable was able to share stories from their personal experiences in the cannabis industry and directly relate these experiences to the importance of cannabis policy reform. The dichotomy around incremental versus comprehensive cannabis policy reform was a central focus in discussion. As around thirty meetings took place throughout the week, the Government Relations team and Evergreen Roundtable caught up with friends, gained valuable insight, and continued to educate Congress. We took this opportunity to show our support and gratitude for all the representatives and senators who constantly support cannabis policy reform. Furthermore, we educated congressional offices with data, testimonials, and research to highlight the necessity for cannabis policy reform at the federal level. There is no doubt that reform is needed for the cannabis community and NCIA will continue to be a resource to all congressional offices.

NCIA’s 9th Annual Cannabis Industry Lobby Days in 2019 May 21-23 2019.
As we monitor the full opening of Capitol Hill, stay tuned for updates regarding NCIA Lobby Days. The Government Relations team is looking forward to our next Mini Lobby Days later this year for all Evergreen members. If you’re interested in learning more or getting involved in our policy work please feel free to reach out to Madeline@TheCannabisIndustry.org.

NCIA’s Evergreen membership is for leading businesses looking to make a meaningful investment in shaping policy for the cannabis industry. This premium membership plan provides your company with a seat on NCIA’s Evergreen Member Roundtable, with exclusive access to private briefings from members of Congress, access to NCIA’s lobbying team, invitations to political events, special membership concierge service, and more.

by Kaveh Newmen of Edlin Gallagher Huie + Blum
The cannabis industry has grown exponentially as an increasing number of states have relaxed state law prohibitions on the use of cannabis for medical and recreational purposes. However, under federal law, cannabis remains classified as a Schedule I controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). This means that the production, distribution, and possession of cannabis remains illegal on the federal level.
Cannabis businesses are treated differently from many other businesses for tax purposes. Under Internal Revenue Code (IRC) §280E (“280E”), which applies to a federal income tax filing, denies deductions and credits for amounts paid or incurred in carrying on the trade or business of cannabis. Cost of goods sold is allowable because it is not considered a deduction, rather it is a reduction of gross receipts (revenue) to arrive at gross profit.
A report published in March 2020 by the U.S. Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration examined California and found that over 50% of marijuana companies had likely underpaid the IRS under IRC§ 280E. The report confirms the IRS is preparing to increase marijuana industry audits nationwide in response.
Currently, the method by which cost of goods sold may be deducted for producers is to use IRC §471(a). This provision discusses how to clearly reflect income by using an inventory method. Therefore, cannabis producers have less of a 280E problem than retailers and distributors.
After the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), effective for tax years beginning January 1, 2018, a provision was passed in the IRC §471(c). There are various opinions with advisors in the industry on whether this code section and method can be used for retailers and distributors. The idea behind IRC 471(c) is that “certain small businesses” can meet the gross receipts test of this subsection for any taxable year in which the corporation’s or partnership’s average annual gross receipts do not exceed $25,000,000 for the 3-taxable-year period ending with the taxable year that precedes such taxable year. Pursuant to IRC §448(c)(1), this type of small business may be able to use a “books and records” method for deducting all costs – rather than being limited to cost of goods sold only. In other words, if one uses 471(c)(1)(B) as an accounting method, in theory, they may also be able to deduct selling expenses and all other costs that were previously not allowed as deductions.
For further discussion on this topic see the following articles: Bloomberg Tax – Cannabis Taxpayers Find Flaws in New Accounting Method Rules and The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: A Comparison for Businesses
Each state in the U.S. is autonomous in that it has the authority to decide whether its income tax laws conform to §280E or not. On October 12, 2019, Governor Newsom signed into law AB 37, which overrides §280E through the following provision:
For each taxable year beginning on or after January 1, 2020, and before January 1, 2025, Section 280E of the Internal Revenue Code, relating to expenditures in connection with the illegal sale of drugs, shall not apply to the carrying on of any trade or business that is commercial cannabis activity by a licensee. – (CAL. REV. & TAX CODE § 17209 (2020). CAL. REV. & TAX CODE § 17209 (2020).
However, AB 37 only applies to state filings with the Franchise Tax Board and is currently only available until January 1, 2025. AB 37 has no impact on federal tax filings, which is where a majority of cannabis entities pay their income taxes with effective tax rates as high as 25% for corporate taxes and up to 37% for individuals.
The IRS has not published nationwide guidance to taxpayers and tax professionals in the cannabis industry. In addition, cash-intensive business issues unique to the cannabis industry such as IRS §280E and banking limitations will remain unresolved unless and until there is uniformity through federal legalization. As a result, compliance-related issues continue to grow and negatively affect cannabis business owners who operate legally under individual state law.
 Kaveh Newmen is an associate at Edlin Gallagher Huie + Blum who handles cannabis law general litigation, and trucking and transportation matters. Kaveh was admitted to practice law by the State Bar of California in 2021. Kaveh earned his J.D. from the University of San Diego School of Law in 2020, where he was a board member of the Criminal Law Society, the Immigration Law Society, the Middle Eastern Law Student Association, and served as an intern at the school’s Immigration Clinic. He is a first-generation Iranian-American and speaks Farsi.
Kaveh Newmen is an associate at Edlin Gallagher Huie + Blum who handles cannabis law general litigation, and trucking and transportation matters. Kaveh was admitted to practice law by the State Bar of California in 2021. Kaveh earned his J.D. from the University of San Diego School of Law in 2020, where he was a board member of the Criminal Law Society, the Immigration Law Society, the Middle Eastern Law Student Association, and served as an intern at the school’s Immigration Clinic. He is a first-generation Iranian-American and speaks Farsi.


By Michelle Rutter Friberg, NCIA’s Deputy Director of Government Relations
Recent polling from Gallup showed that an astonishing 68% of Americans believe that cannabis should be legal. And while support spans age groups and party lines, cannabis is usually thought of as an issue Democrats champion – but one woman is looking to change that.
This week, freshman GOP Congresswoman Nancy Mace (SC) officially threw her hat in the cannabis reform ring with the introduction of the States Reform Act. Notably, this is the second comprehensive cannabis bill introduced by a Republican member of Congress (the other was sponsored by Rep. Dave Joyce, one of the co-chairs of the Cannabis Caucus).
NCIA applauds Rep. Mace for introducing this new and carefully thought out piece of legislation. There are many provisions in the bill that we support: low tax rates and barriers to entry, allowing states to lead – but also many areas with room for improvement like those pertaining to criminal justice and trade. NCIA will continue to work with Rep. Mace’s office to improve this bill and attempt to find common ground across political parties in order to advance cannabis policy reforms.

NCIA chief economist and his cannabis economics firm, Whitney Economics, are collaborating with NCIA to conduct a national survey of businesses and stakeholders in the U.S. cannabis industry. Below, please find a link to the Survey of U.S. Cannabis Industry Sentiment and Business Conditions. It examines the key issues facing the industry including what you are experiencing when doing business in the industry. The survey seeks to investigate what is working and what can be improved from the perspective of businesses and stakeholders in the cannabis industry.
The goal of the survey is to tabulate ancillary business and cannabis operator opinions on the state of the U.S. cannabis market. Responses are confidential and will be kept anonymous.
Your participation and insights will help policymakers understand the issues that face the industry from your perspective. The survey takes between 4–5 minutes to complete. Please complete the survey by Sunday, October 31.
The initial analysis will be made available to all participants later this fall.
If you have any questions regarding the survey, please contact Beau Whitney from Whitney Economics at Beau@whitneyeconomics.com
Thank you for supporting this survey.

NCIA Deputy Director of Communications Bethany Moore checks in with what’s going on across the country with the National Cannabis Industry Association’s membership, board, allies, and staff. Join us every Friday here on Facebook for NCIA Today Live.

New Jersey recently passed the Cannabis Regulatory, Enforcement Assistance, and Marketplace Modernization Act (“CREAMMA”). Among other things, CREAMMA permits adults 21 years and older to consume cannabis and allows New Jersey residents to operate six types of cannabis businesses within the state. The new adult-use marketplace, as well as the already established medicinal marketplace, will be administered by the Cannabis Regulatory Commission (“the CRC”). The CRC is a panel of five appointed members who will oversee the development, regulation, and enforcement of the use and sale of all legal cannabis in New Jersey.
The CRC recently approved its first set of rules and regulations on August 19, 2021. This will enable the start of the licensing process for personal adult-use cannabis operations in New Jersey. Here are the 15 takeaways from the initial rules and regulations:
There are six different license types:
Businesses may also apply for a license to operate a cannabis testing facility or medical cannabis testing laboratory. License-holders may hold multiple licenses concurrently; however, there are limitations on the number and type of licenses that may be held concurrently.
The State only placed a cap on Class 1 licenses for cultivators. In particular, there will be a statewide cap of a total of 37 cultivators until February 22, 2023. Keep in mind that state limits aren’t the end of the inquiry; municipalities may set restrictions on the number of businesses in their jurisdiction.
In an effort to make the application fee reasonable, the CRC will require applicants to only pay 20% of the application fee at the time of application, and the remaining 80% will only be collected at the time the license is approved. The initial application cost may be as low as $100 but successful applicants should be prepared to pay additional fees ranging from a total cost of $500 – $2,000.
Yes. There are annual licensing fees, which can range from $1,000 for a microbusiness to $50,000 for a cultivator, with up to 150,000 square feet of cultivation capacity. This fee range only applies to the adult use marketplace. There is a different licensing fee schedule for the medicinal use marketplace.
Yes. The CRC will prioritize applicants who live in specifically defined economically disadvantaged areas of New Jersey or who have past convictions for cannabis offenses (“Social Equity Applicants”). It will also prioritize applications from minority-owned, woman-owned, or disabled veteran-owned businesses that are certified by the New Jersey Department of the Treasury (“Diversely Owned Businesses”). Businesses in impact zones will also take priority (“Impact Zone Businesses”).
Applicants meeting the criteria described above will have their applications reviewed before other applications, regardless of when they apply. Remember, however, that priority review doesn’t guarantee selection.
No date has been announced, but the CRC promises that it will be soon . The CRC will publish notice in the New Jersey Register announcing its intent to review applications and submissions will be reviewed, scored, and approved on a rolling basis (pun intended), subject to the required priority review for certain applicants.
Applicants will be expected to submit a detailed application that includes specific details for the proposed site for the business (which must be owned or leased), municipal approval, and zoning approval. Applicants must also submit an operating summary plan detailing the applicants’ experience, history, and knowledge of operating a cannabis business. The scoring of applicants and awarding of licenses will be based entirely on the application materials.
Don’t worry, you can apply for a “Conditional License.” A Conditional License is a provisional award that gives the holder 120 days to become fully licensed by satisfying all the requirements for full licensure, including finding an appropriate site, securing municipal approval and applying for conversion to an annual license.
Conditional License applicants must submit a separate application for each cannabis business license requested, along with a background disclosure, a business plan and a regulatory compliance plan to the CRC. At the time of the application, all owners with decision-making authority of the conditional license applicant will need to prove that they made less than $200,000 in the preceding tax year, or $400,000 if filing jointly.
Conditional License holders that convert to an annual license will not have to submit the sections of the application that, under statute, require applicants to demonstrate experience in a regulated cannabis industry. This flexible option offers an opportunity for newcomers to get into the cannabis industry.
Microbusiness licenses are for applicants who want to run a relatively small operation. Applicants may apply for a microbusiness license for any of the six license types. A microbusiness license limits the business to 10 employees; a facility of no more than 2,500 square feet; possession of no more than 1,000 plants per month; and/or a limit of 1,000 pounds of usable cannabis per month.
No. The state must award the cannabis license. Municipalities play a critical role, however, in the licensing process. For example, applicants will only be licensed by the CRC if the applicant has demonstrated support from the municipality, zoning approval, and has been verified to operate in compliance with any other local licensing requirement.
Yes. Municipalities may ban certain businesses from operating within their borders if they enact an ordinance regulating or banning cannabis businesses by August 21, 2021. Municipalities may update their ordinances at any time to remove any restrictions that they previously placed.
The CRC is authorized to inspect cannabis businesses and testing laboratories, issue notices of violations for infractions and issue fines. Standard fines can be no higher than $50,000, while fines for infractions implicating issues of public safety or betrayal of public trust can be as high as $500,000. Licenses may also be suspended or revoked. Don’t take the risk!
These 15 key points present only a quick summary of the CRC’s initial set of rules and regulations. We anticipate there will be a second set of rules released later this year, which will likely resolve issues that weren’t addressed in the initial set of rules and regulations, or CREAMMA. We expect the second set of rules and regulations to focus mainly on the needs of distribution and delivery service, and preparing for the acceptance of applications, before the Garden State is in full bloom…
 Charles J. Messina is a Partner at Genova Burns LLC and Co-Chairs the Franchise & Distribution, Agriculture and Cannabis Industry Groups. He teaches one of the region’s first cannabis law school courses and devotes much of his practice to advising canna-businesses as well as litigating various types of matters including complex contract and commercial disputes, insurance and employment defense matters, trademark and franchise issues and professional liability, TCPA and shareholder derivative actions.
Charles J. Messina is a Partner at Genova Burns LLC and Co-Chairs the Franchise & Distribution, Agriculture and Cannabis Industry Groups. He teaches one of the region’s first cannabis law school courses and devotes much of his practice to advising canna-businesses as well as litigating various types of matters including complex contract and commercial disputes, insurance and employment defense matters, trademark and franchise issues and professional liability, TCPA and shareholder derivative actions.
 Jennifer Roselle is a Partner at Genova Burns LLC and Co-Chair of Genova Burns’ Cannabis Practice Group. She has unique experience with labor compliance planning and labor peace agreements in the cannabis marketplace. In addition to her work in the cannabis industry, Jennifer devotes much of her practice to traditional labor matters, human resources compliance and employer counseling.
Jennifer Roselle is a Partner at Genova Burns LLC and Co-Chair of Genova Burns’ Cannabis Practice Group. She has unique experience with labor compliance planning and labor peace agreements in the cannabis marketplace. In addition to her work in the cannabis industry, Jennifer devotes much of her practice to traditional labor matters, human resources compliance and employer counseling.
 Daniel Pierre is an Associate at Genova Burns and a member of the Cannabis and Labor Law Practice Groups. In addition to labor work, he likewise assists clients in the cannabis industry, from analyzing federal and state laws to ensure regulatory compliance for existing businesses to counseling entrepreneurs on licensing issues.
Daniel Pierre is an Associate at Genova Burns and a member of the Cannabis and Labor Law Practice Groups. In addition to labor work, he likewise assists clients in the cannabis industry, from analyzing federal and state laws to ensure regulatory compliance for existing businesses to counseling entrepreneurs on licensing issues.
For over 30 years, Genova Burns has partnered with companies, businesses, trade associations, and government entities, from around the globe, on matters in New Jersey and the greater northeast corridor between New York City and Washington, D.C. We distinguish ourselves with unparalleled responsiveness and provide an array of exceptional legal services across multiple practice areas with the quality expected of big law, but absent the big law economics by embracing technology and offering out of the box problem-solving advice and pragmatic solutions.
Given Genova Burns’ significant experience representing clients in the cannabis, hemp and CBD industries from the earliest stages of development in the region, the firm is uniquely qualified to advise investors, cultivators, processors, distributors, retailers and ancillary businesses.

by Claudia Della Mora, Black Legend Capital
While marijuana has been around in Mexico since the 1600s, the real story begins in the 20th century during the Prohibitionist Era. After Mexico news outlets widely reported stories of cannabis users committing violent crimes, a cannabis stigma was created, resulting in Mexico banning the production, sale, and use of cannabis in 1920, followed by a ban of exports in 1927. The movement of cannabis was first regulated by the three U.N. conventions on narcotic drugs, beginning with the Single Convention on Drugs in 1961. The prohibition gave rise to the cartel’s involvement in the illegal cannabis industry in the ’80s, and these cartels have consistently supplied the U.S. market since. After the war on drugs significantly increased violence in Mexico and gave the cartels more power than before, Mexico began to alter its stance. In 2015, the country decriminalized cannabis use, and in 2017, legalized medical cannabis containing less than 1% THC. In 2018, the Mexican Supreme Court deemed the prohibition unconstitutional, and in December 2020, the U.N. Commission on Narcotic Drugs transferred cannabis from a Schedule 4 to a Schedule 1 drug under the Single Convention. As of now, Mexico is on the edge of legalizing recreational cannabis use. This bill, “The New Federal Law on the Regulation of Cannabis,” is awaiting approval by the Senate and then only needs to be signed by the President to be passed into law.
With a population of 130 million and over 10 million regular cannabis users, Mexico will generate $1.2 billion in annual tax revenues while saving $200 million annually in law enforcement and creating thousands of new jobs. One estimate has cannabis legalization bringing up to $5 billion to the economy annually. One issue Mexico will face will be keeping the cartels from transitioning to the legal cannabis market. While those with criminal records can’t obtain any cannabis license, cartels have a deep network, and Mexican officials can’t always determine whether someone is connected to a cartel. Mexico’s legislators believe the cartel will be forced to operate legally over time as they won’t be able to compete in the illegal market and keep as much power as they currently have.
There are also many questions regarding how Mexico’s cannabis legalization will affect the U.S. market. The USMCA, formerly known as NAFTA, currently does not include cannabis, raising the question of whether Mexican producers will be able to import cannabis into the U.S. for a much lower price than the U.S. can produce domestically. However, the U.S. will likely implement trade barriers to protect domestic companies. Currently, the U.S. places trade barriers on tomatoes in Mexico, and many see similar actions being placed on cannabis.

There’s no doubt that cannabis legalization in Mexico will create investment opportunities in the U.S. It mostly comes down to whether the U.S. creates trade barriers with Mexico regarding cannabis. If they don’t, the U.S. cultivation and manufacturing sectors will be hurt badly as Mexico can produce much cheaper. The absence of trade barriers will also hurt testing labs as cultivation moves out of the country and uses testing labs in that same country. However, U.S. companies with distribution networks, retail operations, or strong brands will benefit from Mexican legalization through lower costs of goods sold. One solution that would benefit U.S. companies would be legalizing interstate commerce in the U.S. without federally legalizing cannabis. This means other countries wouldn’t export finished products or raw material with THC above 0.3% into the U.S., and the U.S. industry would develop and consolidate. Once the U.S. federally legalizes cannabis, they must create tariffs or some trade barriers against all the developing countries legalizing cannabis, or the U.S. companies will suffer.
Companies are also greatly affected by banking laws. Currently, companies touching the flower in countries where it is not federally legal cannot access regular banking and can’t list publicly on the NASDAQ or NYSE. However, Canadian companies touching the flower can list in the U.S. since it is federally legal in Canada. These laws mean companies operating in Mexico will also be able to list in the U.S publicly. However, the SAFE Banking Act recently passed the House of Representatives in April 2021 and is up for debate in the Senate. Passage of this act would grant banking access to cannabis companies touching the flower and open the door for these companies to list in the U.S publicly. This would create a large flow of money into U.S. cannabis companies and allow them to scale at a much quicker pace than previously available. One important thing to note is that the large U.S. stock exchanges are technically able to accept cannabis companies’ listings if they meet the exchange requirements. However, they don’t accept them to avoid punishment from the federal government. Therefore, as the government moves towards allowing these companies federal banking access, the main question regarding U.S. companies is raised. In absence of government pressure, will these exchanges allow U.S. companies to list and access their own public markets?

Overall, companies and investors looking to take advantage of the booming cannabis market need to stay up to date on the fast-changing cannabis legalization process in many countries. Those that truly understand it will position themselves to benefit from what is projected to be one of the fastest-growing industries over the next decade.
 Ms. Della Mora is the Co-founder of BLC, a financial advisory and investment firm based in Los Angeles with satellite offices in Houston, New York, London, Hong Kong, and Melbourne. During her tenure at BLC, she successfully invested, assisted in the capitalization, and helped business develop small cap oil companies in Kentucky, Texas, Louisiana, Illinois, Colorado, California, Wyoming, North Dakota, and Alaska. She has also structured oil & gas partnerships in several U.S. states, and in Ecuador, Central America. Ms. Della Mora has been involved in many LNG (Liquid to Natural Gas) projects in the U.S., as well as many commodity trades worldwide. She has personally advised also Chinese conglomerates in their U.S. oil & gas investments.
Ms. Della Mora is the Co-founder of BLC, a financial advisory and investment firm based in Los Angeles with satellite offices in Houston, New York, London, Hong Kong, and Melbourne. During her tenure at BLC, she successfully invested, assisted in the capitalization, and helped business develop small cap oil companies in Kentucky, Texas, Louisiana, Illinois, Colorado, California, Wyoming, North Dakota, and Alaska. She has also structured oil & gas partnerships in several U.S. states, and in Ecuador, Central America. Ms. Della Mora has been involved in many LNG (Liquid to Natural Gas) projects in the U.S., as well as many commodity trades worldwide. She has personally advised also Chinese conglomerates in their U.S. oil & gas investments.
Black Legend Capital is a leading Merger & Acquisition boutique advisory firm based in California with offices worldwide. Black Legend Capital was founded in 2011 by former senior investment bankers from Merrill Lynch and Duff & Phelps. We provide M&A advisory services, structured financing, and valuation services primarily in the cannabis, technology, healthcare, and consumer products industries. Black Legend Capital’s partners have extensive advisory experience in structuring deals across Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America.


By Michelle Rutter Friberg, NCIA’s Deputy Director of Government Relations
Last week was undoubtedly one of the most exciting weeks in federal cannabis policy ever! On July 14, Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-NY), along with Sen. Cory Booker (D-NJ) and Senate Finance Committee Chair Ron Wyden (D-OR), unveiled long-awaited draft legislation that would remove cannabis from the schedule of controlled substances while allowing states to determine their own cannabis policies. Let’s take a look at what we know:
You’ll recall that back in February, the trio of Senators announced that they were working on a comprehensive cannabis bill. Since then, NCIA and other advocates have (im)patiently been waiting to see what shape that would take – I was calling it the best-kept secret in Washington! However, at long last, the discussion draft of the Cannabis Administration and Opportunity Act (CAOA) was released.
A discussion draft is exactly what it sounds like – prior to introducing this language as formal legislation, the Senators have shared it in this form, allowing stakeholders, the public, and others the opportunity to weigh in and provide their expertise and feedback.
As I mentioned above, the CAOA removes cannabis from the list of controlled substances, effectively legalizing it at the federal level while still allowing states to set their own policies. According to the bill’s detailed summary, it has a few goals:
“… [it will] Ensure that Americans – especially Black and Brown Americans – no longer have to fear arrest or be barred from public housing or federal financial aid for higher education for using cannabis in states where it’s legal. State-compliant cannabis businesses will finally be treated like other businesses and allowed access to essential financial services, like bank accounts and loans. Medical research will no longer be stifled.”
The bill also includes:
The discussion draft comment and feedback process will be ongoing until September 1. Until then, NCIA will be working with our board, Policy Council, committees, and our members (particularly our Evergreen members!) to solicit their expert input on some of the areas the Senators have expressed interest in. After that deadline, the Senators will take their time to review submissions and subsequently formally introduce the revised language later this year. Stay tuned via our newsletter, blog, and upcoming events to learn the latest on this and how you can actually submit your thoughts to us!

NCIA Deputy Director of Communications Bethany Moore checks in with what’s going on across the country with the National Cannabis Industry Association’s membership, board, allies, and staff. Join us every Friday on Facebook for NCIA Today Live.
Registration to our Midwest Cannabis Business Conference in Detroit is now open with special limited-time super early bird pricing on tickets available, head to www.MidwestCannabisBusinessConference.com today!

 by Beau R Whitney, NCIA’s Chief Economist
by Beau R Whitney, NCIA’s Chief Economist
The first half of the year was a strong one for cannabis revenues. After a strong first quarter, with $5.9 billion in revenue, cannabis retailers are experiencing continued growth in Q2 with preliminary results coming in at $6.2 billion to $6.5 billion.
If this trend remains in the second half of the year, the cannabis retail sales are projected to be $24.5 to $25 billion for the year. This would reflect another cycle of 35% year-over-year growth.
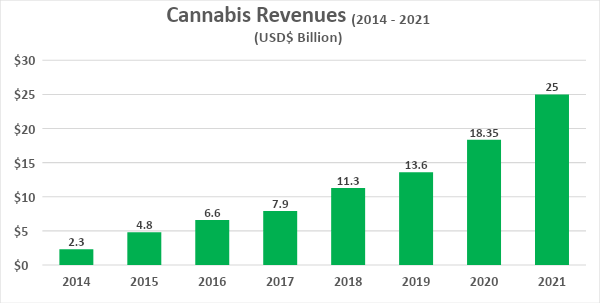
Source: Whitney Economics, Leafly
While the industry has seen strong growth over the past year, this does not necessarily mean that the industry as a whole is in good shape. Retailers are struggling to make profits due in a large part to federal taxation. IRC 280E does not allow entities conducting business in federally illicit trade, such as cannabis, to write off common and ordinary deductions from their federal taxes. As a result, cannabis operators pay significantly more taxes than other businesses. This has long been an issue with the cannabis industry and organizations such as NCIA has been working tirelessly to address this, but as long as it remains a federal policy it will be negatively impacting the industry.
With over $12 billion in first-half revenues, cannabis retailers will be on the hook for $1.2 billion in federal taxes for the first half of the year alone. This is $756 million more than what “normal” businesses would pay. Cannabis retailers are forecasted to pay over $1.5 billion more in taxes in 2021 and, when combined with the rest of the supply chain, will pay over $2.2 billion in additional taxes in 2021.
| 280e Example of Impact on Retail | Normal Business | 280E Business | Comment | |
| Retail mid-Year Revenue | $12,000,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 | Based on data from Whitney Economics | |
| Cost of Goods Sold (COGS = 50%) | $6,000,000,000 | $6,000,000,000 | ||
| Ordinary and Necessary Expenses (30%) | $3,600,000,000 | $3,600,000,000 | Not allowed under 280e | |
| Real Pre-Tax Profit w/o 280e | $2,400,000,000 | $2,400,000,000 | ||
| Taxable Profit | $2,400,000,000 | $6,000,000,000 | Big difference in taxable rates | |
| Fed Tax @21% * | $504,000,000 | $1,260,000,000 | Retailers pay 150% more | |
| Effective tax rate | 21.0% | 52.5% | Some effective tax rates approach 60%-70% | |
| Net Annual Profit (Before State Tax and Debt Service) | $1,896,000,000 | $1,140,000,000 | A difference of $201,000 per year per retailer |
Source: Whitney Economics
*Assumes taxed at C-corporation rates
The effective tax rate increases significantly for retailers and in many cases exceeds 60% to 70%. The level of additional taxes that cannabis operators pay, over the course of the next five years, will increase by an average of $630 million per year for the industry if the business tax rates increase from 21% to 28%. Depending on how corporate tax policy negotiations are settled, things may go from bad to worse for cannabis retailers.
Based on sales data from 2020, there were over 7,550 licensed cannabis retailers in the U.S. with each retailer generating an average of $2.4 million per year. This is right around the amount of revenue required to be a sustainable retail business. In 2021, there have been roughly 1,000 more retailers licensed and even with an increase in sales, retailers are only forecasted to average $2.7 million per year.in sales. In fact, in 13 states, retailers are not projected to average the $2.4 million per year to remain viable. While retailers in some states may be OK, other retailers are not able to make ends meet.
IRC 280E will reduce cannabis retailers cash flow by $200,000 in 2021 and that $200,000 would go a long way in shoring up the finances and provide retailers with the breathing room they need to remain viable. 280E reform would allow retailers to pay for health care for more employees, hire more workers and expand their business. However, in the current environment, many cannabis operators will continue to struggle.
The key message here is that retailers are under duress due to 280E and policy reform in the area of federal taxes may make the difference between success and failure. The time for reform is now, before it is too late.

NCIA Deputy Director of Communications Bethany Moore checks in with what’s going on across the country with the National Cannabis Industry Association’s membership, board, allies, and staff. Join us every Friday here on Facebook for NCIA Today Live.


By Michelle Rutter Friberg, NCIA’s Deputy Director of Government Relations
While it’s become commonplace to hear cannabis come up in the halls of Congress, and increasingly so in the White House, there’s one branch of government that has been quieter on the topic: the Supreme Court (SCOTUS). However, this week, conservative Justice Clarence Thomas changed that when the court actually declined to weigh in on a 280E case.
Towards the end of 2020, a Colorado medical cannabis dispensary decided to ask the U.S. Supreme Court to review a lower-court decision that allowed the IRS to obtain business records in order to apply the 280E provision of the tax code. (Fun fact: NCIA member Jim Thorburn, of the Thorburn Law Group, was actually the counsel on record for this appeal!) According to the filings, the IRS overstepped its authority and also violated the company’s Fourth Amendment privacy rights. Some of the questions the company took to the highest court in the land:
Again, while SCOTUS declined to consider this appeal, Justice Thomas took issue with the underlying state/federal discrepancy in the country’s cannabis laws and issued a searing statement. He specifically discussed a 2005 ruling by SCOTUS in a case called Gonzales v. Raich. In this ruling, the court narrowly determined that the federal government could enforce prohibition against cannabis cultivation that took place wholly within California based on its authority to regulate interstate commerce. Check out a few excerpts from Justice Thomas’ statement below:
Just to be clear, these statements don’t change the law of the land, nor do they indicate formal policy developments. They do, however, show that the constantly shifting public perception of cannabis is affecting the way we as a society think about marijuana, which will, at some point, translate into policy. It’s no small feat that one of the most conservative justices on the Supreme Court has weighed in so substantially on this topic. Continue the momentum and join the movement with NCIA!

 by Beau Whitney, NCIA’s Chief Economist
by Beau Whitney, NCIA’s Chief Economist
Supply tightness in the labor market represents a significant risk to cannabis operators heading into the summer months. With the potential of wage inflation adding to the costs of businesses, many operators that are struggling to make ends meet due to the economic stresses associated with 280E now face higher labor costs. This labor tightness and higher costs could not have come at the worst time.
The recent U.S. Bureau and Labor Statistics jobs report for May, published on Friday, June 4, 2021, indicated that there were 559,000 jobs added in the U.S. economy. This amount was lower than what analysts had predicted, but still strong nonetheless.
The report also showed that the labor force participation rates held steady which is a good sign that people are not getting too frustrated with their job search. The BLS data also indicated that there are still 9.3 million workers unemployed. Even with these higher numbers of displaced workers, this level is roughly 3.6 million workers higher than it was pre-pandemic when unemployment was at record lows. Considering that 1.1 million workers are on temporary layoff status, a remaining 2.5 million delta is a significant improvement relative to the 18.0 million workers displaced in April of 2020.
While there are differing opinions on policy on how to support the unemployed, the key point here is that the labor force is significantly tighter than what most believe and this could become a major issue for the cannabis industry.
Ever since the great recession, there have basically been more workers than jobs. As a result, employers could pick and choose who to hire and offer them lower wages. This recent job report indicates that now there are more jobs than workers, so workers now have the upper hand when it comes to supplying their labor. This is resulting in wage inflation and labor shortages.
This should be a concern for cannabis operators. Labor is one of the highest costs for operators and if wages continue to rise, this will put a squeeze on already slim margins. Reduced labor availability is already being felt across the country and could become very acute as more labor is required to handle increased retail sales and as the outdoor cultivation industry heads into harvest season. Product manufacturers and retailers are already seeing spot shortages even in states where cannabis operators receive living wages such as in Oregon and Colorado.
In reaction to these labor shortages, some MSOs are offering incentives and sign-on bonuses in order to attract workers, even for positions not requiring highly skilled workers. Unfortunately, smaller businesses may not be able to afford these types of incentives. As a result, this will continue to create competitive advantages for MSOs and to generate opportunities that favor larger firms over smaller ones.
Higher costs are not the only concern for cannabis operators. The heavy burden associated with paying higher federal business taxes due to 280E is already driving smaller operators out of the market or forcing them into consolidation with larger, well-financed firms. Smaller entities already have higher costs. The additional risks associated with labor shortages and higher wages could force more operators who are on the edge, into consolidation as well.
Operators who cannot absorb the higher costs for labor, may need to find additional areas in which to cut costs. Unfortunately, this may involve doing more with less (fewer workers), bringing in automation, or reducing product offerings (lower inventory overhead). A common area of cost-cutting is also healthcare, but in an environment of high competition for a limited labor pool, reducing benefits may not be an option.
While many other programs at the federal level have helped struggling businesses outside of the cannabis space, federal tax reform could be a simple, yet elegant solution that would provide widespread relief to struggling cannabis operators and free up cash flow to help offset wage increases.
In the meantime, the anticipated growth in the overall market may decelerate slightly as the industry encounters headwinds as we head into the summer and fall.
NCIA is working with members of Congress to highlight how critically important sound policy is to cannabis operators across the country and how tax reform makes good economic sense. Bringing the voices of cannabis business owners to congress is a very powerful tool in the effort to reform cannabis laws. Now it is up to Congress to act.

By Dr. Dominick Monaco, CLS Holdings
The state of Nevada has always been a unique place to do business. Not only is its economy fueled almost entirely by tourism, but its population is located almost exclusively within a few key urban centers. These factors influence nearly every type of business opportunity in Nevada – including cannabis.
While Nevada’s economic and geographic constraints are unique in themselves, the type of tourist industry found here is one of a kind. Las Vegas is famously known as “Sin City.” It is a place where people flock from around the globe to indulge their vices, such as gambling and clubbing.
As a microcosm of Nevada itself, the Nevada cannabis industry has its own set of challenges and opportunities.
Nevada boasts both medical and adult-use cannabis markets. The state voted to legalize medical cannabis back in 2000, although their first medical dispensary did not open until 2015. While the medical cannabis space in Nevada began with a crawl, the adult-use industry has been quite different.
Nevada voted to legalize adult-use cannabis in late 2016, with the first adult-use dispensary opening mid-2017. Nevada has both medical and recreational dispensaries, although certain stores service both customer bases.
One of the more exciting facets of the Nevada cannabis market has to do with home cultivation. Its unique program allows people 21+ years old to grow at home if they live more than 25 miles from a dispensary. Nevada put these rules in place to accommodate citizens living in rural areas who cannot access dispensaries.
Since Nevada’s legalization, cannabis has become a big business. Here are some statistics for the 2019-2020 fiscal year in the Nevada cannabis industry:
Nevada sales are ahead of other new adult-use recreational markets such as Illinois and Massachusetts to put these numbers in perspective. Nevada falls short compared to more established industries such as Colorado and Washington, but it holds promise for massive growth.
The tourism industry in Las Vegas makes for a unique market. Adult-use market regulations coupled with the global renown of the city lead to an environment where out-of-state visitors greatly influence cannabis sales.
The structure of a cannabis market directly influences business opportunities. In medical cannabis, qualifying conditions and patient counts dictate potential market growth. Conversely, adult-use markets are only limited by people’s age.
The interesting thing about the Las Vegas market is that anyone over 21-years can legally purchase cannabis – this includes out-of-state visitors. According to the Las Vegas Conventions and Visitors Authority website, the city saw 42,523,700 visitors in 2019 alone. These people spent over $10 billion in Las Vegas that year. Within these billions of dollars in tourist money lies an excellent opportunity for adult-use operators in Nevada.
Another fact worth noting is that people flock to “Sin City” to partake in activities inaccessible in other U.S. states. Cannabis fits nicely into this package of taboo activities that can only be done in Las Vegas, NV.
While the tourist money in Las Vegas makes for a very intriguing adult-use market, it is not easy to acquire a cannabis business license. Unfortunately, Nevada has put a cap on the number of licenses available in the state, making it much more difficult to enter than other adult-use states like Colorado.
There are five types of business licenses in the Nevada cannabis industry:
It’s worth noting that both the medical and adult-use markets offer these same business licenses. Similarly, the licensing cap in the state includes both verticals.
As of early 2021, the state of Nevada awarded 132 dispensary licenses. However, these licenses did not go to 132 different operators. Certain businesses acquired multiple licenses, with some able to open as many as seven retail stores. While Nevada has issued 132 retail licenses, there are only 80 dispensaries operational at this point.
The licensing situation in Nevada is frustrating for local investors and outside interests alike. Namely, because studies show that the Nevada economy could support as many as 1,283 more dispensaries than it has issued licenses for. Aggravation mounts with a lack of expansion opportunities in the area.
The state of Nevada only accepts additional cannabis business license requests during “application periods.” These short windows are scheduled by the Nevada Cannabis Compliance Board and stay open for just ten days. However, there has not been an application opportunity since 2018, and it doesn’t appear there will be one anytime soon. As such, it appears that plant-touching opportunities in Nevada are limited to current license holders.
While many believe there is ample room for new players in the Nevada cannabis market, the state does not agree at this point. As a result, if you are looking to get involved in the Nevada industry, you are well-advised to look into ancillary business models instead of plant-touching businesses.
With such promise in the Nevada market, you can rest assured that those cannabis companies that have won licenses will be extremely busy. Ancillary operators can take advantage of this climate by developing models that operate in the business-to-business (B2B) vertical. To help plant-touching companies in Nevada, both product-based and service-based ancillary businesses could prove profitable. Examples of product-based companies include business management software and cultivation technology, while service-based businesses work in marketing, staffing, and consulting.
Opening an ancillary cannabis company in Nevada gives you the ability to enter the market by circumventing the licensing process. Even more, you don’t have to worry about application fees, compliance mandates, and other stressors faced by plant-touching companies. You also have the option to operate across state and national borders if you so desire.
There is no doubt that the Nevada cannabis industry is one-of-a-kind. While there is a good deal of excitement surrounding the market, many feel it hasn’t even come close to reaching its potential. To this end, the adult-use market in Nevada was only 1.5 years old when the COVID-19 pandemic struck. The financial blow of the pandemic was cataclysmic in Las Vegas, as the tourism industry dropped to 50% below average in 2020.
With the pandemic on the downswing in 2021, there is an unmistakable air of excitement across the globe. Some economists feel that we are about to enter a new “roaring 20’s” period, where people celebrate by spending travel money that was unusable during COVID-19. With this celebratory outlook on the near feature, there is no doubt Sin City will see its share of visitors. With the casinos and hotels full again, maybe we will finally see what the Nevada cannabis market can really do.
 Dr. Monaco is the Director of Laboratory Operations for CLS Holdings’ newly opened approximately $4 million laboratory, and is responsible for all day-to-day operations inside the North Las Vegas facility. Dr. Monaco brings over 8 years of licensed & regulated cannabis experience, starting back in 2012 when medical marijuana first opened in Arizona, he has held numerous positions, with escalating responsibilities year over year. He graduated from the University of Arizona College of Pharmacy, in Tucson, Arizona, with a Doctor of Pharmacy in 2010.
Dr. Monaco is the Director of Laboratory Operations for CLS Holdings’ newly opened approximately $4 million laboratory, and is responsible for all day-to-day operations inside the North Las Vegas facility. Dr. Monaco brings over 8 years of licensed & regulated cannabis experience, starting back in 2012 when medical marijuana first opened in Arizona, he has held numerous positions, with escalating responsibilities year over year. He graduated from the University of Arizona College of Pharmacy, in Tucson, Arizona, with a Doctor of Pharmacy in 2010.

 By Morgan Fox, NCIA’s Director of Media Relations
By Morgan Fox, NCIA’s Director of Media Relations
The cannabis world is still eagerly awaiting the introduction of Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer’s comprehensive descheduling legislation, but that doesn’t mean things haven’t been moving on the policy front in recent weeks!
First up, the DEA announced that it was finally moving forward with approving applications to cultivate cannabis for research purposes, which would effectively end the federal government’s stranglehold on research production. The agency spent years fending off lawsuits from applicants, who correctly asserted that not only was the monopoly limiting research, but the cannabis being grown at the single licensed facility at the University of Mississippi was basically unusable for research purposes anyway. This announcement comes several years after the DEA publicly stated that it would begin the licensing process. Better late than never.
Of course, we don’t think the DEA should be involved in cannabis research whatsoever, seeing as how they are a law enforcement organization and not, you know, scientists.
Next, Sen. Ron Wyden, who is also working closely with Majority Leader Schumer on descheduling along with Sen. Cory Booker, introduced S. 1698 last week. While text of this bill is currently not publicly available, the name suggests that this legislation would direct the FDA to allow hemp-derived CBD, made legal under the 2018 Farm Bill, to be used as a dietary supplement or in food. Some perceive this bill as necessary to get some regulatory clarity from the FDA, which has been dragging its feet and missed several deadlines for CBD regulations. Many in the industry blame this lack of regulation for larger retailers staying out of the CBD market, which has led to massive supply gluts of the substance and has been hypothesized to be a leading cause for the recent boom in Delta 8 THC production.
And earlier this month, Rep. David Joyce, an Ohio Republican who co-chairs the Congressional Cannabis Caucus, introduced a narrowly tailored bill to remove cannabis from the schedule of controlled substances. The bill assigns regulatory responsibilities to the FDA and the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau and gives them a one-year deadline to come up with a regulatory structure similar to alcohol. It also contains provisions similar to the protections that exist in the House-approved SAFE Banking Act, calls for studies on how cannabis impacts pain and driving, and improves access for veterans. Notably, this bill does not contain any social equity or restorative justice language.
While the chances of such legislation passing in the Democrat-controlled House are slim, it could serve as a doorway to get fence-sitting Republicans into the debate. It could also be a tool to identify those members of the GOP who are steadfastly opposed to any legalization bill and out of touch with their constituents, many of whom would directly benefit from cannabis policy reforms and who are increasingly in support of ending federal prohibition.
We’re also getting word that the Marijuana Opportunity, Reinvestment, and Expungement (MORE) Act is getting reintroduced in the House this week (and may have already been at the time of this publication). This legislation made history last December when it became the first descheduling bill to receive a floor vote – and pass – in either chamber of Congress. We are hopeful that there will be some revisions from the previous bill, including the removal of a provision that would allow federal licensors to deny applications for cannabis business licenses based on prior state or federal felony convictions, and the inclusion of a more sensible and robust regulatory framework.
We are less than halfway through the calendar year, and it is shaping up to be a momentous one for cannabis advocacy! Stay tuned for more updates from Capitol Hill.
P.S. On the state side, Alabama became the latest state to approve an effective medical cannabis law. Yes, Alabama. That brings the count of medical states to 36, after unfortunately losing Mississippi to a shameful court decision. So far in 2021, four states have approved adult-use or medical cannabis legislation, and more are expected to do so in the coming weeks and months.

By Mell Green, CBD Oracle
Medical cannabis hasn’t always had a smooth go in the United States. Thankfully, as time has slowly started to change and viewpoints have shifted, cannabis legalization is finally gaining traction state-wide. While this is an incredible feat for so many different reasons, many states see long-term benefits of cannabis legalization much further reaching than anyone could have imagined.
Today, we’re talking about how cannabis legalization in Minnesota may actually help further equality and break down barriers that have long been deeply rooted. Let’s get started.
Quickly, it’s essential to understand the tumultuous history behind marijuana and just how far we’ve come as a society. However, seeing this rocky past also helps illuminate how much further we still have to go.
The cannabis plant has existed for millennia on planet Earth. Its therapeutic benefits have supported civilizations in spiritual, religious, and medicinal ceremonies across the globe. As this idea spread to Western societies, the plant was, at first, welcomed with open arms. At the start of the 20th century, all of this changed entirely in the United States.
During the Mexican Revolution from 1910-1920, many Mexican citizens fled their war-torn home country in search of a safer, more promising future. With this, the U.S. saw an influx of Mexican immigrants.
Throughout Mexico, enjoying cannabis for its recreational effects wasn’t a new idea. So, when citizens began migrating North, they also brought more normalized recreational cannabis use. At first, for those in the U.S. who already adored cannabis, this was incredibly exciting. But, for many in positions of power, class, and wealth, this type of cannabis use wasn’t going to fly. Thus came the Reefer Madness film and decades-long racially charged cannabis persecutions.
It took way too long, but the United States finally started getting on board with cannabis decriminalization and legalization back in the 80s and 90s. With this, the exposure to cannabis science became more extensive, and it was easier to see that the plant did (and still does) have some serious medicinal benefit. Seeing these facts caused a lot of opinions to change, resulting in an almost domino-like effect of cannabis legalization across the country.
Now, 36 states have legalized medical cannabis, allowing more people than ever access to the precious plant they love. But has this legalization impacted the people most disproportionately punished? Not really.
Still today, we see Black men arrested for cannabis crimes at disproportionately high rates, even though cannabis is legal in most states across the U.S. If anything, these legal changes have made the divide all the more evident, allowing the country to see just how horrific the cannabis industry can be for people of color. At the same time, it simultaneously celebrates white American consumers. This may help boost PR for big business, but it doesn’t help local (black-owned or otherwise) businesses on the ground. Legally or economically.
So, what can we do to change this? How can cannabis legalization help to further the progress we’ve made?
I know, it sounds like we’re a bit cynical, but it’s crucial to bring up these divides before discussing how we can move further. The country often loves to praise all the beauty that the cannabis industry brings, forgetting the intense harm it has caused so many communities.
Let’s talk about Minnesota, for example. In May, it looks as though the state is going to vote to pass adult-use cannabis use. If this happens, here’s what could potentially occur in terms of furthering equality — but, at the end of the day, this change is up to you.
Realistically, the legalization of cannabis should help reduce the number of victimless crimes in the area, helping the community feel more at ease. With this, you would also expect a lowered number of consistent police presence in areas where cannabis use was a previous “problem.” Often, when communities of color experience increased and frequent police presence, this does not provide a sense of safety. Typically, it provides the opposite. Thus, legalizing cannabis in places like Minnesota may be able to create an environment that not only feels safer but feels more accepting of all residents. Feeling safe is great for business, big and small – but especially small. Reduction of victimless crimes and less police presence could really boost the state economy, and additionally enhance everyone’s sense of community and unity.
Furthering equality through the legalization of cannabis can be done, but the work goes much deeper than just on a legal level. As we’ve seen, just because the law says one thing, that doesn’t mean it applies to all groups of people. So, once legalization happens in Minnesota — or your state — the next steps are in your hands.
With this, you’ll also understand how legalization is not an end-all-be-all solution. If we want to erase cannabis’s racially charged stigma, the answer is holistic: it starts with a community.
 Mell Green is a content creator who believes that cannabis can help anyone achieve a life-enhancing experience. Her participation in the advocacy of the plant for the last several years has not only allowed her to create solid relationships with the world’s leading cannabis companies, but it has also helped her to educate and spread awareness on the power of alternative medicine.
Mell Green is a content creator who believes that cannabis can help anyone achieve a life-enhancing experience. Her participation in the advocacy of the plant for the last several years has not only allowed her to create solid relationships with the world’s leading cannabis companies, but it has also helped her to educate and spread awareness on the power of alternative medicine.
CBD Oracle is a California-based online magazine dedicated to cannabis and CBD education. The company has made it its mission to provide specialized, expert advice to those who need it, publishing detailed, informative, and entertaining articles, guides, and reviews, all backed by the latest scientific studies and research.

By Charles J. Messina, Esq., Jennifer Roselle, Esq. and Donald W. Clarke, Esq. of Genova Burns LLC
After several failed attempts, and seemingly the result of catching significant political heat as of late, Governor Cuomo is allowing the adult-use cannabis industry to blaze forward in New York.
With Gov. Cuomo’s signature, the bill (S.854-A), known as the “Marihuana Regulation and Taxation Act” (MRTA), establishes the legislative foundation upon which a regulatory infrastructure will be built to host a network of licensed operators to cultivate, process, distribute, sell, and host cannabis consumers. In addition to regulating adult use of cannabis, MRTA also amends the state’s existing medical use law (the New York Compassionate Care Act) and provides, among other things, rules for hemp, CBD, and other cannabis extracts.
First, adults may personally possess up to 3 ounces of plant cannabis (and 24 grams of “concentrated cannabis”) without being prosecuted or arrested. In addition to decriminalization, the law also expunges convictions based on conduct which is now authorized under MRTA.
Unlike New Jersey’s recently approved cannabis legislation, consumption of cannabis will be permitted in the same (or similar) places as vaping and cigarettes. Also, New Yorkers will be able to grow their own cannabis. Although “home grow” will be delayed for months until after more rules are promulgated and retail sales commence, a household will be able to grow a maximum of up to twelve plants (six mature, and six immature), with a five-pound possession limit for adults.
Throughout MRTA, there is a heavy focus on social and economic equity. This is integrated in the application process, apportionment of tax revenue, and adjustments made to the penal code. Certain applicants can qualify as a “social and economic equity applicant” to help the Office of Cannabis Management reach its goal of awarding 50% of licenses to minority or woman-owned business enterprises, distressed farmers, or service-disabled veterans.
Similar to New Jersey, the law’s terms will be supplemented by not-yet-created regulations. The regulatory framework will be created by a cannabis Advisory Board and carried out by the newly established Office of Cannabis Management (OCM). The OCM will be an independent office operating as part of the New York State Liquor Authority. It will have a five-member board, with three members appointed by the Governor and one appointed by each house.
Because much of the regulatory licensing framework does not yet exist, there is no established start date. Reports suggest sales could commence as early as December 2022. Home-growers for recreational use must wait no less than 18 months after the initial retail sales to plant their seeds. The tiered licensing structure prohibits those upstream in the production process from selling to the general public.
The available licenses include:
*Cultivator License—includes the agricultural production of cannabis and minimal processing and preparation.
*Processor License—includes blending, extracting, infusing, packaging, and preparing cannabis for sale. There is a limit of one license per processor, but each license can authorize multiple locations.
*Distributor License—authorizes the acquisition, possession, distribution, and sale of cannabis from a licensed cultivator or processor to retail dispensaries and on-site consumption sites.
*Retail Dispensary License—authorizes the sale of cannabis to consumers, with a limit of three retail dispensary licenses per person. A retail licensee may not also hold a Cultivator, Processor, Microbusiness, Cooperative, or Distributor License.
*Cooperative License—authorizes the acquisition, possession, cultivation, processing, distribution, and sale from the licensed premises of the cooperative to distributors, on-site consumption sites, and retail dispensaries, but not directly to consumers.
*Microbusiness License—authorizes limited cultivation, processing, distribution, delivery, and dispensing of the licensee’s own adult use cannabis and cannabis products. A microbusiness licensee may not hold any other license, and may only distribute its own products to dispensaries.
*Delivery License—authorizes the delivery of products by licensees independent of another license.
*Nursery License—authorizes the production, sale, and distribution of clones, immature plants, seeds, and other agricultural products used specifically for the planting, propagation, and cultivation of cannabis by cultivators, cooperatives, and microbusinesses.
*On-Site Consumption License—authorizes the establishment of a location for the on-site consumption of cannabis.
MRTA places the tax on cannabis based upon the amount of the chemical compound that delivers effects to users (THC). There will be a 9% state tax at the retail level. A local excise tax will be 4% of the retail price. Counties will receive 25% of the local retail tax revenue, and 75% will go to the municipality. Municipalities can, however, enact legislation to opt out of permitting retail dispensaries or on-site consumption licenses within its borders.
MRTA mandates that 40% of the estimated $350 million in tax revenues will go to community grants and reinvestment, and 20% will go to drug treatment and education. The final 40% is earmarked for schools as of now.
Employers have no legal obligation to permit adult-use cannabis in their workplace. In addition, while offsite usage is protected, the law includes provisions that allow employers to take action against employees who are impaired at work if their performance is lessened, or the employee’s conduct interferes with the ability to provide a safe and healthy workplace. Employers may likewise act to comply with local, state, or federal laws or allow conduct that would result in loss of a federal contract or federal funding.
 Charles J. Messina is a Partner at Genova Burns LLC and Co-Chairs the Franchise & Distribution, Agriculture and Cannabis Industry Groups. He teaches one of the region’s first cannabis law school courses and devotes much of his practice to advising canna-businesses as well as litigating various types of matters including complex contract and commercial disputes, insurance and employment defense matters, trademark and franchise issues and professional liability, TCPA and shareholder derivative actions.
Charles J. Messina is a Partner at Genova Burns LLC and Co-Chairs the Franchise & Distribution, Agriculture and Cannabis Industry Groups. He teaches one of the region’s first cannabis law school courses and devotes much of his practice to advising canna-businesses as well as litigating various types of matters including complex contract and commercial disputes, insurance and employment defense matters, trademark and franchise issues and professional liability, TCPA and shareholder derivative actions.
 Jennifer Roselle is Counsel with Genova Burns LLC and Co-Chair of Genova Burns’ Cannabis Practice Group. She has unique experience with labor compliance planning and labor peace agreements in the cannabis marketplace. In addition to her work in the cannabis industry, Jennifer devotes much of her practice to traditional labor matters, human resources compliance and employer counseling.
Jennifer Roselle is Counsel with Genova Burns LLC and Co-Chair of Genova Burns’ Cannabis Practice Group. She has unique experience with labor compliance planning and labor peace agreements in the cannabis marketplace. In addition to her work in the cannabis industry, Jennifer devotes much of her practice to traditional labor matters, human resources compliance and employer counseling.
 Donald W. Clarke is Counsel at Genova Burns LLC and a member of the firm’s Bankruptcy, Reorganization and Creditors Rights and Cannabis Law Groups. He has extensive experience with complex restructuring matters and a comprehensive understanding of federal, state, and local laws, including regulatory requirements, across all industries. This experience has enabled Mr. Clarke to assist clients with their navigation of such regulatory schemes outside of bankruptcy, including in the space of cannabis law.
Donald W. Clarke is Counsel at Genova Burns LLC and a member of the firm’s Bankruptcy, Reorganization and Creditors Rights and Cannabis Law Groups. He has extensive experience with complex restructuring matters and a comprehensive understanding of federal, state, and local laws, including regulatory requirements, across all industries. This experience has enabled Mr. Clarke to assist clients with their navigation of such regulatory schemes outside of bankruptcy, including in the space of cannabis law.
For over 30 years, Genova Burns LLC has partnered with companies, businesses, trade associations, and government entities, from around the globe, on matters in New Jersey and the greater northeast corridor between New York City and Washington, D.C. We distinguish ourselves with unparalleled responsiveness and provide an array of exceptional legal services across multiple practice areas with the quality expected of big law, but absent the big law economics by embracing technology and offering out of the box problem-solving advice and pragmatic solutions.
Given Genova Burns’ significant experience representing clients in the cannabis, hemp and CBD industries from the earliest stages of development in the region, the firm is uniquely qualified to advise investors, cultivators, processors, distributors, retailers and ancillary businesses.


by Michelle Rutter Friberg, NCIA’s Deputy Director of Government Relations
It’s hard to believe that somehow it’s March again, but all the while, the NCIA team in D.C. has been hard at work lobbying and advocating on behalf of you and your business. Things are really beginning to warm up and spring into action, so keep reading below for a quick update on where things are at with SAFE Banking, comprehensive reform, appropriations, and more!
Bill reintroductions in both chambers have been off to a slow start. Between a new session, most people still working remotely, a delayed organizing resolution in the Senate, and a somewhat contentious COVID relief package that’s finally passed, members of Congress and their staff have been incredibly busy. But, now that that’s all behind us, I’d suggest preparing for many cannabis bills to be introduced soon.
Specifically, you can expect the reintroduction of the SAFE Banking Act to happen in both the House of Representatives and the Senate within the next couple of weeks. When the bill was introduced in the House during the 116th Congress, it had over 100 cosponsors. In the Senate, it was introduced with more than 20 — that’s more than a fifth of the entire chamber! The bill later went on to be passed by the entire House of Representatives in September 2019 by a vote of 321-103.
You’ll remember that the SAFE Banking Act addresses urgent public safety concerns by allowing tightly regulated marijuana businesses the ability to access the banking system and make our communities safer. The bill also provides protections from money laundering laws for any proceeds derived from these state-legal marijuana businesses. The bill also includes the Financial Institution Customer Protection Act and protections for hemp and hemp-derived CBD-related businesses, which sometimes still struggle in accessing financial services despite the legalization of hemp in the 2018 Farm Bill.
Don’t expect any big changes, however — the bill this Congress includes minor technical changes to the safe harbor language, strengthened hemp provisions, and other technical updates.
While SAFE Banking’s timeline is clear, the same can’t completely be said for more comprehensive reform. When I say comprehensive reform, I’m talking specifically about bills that would remove marijuana from the Controlled Substances Act like the MORE Act and the upcoming Schumer-Booker-Wyden bill.
In the House, we are continuing to work with various committees and members to determine the best path forward for the MORE Act and what changes should be made. I wouldn’t be surprised if that bill gets reintroduced sometime this spring, but the process is truly still in flux, so I also wouldn’t be surprised if it was postponed awhile. This will be determined by the lead sponsors’ offices and also by the congressional calendar and how various bills/issues move through the legislative process.
In the Senate, we’re excited to be working with Leader Schumer (D-NY) and Sens. Booker (D-NJ) and Wyden (D-OR) on their new cannabis bill. That bill will draw heavily on provisions from the MORE Act, but will also include expanded language on taxation and smart regulations. Now that the COVID relief bill has passed into law, I think we can expect to see their bill be introduced sometime in the near future.
It’s spring, which means it’s appropriations season here in D.C.! These bills are legislation that “appropriates,” or sets aside, federal funds to be divided between specific federal government departments, agencies, and programs. For a refresh on the history of appropriations, click here, or, if you’re interested in how these provisions relate to cannabis, click here.
While the appropriations amendment that protects medical cannabis businesses, patients, and programs has been in law since 2014, we’ve had difficulty expanding those provisions and passing new cannabis-related amendments due to the formerly-Republican controlled Senate. However, now that Democrats control both houses of Congress, we’re excited to go back to the drawing board and get creative with the appropriations process to help provide some certainty and relief to the cannabis industry.
We’ll be looking at amendments pertaining to adult-use cannabis programs, banking, veterans access, allowing Washington, D.C. to finally implement a functioning 21+ cannabis program — and that’s just scratching the surface!
All of this is to say: things are really springing into action in D.C.! Prepare for many cannabis bills to begin getting reintroduced, and remember that the appropriations process takes months, so stay tuned via our blog, newsletter, NCIA Connect, and the new NCIA Mobile App to remain in the loop and get involved!

The Marijuana Opportunity, Reinvestment, and Expungement Act (H.R. 3884) is expected to come to a vote in the U.S. House of Representatives in December 2020. NCIA has been building support for this bill in Congress for the last year and now we need your help!
Look up your congressional representative and contact info by zip code, here.
Reference our congressional scorecard to find out if your representatives are sponsoring NCIA’s priority legislation, including the MORE Act.
Hello! My name is _______________ and I am a constituent of yours in (city, state, zip code). I am calling today to ask that Representative _____________ votes “Yes” on H.R. 3884, the MORE Act, when it comes to the Floor for a vote in December.
This bill would remove cannabis from the Controlled Substances Act at the federal level, leaving marijuana policy up to the individual states. It also creates avenues towards expungement, re-sentencing, and assists those communities that have most been impacted by the failed war on marijuana. Additionally, legal cannabis is a huge economic driver and would help both the federal government and states’ revenue shortfalls during this pandemic.
Thank you for your time today. Again, I hope Representative _____________ will vote “Yes” on H.R. 3884, the Marijuana Opportunity, Reinvestment, and Expungement Act.
*Feel free to tell a personal story if you feel it is relevant or powerful, but remember that staffers are busy so sometimes short and sweet is best!*
The Marijuana Opportunity, Reinvestment, and Expungement Act (H.R. 3884, S. 2227), commonly known as the MORE Act, was introduced in 2019 by House Judiciary Committee Chairman Jerry Nadler (D-NY) and Senator (now Madam Vice President-Elect) Kamala Harris (D-CA).
This bill would:

by Morgan Fox, NCIA’s Director of Media Relations
While the country waits for the outcomes of national elections that could very well impact the future of cannabis policy reform advocacy, we do have a LOT to be happy about today!
Last night, adult-use and medical ballot initiatives SWEPT the elections, passing in every state in which they were considered!
Voters in Arizona, Montana, New Jersey, and South Dakota all passed measures making cannabis legal and regulated for adults. South Dakota also approved a medical cannabis initiative by an even greater margin, and was joined by Mississippi where an overwhelming majority of voters not only supported medical cannabis but chose the much more comprehensive of two competing options.
You can learn more about these initiatives here and how they fared in the elections here.
First, let’s talk about New Jersey. Roughly two thirds of voters in the state approved this ballot measure, which was referred to them after lawmakers were unable to pass similar legislation last year. This is a big jump in ballot approval margins; before now, the most popular legalization referendum was in California, which approved Proposition 64 in 2016 with 57% of the vote. That’s a 10% margin increase in just four short years! The large population and huge market potential (more than $1.5B by 2025) are sure to have a major impact on the industry. Regionally, passage of this initiative is certain to add urgency to adult-use cannabis regulation efforts in states like New York, Pennsylvania, Connecticut, Delaware, and Rhode Island.
South Dakota also set a record by becoming the first state to approve an adult use law before having an established medical cannabis system, and in a very conservative state no less! Voters supported both medical and cannabis initiatives despite strong opposition from the governor and other officials.
In Arizona, after voters narrowly defeated a legalization initiative in 2016, a significant swing brought a 10% increase in support resulting in passage. This long-overdue change is especially important because Arizona is the only state where simple possession is a felony and nearly 15,000 people are arrested every year.
So what does this mean for future reform efforts?
First and foremost, the passage of the adult use initiatives means nearly 34% of Americans now live in states with laws making cannabis legal and regulated for adults. These four states account for roughly 60,000 marijuana arrests every year, mostly for simple possession. Congressional representation of states where cannabis is legal for adults will increase by 29 representatives and eight senators. This doesn’t guarantee their support for cannabis legislation, but it certainly increases the chances.
Second, passage of cannabis policy reform initiatives in conservative states like Mississippi, Montana, and South Dakota should send a signal to Republican lawmakers in Congress that this is an issue that they can support, and one which they will face political consequences for impeding. The fact that all three of these states had multiple cannabis-related issues on the ballot and voters were not swayed or confused is a testament to the will for change in these areas and a growing understanding of the issue.
Long story short: more and more states will continue to enact sensible, modern cannabis policies in the coming years, and every state that does so will help add to the chorus of voices from the public and in Congress calling for an end to outdated federal prohibition policies.

by Morgan Fox, NCIA’s Director of Media Relations
 Ballot: Proposition 207, Smart & Safe Act (adult use)
Ballot: Proposition 207, Smart & Safe Act (adult use)
Summary: https://smartandsafeaz.com/about/
Full language: https://mk0adassociatioy1jbg.kinstacdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/I-23-2020.pdf
Main backers: Smart and Safe Arizona
Possession: Adults 21+, 1 ounce flower or 5 grams concentrate
Home cultivation: YES, adults 121+ may have up to 6 plants in an enclosed locked location out of public view.
Licenses:
Social Equity:
Department of Health Services would be required to establish a Social Equity Ownership Program to promote cannabis business ownership and employment for individuals from communities disproportionately impacted by the enforcement of previous marijuana laws.
Proposition 207 would establish a fund called the Justice Reinvestment Fund (JRF). Revenue in the JRF would be allocated as follows:
Taxes & Revenue:
Transaction Privilege Tax (currently 5.6%)
Specific 16% excise tax (non-medical)
Revenue from the excise tax and license fees would be deposited into the Smart and Safe Arizona Fund. First, revenue would be used to implement and enforce marijuana regulations. The remaining revenue would be allocated as follows:
Additional Resources: Proposition 7 Information, FAQ

Ballots: Initiative 65 (medical), Alternative 65A (medical, terminally ill patients only)
Summary:
Full Language:
Main Backers:
Possession:
Home Cultivation: NO
Licensing:
Social Equity: None explicitly included in either initiative.
Taxes & Revenue:
Additional Resources: Overview and Sample Ballot Question – IMPORTANT! These questions are worded in a confusing manner on ballots.
 Ballots: Initiative 190 Marijuana Legalization Initiative (adult use), CI-118 Allow for a Legal Age for Marijuana Amendment
Ballots: Initiative 190 Marijuana Legalization Initiative (adult use), CI-118 Allow for a Legal Age for Marijuana Amendment
Summary:
Full Language:
Main Backers: New Approach Montana
Possession: Adults 21+, up to one ounce of flower or 8 grams of concentrate
Home Cultivation: YES, up to four (4) plants per adult, maximum eight (8) per household.
Licensing:
The Department of Revenue shall develop rules and regulations regarding licensing of providers, marijuana-infused products providers, and dispensaries for adult use. For the first 12 months, only existing medical cannabis licensees may apply. Provider licenses are established in tiers based on canopy size and also include micro-business licenses. Applicants must have resided in Montana for at least one year prior and may not have been convicted of a felony involving fraud, deceit, or embezzlement or for distribution of drugs to a minor within the past 5 years. Cannabis businesses may not be located within 500 feet of a school or place of worship unless permitted by the local jurisdiction.
Social Equity: Persons convicted of behavior permitted by Initiative 190 may apply for resentencing or expungement.
Taxes & Revenue:
Additional Resources: Initiative 190 Information
 Ballots: Question 1, Marijuana Legalization Amendment (2020)
Ballots: Question 1, Marijuana Legalization Amendment (2020)
Summary: https://www.njcan2020.org/whats-on-the-ballot/
Main Backers: NJ Can 2020
Possession: 21+, limits TBD by Legislature
Home Cultivation: TBD by Legislature
Licensing: TBD by Legislature, regulated by existing Cannabis Regulatory Commission
Social Equity: TBD by Legislature
Taxes & Revenue: Standard state sales tax of 6.625%; Legislature can authorize municipalities to impose up to an additional 2% local tax
DONATE NOWAdditional Resources:
 Ballots: Measure 26 (medical), Amendment A (adult use)
Ballots: Measure 26 (medical), Amendment A (adult use)
Summaries: https://www.southdakotamarijuana.org/the-initiatives
Full Language:
Main backers:
Possession:
Home Cultivation:
Licensing:
Social Equity: None explicitly included in initiative language
Taxes & Revenue:
Additional Resources:

by Calvin Shannon, CPA, CVA, Principal at Bridge West LLC, and Nicholas J. Richards, Esq., Partner at GreenspoonMarder LLP
On March 30, 2020, the Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration issued a report titled “The Growth of the Marijuana Industry Warrants Increased Tax Compliance Efforts and Additional Guidance.” The 53-page report discussed several different topics, including that the IRS should conduct more audits under Section 280E, and this discussion focuses on Section 471(c).
The report states that certain qualifying cannabis taxpayers, who would otherwise be subject to business expenses being disallowed under Section 280E, could potentially account for their inventory under Section 471(c) using a method that would classify most or all of their expenditures as inventoriable costs and avoid Section 280E’s disallowance of such expenditures. Accordingly, as all the costs would be capitalized into inventory, they would then reduce taxable income as the inventory was sold. In other words, expenditures previously disallowed under Section 280E would be part of the cost of goods sold and allowed as a reduction of gross receipts. There was no public comment from the IRS in the report on the potential that 471(c) may eliminate 280E.
Before continuing to provide our additional comments, it is important to mention the impact of Section 471(c) on Section 280E has not been reviewed by the Courts and the Inspector General also stated that necessary guidance addressing 471(c) is lacking from the IRS. As such, the impact cannot be stated in certain terms.
The curse of Section 280E on the cannabis industry cannot be overstated – some businesses actually end up paying more in tax than they make and Section 280E can turn an economic loss into a taxable gain. This seemingly unconstitutional result has been justified by the courts and IRS under a very old principle of taxation that “deductions are a matter of legislative grace.” New Colonial Ice Co. v. Helvering, 292 U.S. 435, 440 (1934) Legislative grace, according to these authorities, means the legislature has the power to deny all deductions, if they so choose, and it should be said that the limitation of such grace, under the 16th Amendment to the US Constitution, is that 280E cannot disallow costs of goods sold. With Section 471(c), however, legislative grace appears to be on the side of the cannabis industry because, as discussed below, Congress created Section 471(c) and it appears to allow inclusion of deductions into the cost of goods sold where they can’t be disallowed under Section 280E.
The Code states that Section 471(c) allows a small taxpayer, one with less than $25 million in revenues, who is not a tax shelter or public company to account for inventory according to their applicable financial statements, or absent applicable financial statements, according to the actual books and records of the taxpayer. For a qualifying business that doesn’t have applicable financial statements, if their books and records include deductions in COGS, then these deductions may not be subject to 280E.
It is our opinion that under IRC § 451(b)(3) if a taxpayer is required to issue audited financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) for credit purposes, to owners, or for any other nontax purpose, they have applicable financial statements. It would seem that “any other nontax purpose” would include audited GAAP statements required to be issued to state regulatory agencies. As such, because GAAP requires accounting for inventory in a manner similar to Section 471(a), taxpayers who have Applicable Financial Statements appear to be precluded from adding costs disallowed under Section 280E into COGS pursuant to Section 471(c). Of concern are states that require license holders to provide their licensing agency with audited financial statements. However, if the state doesn’t require GAAP financials, then the “Applicable Financial Statements” provision shouldn’t be a problem.
If the taxpayer does not have applicable financial statements, then they are allowed to account for inventory for tax purposes in the same way as they account for inventory on their internal books and records. Thus, their books and records would have to mirror their method of accounting for tax purposes.
As noted above, there is currently no guidance from the IRS regarding this question and, we should assume, that the IRS will not acquiesce to the position that 471(c) eliminates 280E. So, let’s consider the arguments the IRS might make. First to consider is the Service’s conclusion in Chief Counsel Memorandum Number 201504011 regarding Sec 263A. Early on, cannabis taxpayers attempted to use Sec 263A to capitalize general and administrative costs, otherwise subject to 280E, into inventory and then deduct them as part of COGS. This does sound somewhat similar to the approach we are looking at under 471(c).
The IRS concluded in CCA 201504011 that Sec. 263A would not allow an expense disallowed under Section 280E to be added to COGS because of “flush language” added to Sec. 263A(a)(2) in a subsequent congressional amendment. The flush language states:
Any cost which (but for this subsection) could not be taken into account in computing taxable income for any taxable year shall not be treated as a cost described in this paragraph.
The U.S. Tax Court agreed with the Chief Counsel memo in several opinions including Patients Mutual Assistance Collective Corporation d.b.a. Harborside Health Center v. Commissioner.
However, where this language was fatal to the cannabis industry’s attempt to use Section 263A to its benefit – it may help in the case of Section 471(c). It appears to have been necessary for the U.S. Congress to add the Flush Language to Section 263A to prevent the inclusion of otherwise disallowed expenses into COGS. There is no equivalent language added to Section 471(c) and so the argument is that in the absence of an equivalent provision, Section 471(c) can be used to include expenses disallowed under 280E into COGS where they can be used to reduce taxable income.
Another argument the IRS may make is that Treas. Reg. § 1.61-3(a) prevents the inclusion of deductions into cost of goods sold because the regulation states that Gross Income is determined without subtraction of “…selling expenses…” However, Section 1.61-3(a) is part of the Treasury Regs defining gross income and its reference to the non-inclusion of “selling expenses” is from the regulations under Section 471(a). Section 471(c) specifically states that Section 471(a) does not apply (which include the regulations) and a taxpayer’s method of accounting for inventory under Section 471(c) does not fail to accurately reflect income. And, Section 471(c) is a higher authority than the regulations. Thus, it appears that Section 471(c) trumps Treas. Reg. § 1.61-3(a).
Every taxpayer is different, and accounting for inventory under Section 471(c) is not right for everyone in the cannabis industry. It is also important to understand that it may not work and for taxpayers who use the method to do so with caution and understanding. However, below is a list of issues to discuss with your tax professional:
What is your tolerance for risk and a legal dispute with the IRS? Such a dispute could be time-consuming and costly.
If 471(c) is proven not to eliminate 280E – how will you manage additional tax, interest, and possibly penalties?
Should the position be disclosed as part of your tax filing?
Does the entity have applicable financial statements?
Is the cannabis business a tax shelter?
How aggressive does management and ownership want to be regarding the position?
How will management accomplish the necessary accounting and records to support such a position?
In summary, 471 (c) has left the cannabis industry with several questions and definitive answers are probably not immediately available. License holders should work closely with their advisors as they navigate these questions. But, there is a possibility that Section 471(c) eliminates Section 280E for qualifying taxpayers. Cannabis businesses should take the necessary steps to understand it and protect their ability to benefit from Section 471(c) if it does work.
The Bridge West and GreenspoonMarder teams work tirelessly to understand the tax and accounting issues facing businesses in the cannabis industry and provide the best possible solutions to their clients.
To discuss any of the questions within this article please feel free to contact Calvin Shannon, Nick Richards or any of their team members.
 Calvin Shannon is a Pricipal of Bridge West and has over 17 years of experience providing tax, audit, estate planning and trust services. Calvin is skilled at understanding client’s challenges and working with them to develop and implement innovative and unique solutions. Assists organizations to address the industry’s unique and ever-evolving issues. He enjoys having the opportunity to work with cannabis clients to understand their business needs, and to provide timely solutions
Calvin Shannon is a Pricipal of Bridge West and has over 17 years of experience providing tax, audit, estate planning and trust services. Calvin is skilled at understanding client’s challenges and working with them to develop and implement innovative and unique solutions. Assists organizations to address the industry’s unique and ever-evolving issues. He enjoys having the opportunity to work with cannabis clients to understand their business needs, and to provide timely solutions
Calvin can be reached at: cshannon@bridgewestcpas.com and 651-287-6327.
Nick Richards is a Partner in the Tax practice group at Greenspoon Marder LLP. He represents individuals and businesses in tax audits & trials, M&A, in managing tax debt, and he advises cannabis companies, owners and investors regarding tax and regulatory compliance matters. Mr. Richards has been a tax attorney for more than twenty years beginning his career with the IRS where he was a leading trial attorney, a Chief Counsel advisor, and a Special Assistant United States Attorney.
With his broad experience and understanding at all phases of the tax system, from reporting and assessment through appeals, court, and tax debt resolution, Mr. Richards achieves successful legal solutions tailored to his individual client’s needs. Mr. Richards also teaches tax attorneys and CPAs throughout the US and he is an Adjunct Professor of Law at the University of Denver, Graduate Tax Program, where he teaches State and Local Tax and Civil and Criminal Tax.
Nick can be reached at: nick.richards@gmlaw.com and 720-370-1169.
This site uses cookies. By using this site or closing this notice, you agree to the use of cookies and our privacy policy.